
Concept explainers
a) CH3CHNH2 or CH3CH2 CONH2
Interpretation:
The levis concept (due to GN levis) which is the most general concept of a base defines a base as any species which is sufficient electron rich and contains at last one or more unshared electron pains available for donation, which subsequent electronic interaction or an apparent band formation with an acid, an electron deficient species.
Answer:
Ethylamine CH3CH2NH2 is more basic the amide (ethylamide) CH3CH2CoNH2.
Explanation:
Thus basicity is an attribute defecting the extent of overlapping of this done electron pain donation. Quantitative it is measured by this extent; and also, any structural or chemical environmental factor that tends to increase or active increase the extent of available of donation of this electron pain(s) to a nembutal acid is acid to enhance the basicity of a levis base.
On the basis of the above, we examine what structure or other factor in the two given molecules amide and amine lead then to the bases at all in the fast; and what facter causes them to be which laser copying strengths.
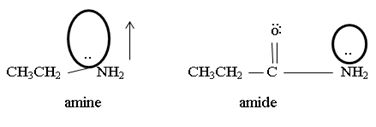
1) Fact I, Both are nitrogenous bases ie the basicity is due, intermediate to the problem of an unshared electron pair on the nitrogen atom of the –NH2-amine group. Thus more available then electron pair of on incident acid, the stronger is the base. Closely, the base strength all the diminished of any factor causes this electron pair to the less available for be genetics within appropriate acid.
2) Fact II, → considered ethylamine and ethanamide.
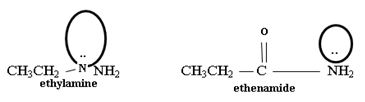
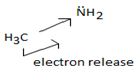
Ethanamide is much stronger base because of the electron releasing positive inductive +g effect of the ethyl (alkyl) group makes the N lone pair more available to any incident proton H+.
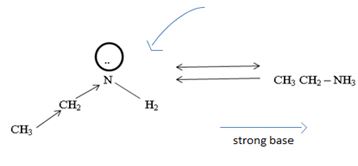
Havens is ethanamide, true is an incident stability caused by delocalization of the nitrogen line-pair electron through orbital overall with the carbonyl group. In resonance terms, amides are more states, and also then reactive than amides because this are hybrids of two resonance forms this amide resonance stabilization is lost when the nitrogen atom is protonated. So petroleum is disfavored. The following structural resonance form and electron density diagrams shown a significants reduced electron density on the amide nitrogen.
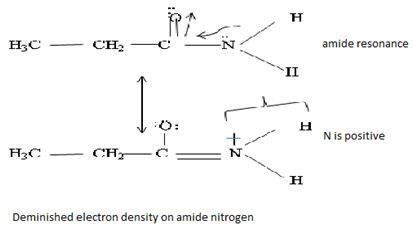
Oxygen – pauling electrons acids = 3.44
Nitrogen – pauling electrons acids = 3.04
Further the very electrons acid values of N is O, specifies the electron delocalization form N to O in amides, and consolidate the structure resonance forms.
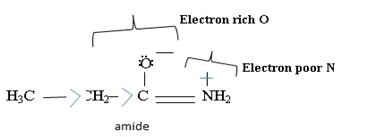
Thus, the very factor that lands amides then reactive also causes their reduced basicity than
Conclusion:
Form the above teach of relative basicity, it comes urtherit saying that population bile basics acids are governed by structural features in substances and chemical environments.
b) NCOH or CH3NH2
Interpretation:
As the outset, let it be said that acidity and basicity are measures of equilibrium (
Sodium hyduxide is a potentates much stronger base than methylamine.
Explanation:
The stronger this officials the more is the ease of proton uptake, and more is the hold on this proton; thus the stronger the species as a base.
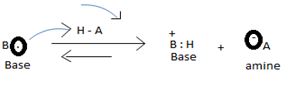
Organic bases are potencies much stronger bases than organic bases, v3 amines. Thus NCOH is a much stronger base then CH3NH2 an methylamine CH3NH2, the basicity is attributed to the presence of the unshared electron paid on the nitrogen of the amino group. The extent of available of this electron pair is increased by the inductive release of electron dentist by the methyl group. This miles methylamine strong organic base, but ten, then NAOH, the inorganic base.
Conclusion:
Sodium hyduxide is a potentates much stronger base than methylamine.
c) CH3NHCH3 or pyridine
Interpretation:
In organic bases, the basics is exhibited to the extent of available of a lone pair(s) of electron an nitrogen atom of the amino group, the more available then electron pair for uptake of a proton, the stronger the base.
Explanation:
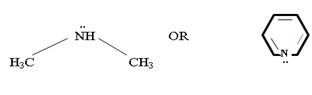
In dimethyl amine, inductive release of electrons by the two methyl groups increase the electron density on the nitrogen atom to an appropriate degree. The compound is thus a very strong base, convenes, in the heterocyclic amine pyridine, the line electron pair on nitrogen is lost by amides delocalization into the benzene ring and nitrogen causes c positive change. Thus it is a very week base.
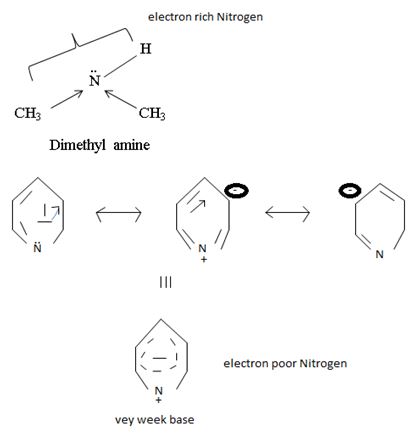
Conclusion:
Basicity in organic amines thus is a measure of the extent of availability of an unshared electron pair on the amines stronger amines than both
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 24 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Rank the compounds in each set in order of increasing acid strength.(a) CH3CH2COOH CH3CHBrCOOH CH3CBr2COOHarrow_forward(a) Draw two different enol tautomers of 2-methylcyclohexanone. (b) Draw two constitutional isomers that are not tautomers, but contain a C=C and an OH group. 2-methylcyclohexanonearrow_forwardRank each set of compounds in order of increasing basicity.(a) NaOH, NH3, CH3NH2, Ph¬NH2 (arrow_forward
- Draw the line structures and provide common names for the following ketones: (a) 1-Phenylpropanone (b) 2-Methylpentan-3-one(c) 1-Cyclohexyl-3,3-dimethylbutan-2-onearrow_forwardName the following carboxylic acid derivatives, giving both a common name and anIUPAC name where possible.(a) PhCOOCH2CH(CH3)2arrow_forwardArrange the four compounds in increasing order according to the acidity of conjugate acid. (CH3)2NH CH3NH2arrow_forward
- Nepheliosyne B is a novel acetylenic fatty acid isolated from a New Caledonian marine sponge. (a) Label the most acidic H atom. (b) Which carbon–carbon σ bond is shortest? (c) How many degrees of unsaturation does nepheliosyne B contain? (d) How many bonds are formed from Csp–Csp3? (e) Label each triple bond as internal or terminal.arrow_forwardPQ-17. What is the major product of this reaction? (A) H3CO њсоян (B) OH OH (C) OH O H OH OH 1) CH,MgBr (1 eq.) 2) NHÀ -OH (D) онянarrow_forwardIn each pair of compounds, select the stronger base, and explain your choice.(a) HOCH2CH2NH2 or CH3CH2NH2 (b) PhNH2 or PhCH2NH2arrow_forward
- 1.(a) Which of the following groups has the LOWEST IUPAC priority?(A) CH3 (B) NH2 (C) OH (D) COOH (E) Br (b)Which of the following corresponds to the strongest acid?(A) (CF3)3C-COOH (B) (CF3)3 C-OH(C) CH3COOH (D) CH3OH(E) HOCH2CH3arrow_forwardName the following carboxylic acid derivatives, giving both a common name and anIUPAC name where possible. (c) PhCH(CH3)COOCH3arrow_forwardFor each of the following pairs, predict which substance is more soluble in water. (a) CH3CH2NH2 or NH3 (b) (CH3)3COH or CH3(CH2)5OH (c) CH3CH2CH2OH or CH3CH2CH2CH3 (d) CH3CH2CN or CH3CH2OCH3 (e) CH3CH2OH or CH3CH2CH2OH (f) CH3CH2OCH3 or CH3CH2CO2Harrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





