
(a)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanamine (
Concept introduction:
Leveling effect refers to the effect of a solvent on the properties of acids and bases. For an acid-base reaction, the strength of the strong acid is limited or leveled by the basicity of the solvent. Similarly, the strength of the strong base is leveled by the acidity of the solvent. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.46P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanamine is a suitable solvent for a reaction involving the chloride ion
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of chloride ion
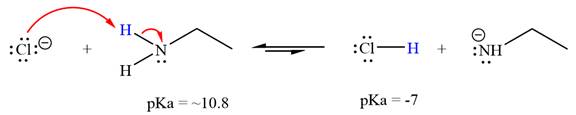
Hydrochloric acid,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(b)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanamine (
Concept introduction:
Leveling effect refers to the effect of a solvent on the properties of acids and bases. For an acid-base reaction, the strength of the strong acid is limited or leveled by the basicity of the solvent. Similarly, the strength of the strong base is leveled by the acidity of the solvent. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.46P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanamine is a not suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
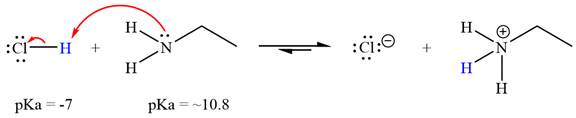
Hydrochloric acid,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(c)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanamine (
Concept introduction:
Leveling effect refers to the effect of a solvent on the properties of acids and bases. For an acid-base reaction, the strength of the strong acid is limited or leveled by the basicity of the solvent. Similarly, the strength of the strong base is leveled by the acidity of the solvent. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.46P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanamine is not a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
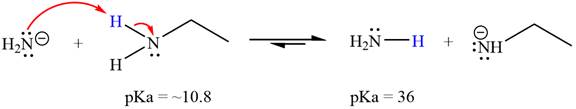
The reaction of

Ethanamine,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(d)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanamine (
Concept introduction:
Leveling effect refers to the effect of a solvent on the properties of acids and bases. For an acid-base reaction, the strength of the strong acid is limited or leveled by the basicity of the solvent. Similarly, the strength of the strong base is leveled by the acidity of the solvent. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.46P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanamine is not a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
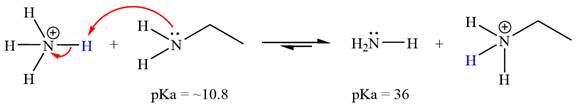
The reaction of
Ethanamine,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(e)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanamine (
Concept introduction:
Leveling effect refers to the effect of a solvent on the properties of acids and bases. For an acid-base reaction, the strength of the strong acid is limited or leveled by the basicity of the solvent. Similarly, the strength of the strong base is leveled by the acidity of the solvent. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.46P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanamine is not a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
Ethanamine,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(f)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanamine ( ) as a solvent with respect to leveling effect.
Concept introduction:
Leveling effect refers to the effect of a solvent on the properties of acids and bases. For an acid-base reaction, the strength of the strong acid is limited or leveled by the basicity of the solvent. Similarly, the strength of the strong base is leveled by the acidity of the solvent. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.46P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanamine is not a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of hydroxide ion
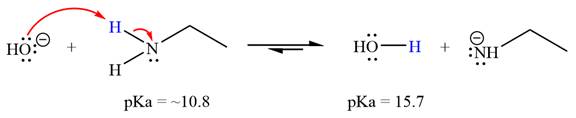
Ethanamine,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- Formaldehyde, H2C=O, is known to all biologists because of its usefulness as a tissue preservative. When pure, formaldehyde trimerizes to give trioxane, C3H6O3, which, surprisingly enough, has no carbonyl groups. Only one monobromo derivative (C3H5BrO3) of trioxane is possible. Propose a structure for trioxane.arrow_forwardWrite the products of the reaction of diphenhydramine (a base) with the acid HCI shown below. -COCH,CH,NCH3 + HCl CH3arrow_forwardAn unknown hydrocarbon Q has a formula C6H12. Q Reacts with osmium tetroxide to give a diol R. When oxidized with KMnO4 in an acidic medium, Q gives two products. One product is propanoic acid and the other a ketone S. Provide reaction equations to identify the possible structures of Q, R and S.arrow_forward
- CH3CH(NH2)CO2H in (zig-zag) structurearrow_forwardDraw the complete Lewis structure of (CH3)2CHCH(NH2)CO2H and identify all H-bond donors and all H-bond acceptors.arrow_forwardThe five parts of question 16 relate to the following three molecules: N-H А в с A (a) Which of the three molecules above are structural isomers? (b) Which of the molecules contains a carbon with linear geometry? (c) Which molecule contains a tertiary amine? (d) Which molecule only contains sp³ hybridized atoms (not including hydrogen)? (e) Which molecule is chiral? Circle the stereocentre in this molecule.arrow_forward
- Assignment # 5 This question is about colorful compounds: Colorful molecules are found in leaves (Bcarotene and chlorophyll), blood (hemoglobin), skin (melanin), and multivitamin supplements. They are all organic compounds with alternating single and double bonds. Organic compounds (a) A simple molecule with alternating single and double bonds is buta-1,3-diene. (i) Draw its skeletal structure. (ii) Write its molecular formula and empirical formula. (iii) How many carbon atoms have sp? hybridization in buta-1,3-diene?arrow_forwardIn an advanced analytical chemistry lab, a team analyzing a compound 'Q' known to be a structural isomer of octane (C8H18). To determine the specific structure of 'Q', a series of spectroscopic analyses are performed. The sequence of the analysis involves: Infrared (IR) spectroscopy, which indicates the absence of functional groups like alcohols, ketones, and carboxylic acids. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, showing signals indicative of only methyl and methylene groups, with no evidence of methine (CH) or quaternary carbon environments. Mass spectrometry (MS), revealing a fragmentation pattern consistent with branched alkane structures. Based on this sequence of analyses, what is the most likely structure of compound 'Q'? Options: A. 2,2,4- Trimethylpentane B. n-Octane C. 2-Methylheptane D. 3-Ethylhexane Don't use chatgpt please provide valuable answerarrow_forwardDraw the structure for the following compounds:(i) Ethanoic acid(ii) Bromopentane(iii) Butane(iv) Hexanalarrow_forward
- 1: In the sweetening MEROX process for kerosene the mercaptans are converted into (a) Sulpher (b) Disulphide (c) Hydrogen sulphide (d) None of these 2: Which of the following products contain maximum sulphur? (a) Diesel fuel (b) Fuel oil (c) Jet fuel (d) LPG 3: Which of the following petroleum product has a maximum C/H ratio (by weight)? (a) Light diesel oil (b) Fuel oil (c) Naphtha (d) Heating oil 4: Which of the following hydrocarbon are most desirable in gasoline? (a) Paraffins (b) Isoparaffins (c) Naphthenes (d) Aromatic 5: Octane no. of paraffins: (a) Remain constant with change in the number of carbon atoms (b) Increases with increase in the number of carbon atoms (c)Decreases with increase in the number of carbon atoms (d)None of the above 6: Which of the following hydrocarbons has a maximum octane number? (a) Benzene (b) Cyclohexane (c) Hexane (d) Iso-hexane 7: Which of the following petroleum products has a minimum flashpoint? (a)Gasoline (b) Kerosene (c) Fuel oil (d) Heating…arrow_forwardIn an advanced synthetic chemistry experiment, a researcher prepares a compound, ZY-7, by reacting a ketone (C5H100) with hydroxylamine (NH2OH), followed by heating in the presence of an acid catalyst. The resulting compound, ZY-7, is then treated with a solution of sodium nitrite (NaNO2) and hydrochloric acid (HCI) at low temperature. Identify the class of compound that ZY-7 most likely belongs to after this series of reactions." A) Amide B) Oxime C) Nitro compound D) Diazonium salt E) Ester Don't use chatgpt please provide valuable answerarrow_forwardwhat is the term used to describe organic reactions in which each atom of a diatomic molecule is transferred to one of the carbons in a double bond?arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning

