
(a) Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanol as a solvent with respect to leveling effect.
Concept introduction:
The solvent affects the properties of bases and acids. This effect is referred as leveling effect. For an acid-base reaction, the basicity of the solvent levels or limits the strength of the strong acid. Similarly, the acidity of the solvent levels the strength of the strong base. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.45P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanol is not a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
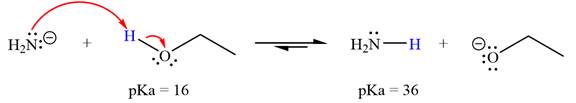
Ethanol,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(b)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanol as a solvent with respect to leveling effect.
Concept introduction:
The solvent affects the properties of bases and acids. This effect is referred as leveling effect. For an acid-base reaction, the basicity of the solvent levels or limits the strength of the strong acid. Similarly, the acidity of the solvent levels the strength of the strong base. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.45P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanol is a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of the acetate ion
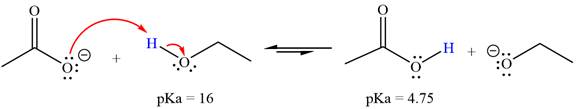
Acetic acid,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(c)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanol as a solvent with respect to leveling effect.
Concept introduction:
The solvent affects the properties of bases and acids. This effect is referred as leveling effect. For an acid-base reaction, the basicity of the solvent levels or limits the strength of the strong acid. Similarly, the acidity of the solvent levels the strength of the strong base. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.45P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanol is a suitable solvent for a reaction involving chloride ion
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of chloride ion
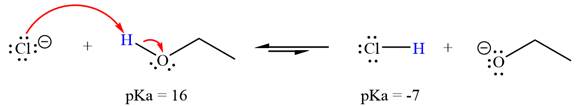
Hydrochloric acid,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(d)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanol as a solvent with respect to leveling effect.
Concept introduction:
The solvent affects the properties of bases and acids. This effect is referred as leveling effect. For an acid-base reaction, the basicity of the solvent levels or limits the strength of the strong acid. Similarly, the acidity of the solvent levels the strength of the strong base. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.45P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanol is a suitable solvent for a reaction involving phenoxide ion (
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of phenoxide ion (
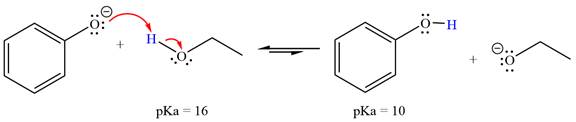
Phenol,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(e)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanol as a solvent with respect to leveling effect.
Concept introduction:
The solvent affects the properties of bases and acids. This effect is referred as leveling effect. For an acid-base reaction, the basicity of the solvent levels or limits the strength of the strong acid. Similarly, the acidity of the solvent levels the strength of the strong base. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.45P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanol is a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of cyanide ion
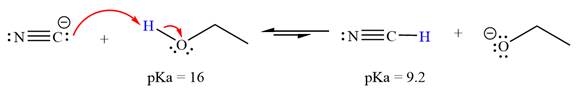
Acetylene,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(f)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanol as a solvent with respect to leveling effect.
Concept introduction:
The solvent affects the properties of bases and acids. This effect is referred as leveling effect. For an acid-base reaction, the basicity of the solvent levels or limits the strength of the strong acid. Similarly, the acidity of the solvent levels the strength of the strong base. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.45P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanol is not a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of propyl group
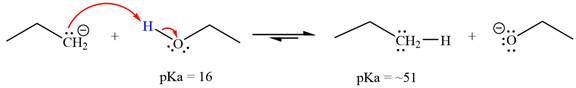
Ethanol,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- The addition of water to aldehydes and ketones occurs rapidly, although it is not thermodynamically favored. What would be the product for the reaction above? Hint: Think of the self-ionization of water and the polarity of the carbonyl group.arrow_forward4) Benzene, CeH6, can be described as an aromatic substance and is a starting material for many organic processes as seen in the following. NO₂ benzene Compound B Compound A Compound C a) Provide details of the bonding structure of benzene and sketch a diagram to show (3) this. b) For any one of these reactions above: 1) State the reagents required and include the details of the formation of the (3) reactive species required to start the reaction. ii) Provide details of the reaction mechanism for this chemical process making clear any intermediates formed. (3) c) in the context of benzene chemistry, a halogen substituent can be described as weakly activating. Explain the impact this has on the reaction rate of compound B relative to benzene in these types of reactions and provide a reason for this effect (3) faming sulfuric acidarrow_forward(a) Tsomane and Nyiko were given a task of synthesising methylenecyclohexane 2. After a brief discussion with each other, Tsomane proposed Method A to synthesise 2 from cyclohexanone 1 while Nyiko proposed Method B that started from hydroxymethylcyclohexane 3. Each student believed that their proposed method is better than the other. (Scheme below) (1) Ph Ph 8*8 Ph THF A 1 Santande B H₂SO4 100 °C 3 OH Using curly arrows, provide full mechanistic details accounting how methylenecyclohexane 2 was synthesised according to both Methods A and B.arrow_forward
- provide appropriate names for the following moleculesarrow_forward(a) Tsomane and Nyiko were given a task of synthesising methylenecyclohexane 2. After a brief discussion with each other, Tsomane proposed Method A to synthesise 2 from cyclohexanone 1 while Nyiko proposed Method B that started from hydroxymethylcyclohexane 3. Each student believed that their proposed method is better than the other. (Scheme below) (1) 1 Ph THF A Ph Ph B H₂SO4 100 °C 3 OH What is the name of the reaction that is followed by reaction Method A?arrow_forward(b) The activating and deactivating groups could affect the position(s) of the next incoming group(s) to the benzene ring. Based on the structure below, analyze and explain the group(s) on the benzene ring is activating or deactivating group. Then, identify the product(s) formed from the following reactions. NH, CC, CH;CH,COCI AICI, (i) NH, HNO, H,SO, (ii) H Br AICI, (iii) Page 3 of 4arrow_forward
- (a) Tsomane and Nyiko were given a task of synthesising methylenecyclohexane 2. After a brief discussion with each other, Tsomane proposed Method A to synthesise 2 from cyclohexanone 1 while Nyiko proposed Method B that started from hydroxymethylcyclohexane 3. Each student believed that their proposed method is better than the other. (Scheme below) Ph THF A Ph Ph B H₂SO4 100 °C 3 OH (iii) In analysing both these methods, are there other possible alkene products other than methylenecyclohexane 2? Use mechanistic details to support your answer.arrow_forwardBy drawing the lewis structure of the cyanide anion, interpret according to the molecular orbital theory on which atom the active end is on, that is, which atom it react in a reaction?arrow_forwardPredict (by name) the products of the following reaction.arrow_forward
- Give the product ( name and condense structure) of thereaction.arrow_forward3. It is required to introduce a halogen group to a five membered ring, thiophene. Discuss the reaction mechanism involved in the reaction by selecting a suitable halogen group and analyze why a particular substituted product obtained after the reaction is predominant over the other possible product(s) with the help of reactions. To meet the ever increasing demand of global population, the demand for textile products and consumption of dyes by these industries is increasing.arrow_forwardDraw the product of the following Lewis acid-base reaction. Discuss whether the product will retain its monomeric form or if it will dimerise and why. (c) Ph Toluene AICI CHO Pharrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

