
a)
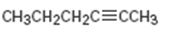
Interpretation:
The terminal alkyne and the alkyl halide from which the compound shown can be obtained are to be shown. If two routes are possible both has to be listed.
Concept introduction:
The alkylation of
To show:
The terminal alkyne and the alkyl halide from which the compound shown can be obtained. Further to list both routes if two routes are possible.
b)
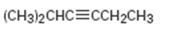
Interpretation:
The terminal alkyne and the alkyl halide from which the compound shown can be obtained are to be shown. If two routes are possible both has to be listed.
Concept introduction:
The alkylation of alkynes is an efficient method for preparing higher alkanes. Acetylene upon alkylation gives a terminal alkyne while further alkylation of a terminal alkyne leads to the formation of an internal alkyne. The actylide anion, being nucleophilic in nature, displaces the halide ion when treated with alkyl halide and gets itself attached to the alkyl group to yield a terminal alkyne. Only primary alkyl halides can be used in the reaction because when secondary and tertiary alkyl halides are used elimination of a hydrogen halide occurs instead of substitution.
To show:
The terminal alkyne and the alkyl halide from which the compound shown can be obtained. Further to list both routes if two routes are possible.
c)
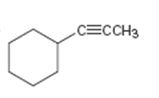
Interpretation:
The terminal alkyne and the alkyl halide from which the compound shown can be obtained are to be shown. If two routes are possible both has to be listed.
Concept introduction:
The alkylation of alkynes is an efficient method for preparing higher alkanes. Acetylene upon alkylation gives a terminal alkyne while further alkylation of a terminal alkyne leads to the formation of an internal alkyne. The actylide anion, being nucleophilic in nature, displaces the halide ion when treated with alkyl halide and gets itself attached to the alkyl group to yield a terminal alkyne. Only primary alkyl halides can be used in the reaction because when secondary and tertiary alkyl halides are used elimination of hydrogen halide occurs instead of substitution.
To show:
The terminal alkyne and the alkyl halide from which the compound shown can be obtained. Further to list both routes if two routes are possible.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 9 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Predict the products of the following reactions. Show stereochemistry and regiochemistry of the product, where relevant.arrow_forwardThe Wolff–Kishner reaction uses hydrazine (H2NNH2) and hydroxide (–OH) to reduce a carbonyl to the alkane. The first steps of the mechanism convert a carbonyl to a hydrazone in a manner similar to imine formation. Draw the mechanism arrows for the reaction from the hydrazone to the alkane. Be sure to add lone pairs of electrons and nonzero formal charges to all species.arrow_forwardIf the given alkyne product below is subjected to acetylide formation followed by nucleophilic substitution by a primary alkyl halide, show how the following product (lower part of the pic) is formed.arrow_forward
- Provide the primary product and the mechanisms of the reaction shown below.arrow_forwardWrite down all possible alkene products from the following Elemination reaction (no mechanism is required) indicate which one will be major product. And explain it?arrow_forwardShow how to synthesize the following product as the major product starting with 2,2- dimethylpropane as the starting material. You may use additional reagents and any number of steps. Be sure to list each step with all reactants/reagents/conditions required. (Do not use hydrogenation reactions) fromarrow_forward
- Provide the major product for the following reactions. Show all mechanisms in detail.arrow_forwardWhat product or products are produced in each of the following reactions? By what mechanism ( SN1, SN2,E1 or E2 ) does each react? Show the resulting products as single product, main product and by-product.arrow_forwardProvide a step-by-step mechanism to account for the product of the following reaction. Show the structure of each of the intermediates and use curved arrows to indicate electron flow in each of these stepsarrow_forward
- Give the products of the following substitution reactions. For every reaction, show electron pairs on both nucleophile and leaving group.arrow_forwardWhat is the major substitution product for the following reaction? Show the mechanism for the reaction.arrow_forwardWhat product or products are produced in each of the following reactions? By what mechanisms (SN1, SN2, E1 or E2) does each react? Show the resulting products as single product, main product and by-product.arrow_forward
