
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130970695
Author: Peter S. Shaffer, Lillian C. McDermott
Publisher: Addison Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 24.1, Problem 3bTH
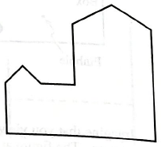
A student is looking at the building shown at right. The student then turns around and views the building through a pinhole camera. In the space below, sketch what the student would see in the camera. Explain your reasoning.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Choose two location of object (except at focal point),one from curved mirror and one from lenses. Using ray diagram method,illustrate the image formation as described in the table. Do the same with lenses. One diagram for Curved mirror and one diagram for lenses. Use the table below as your reference.
The figure below shows a small light source with two rays from the light hitting the top surface
of a solid piece of plastic. The path that the light ray on the left follows as it goes through the
plastic is also shown.
Draw, specifically and precisely, the path the ray on the right follows through the plastic.
Explain, based on your findings from previous investigations, how you determined where to
draw the path in the plastic for the second ray.
In the figure at right the light is crossing a vertical interface with the normal
Medium n1
marked as a dashed line. The light is coming from the left and crossing to
the right..
Medium n2
normal
Which is larger?
The index of refraction is larger
The speed of light is faster in
Choose the equation or equations that you will need to use to calculate n2 given the angles of incidence and
refraction and then to find the speed of light in medium n2.
Select one or more:
a. Force on an object mass m moving in a circle of radius R: F = mv2/R
b. B-field of a long straight wire: B = Hol/2nR
c. Snell's law: n;sin0, = n2sin02
d. Doppler shift: f' = f(1 ± u/c)
e. C =
= fA
f. Magnetic Force on a moving charge: F = qvBsin0
g. Force on a current carrying wire: F = BILsine
h. Mirror or Thin Lens Equation: 1/d, + 1/d; =1/f, h/h¡ = -d/d;
Chapter 24 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Ch. 24.1 - On the diagram, sketch what you would see on the...Ch. 24.1 - The small bulb is replaced by three longfilament...Ch. 24.1 - The three longfilament bulbs are replaced by a...Ch. 24.1 - Predict the size and shape of the shadow that will...Ch. 24.1 - Is it possible to place the bulb in another...Ch. 24.1 - Prob. 2cTHCh. 24.1 - Prob. 2dTHCh. 24.1 - Prob. 3aTHCh. 24.1 - A student is looking at the building shown at...Ch. 24.1 - Prob. 4aTH
Ch. 24.1 - Suppose that this student were walking through the...Ch. 24.2 - The top view diagrams at right were drawn by a...Ch. 24.2 - Draw a ray diagram to determine the location of...Ch. 24.2 - Describe how you could use a ray diagram to...Ch. 24.2 - A pencil is placed in front of a plane mirror as...Ch. 24.2 - Prob. 3bTHCh. 24.3 - Prob. 1aTHCh. 24.3 - A pin is placed in front of a semicylindrical...Ch. 24.3 - Prob. 1cTHCh. 24.3 - Prob. 2aTHCh. 24.3 - A very small, very bright bulb is placed for from...Ch. 24.4 - The following are top view diagrams of solid...Ch. 24.4 - The following are top view diagrams of solid...Ch. 24.4 - The following are top view diagrams of solid...Ch. 24.4 - The following are top view diagrams of solid...Ch. 24.4 - Prob. 2THCh. 24.4 - Prob. 3aTHCh. 24.4 - Prob. 3bTHCh. 24.4 - Is the image(s) of the nail real or virtual?...Ch. 24.5 - Suppose that the bulb is placed as shown. Using...Ch. 24.5 - Prob. 1bTHCh. 24.5 - Prob. 1cTHCh. 24.5 - Prob. 1dTHCh. 24.5 - Prob. 2aTHCh. 24.5 - Treat the image produced by lens 1 as an object...Ch. 24.5 - Repeat parts a andb for the case in which lens 2...Ch. 24.6 - Reproduced below is a side view diagram of the...Ch. 24.6 - In section III of the tutorial Magnification, you...Ch. 24.6 - Two thin convex lenses and an object are arranged...Ch. 24.6 - Prob. 3bTHCh. 24.6 - Two thin convex lenses and an object are arranged...Ch. 24.6 - Prob. 3dTHCh. 24.6 - Two thin convex lenses and an object are arranged...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
*Terminal speed of balloon A balloon of mass m drifts down through the air, The air exerts a resistive drag for...
College Physics
3. What is free-fall, and why does it make you weightless? Briefly describe why astronauts are weightless in th...
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
16.7 A submerged scuba diver hears the sound of a boat horn directly above her on the surface of the lake. At t...
University Physics (14th Edition)
17. A speed skater moving to the left across frictionless ice at 8.0 m/s hits a 5.0-m-wide patch of rough ice....
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (4th Edition)
What class of motion, natural or violent, did Aristotle attribute to motion of the Moon?
Conceptual Physics (12th Edition)
During a hailstorm, hailstones with an average mass of 2 g and a speed of 15 m/s strike a window pane at 45 ang...
An Introduction to Thermal Physics
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Physics Questionarrow_forwardFor each case below draw a ray diagram. Draw the image as an arrow and give a description of the image: (real, virtual or no image formed), (upright or inverted) and (enlarged, reduced or same size). 1.) Converging lens A.) C.) 9 2F B.) 1 2F 1 F 2F D.) 2F 2Farrow_forwardLOCATING IMAGES IN A PLANE MIRROR Part A - Drawing an Image Point Object First Ray 1. Draw an incident ray from the object to some point of incidence on the mirror. 2. Draw the point of incidence. 3. Draw the normal from the point of incidence. 4. Measure the angle of incidence, and then draw the reflected ray. 5. Extend the reflected ray behind the mirror. Use a dashed line behind the mirror. Second Ray (use a different colour if possible) 1. Draw a second incident ray from the object to some other point of incidence on the mirror. 2. Draw the new point of incidence. 3. Draw the normal from this new point of incidence. 4. Measure the angle of incidence, and then draw the new reflected ray. 5. Extend this reflected ray behind the mirror. Use a dashed line behind the mirror. The point where the two extended rays cross behind the mirror is where the image of the object should be located. Label it I.arrow_forward
- For each case below draw a ray diagram. Draw the image as an arrow and give a description of the image: (real, virtual or no image formed), (upright or inverted) and (enlarged, reduced or same size). 1.) Converging lensarrow_forwardIn the following situations 1. Draw for any mirror or lens, draw at least 3 principal rays and determine the location of the image (for actual rays use unbroken lines and for virtual or inferred rays use broken lines) (The dots represent the focal points of the lenses or mirrors and the vertical lines represent the location of the lens or mirror. Please note that the shape of the lens or mirror is intentionally not drawn) State whether the image is real or virtual 2. convex lens concave lens concave mirrorarrow_forwardA concave lens refracts parallel rays in such a way that they are bent away from the axis of the lens. For this reason, a concave lens is referred to as a diverging lens. Part A: Consider the following diagrams, where F represents the focal point of a concave lens. In these diagrams, the image formed by the lens is obtained using the ray tracing technique. Which diagrams are accurate?(Figure 1) *Type A if you think that only diagram A is correct, type AB if you think that only diagrams A and B are correct, and so on. Part B: If the focal length of the concave lens is -7.50 cm , at what distance d_o from the lens should an object be placed so that its image is formed 3.70 cm from the lens?arrow_forward
- A ball is dropped from rest 3.20 m directly above the vertex of a concave mirror having a radius of 1.50 m and lying in a horizontal plane. a) Describe the motion of the ball's image in the mirror by filling in the table below. b) At what two times do the ball and its image coincide? (List the lesser time first.)arrow_forwardAn image seen through a convex mirror cut from a sphere of radius 20cm is exactly half size of the object. Where must the object and image be located? Support your work with a ray diagram. Hint: Remember that virtual distances are negative when using the mirror equation. Follow grading rubric. Explain answer.arrow_forwardHello I have a question in regards to b. I have attached the pictures along with my work. Normally, to find an angle it’s arctan (y/x) , but in the answer key they use arctan(x/y) I also don’t understand how they simplify it. Thank you I have attached, the question, the diagram, my work, and the answer key. My work for part a is correctarrow_forward
- Show every step of the problem. That is the only way I will know how you solved the problem. Directions: See the directions attached. Please change 120N to 100N and change 150N to 120N (see the image attached). The first attachment is the specific question directions. The second attachment is the diagram to answer the directions in the first attachment. Don’t forget to “change 120N to 100N and change 150N to 120N”. Very IMPORTANT!!!arrow_forwardUse the information from the lecture on the rules for ray tracing to complete the ray tracing for the different situations below. This part is graded on completeness so just try it out even if you feel it is wrong. Notice it is important to not get confused between the rules for lenses and mirrors. 1. Consider a concave mirror. An object is placed at various object distances from the mirror. For each case, use ray tracing to determine the following characteristics of the image: * is it real or virtual? n is it upright or inverted? n is it smaller or bigger than the object (or the same size)? n where is the image located? (approximate location – does not have to be exact) Assume a concave mirror with a focal length of f=5cm. Make sure to use a ruler and follow the ray-tracing rules. Draw a diagram for each of the following cases: (a) object is at f/2 (b) object is at f (c) object is at 3f/2 (halfway between center of curvature and focal length) (d) object is at 2f (exactly at center of…arrow_forwardWhen considering the location of images formed by lenses, we often like to employ ray tracing diagrams. To do this we draw three rays of light and see where they intersect. 1. A ray parallel to the axis refracts through the far focal point. 2. A ray that enters the lens along a line through the near focal point emerges parallel to the axis. 3. A ray through the center of the lens does not bend. This method was shown to you in class for the following situation: An object and converging lenses with the distance to the object being greater than the focal length, do > f. object focal point do focal point Now you will complete the ray tracing diagram for an object that is closer than the focal length: de focal point image Answer the following based on your ray tracing: (a) Is the image real or virtual? (b) is the image larger or smaller than the object? focal pointarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON
Domestic Electric Circuits; Author: PrepOnGo Class 10 & 12;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2ZvWaloQ3nk;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY