
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780618974122
Author: Andrei Straumanis
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 9, Problem 11CTQ
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation: The correct product needs to be identified for the given reaction.
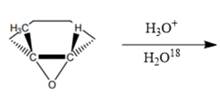
Concept Introduction: The given reaction is an acid-catalyzed
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A common method where one alkyl halide is converted to another alkyl halide is known as Finkelstein reaction. In one example of this reaction the reaction of an alkyl chloride with potassium iodide is generally carry out in acetone to maximize the amount of alkyl iodine that this formed. Why does the solvent increase the amount of alkyl iodide. Hint: potassium idioide is soluble in acetone but potassium chloride is not.
ONLY SOLVE BOLDED QUESTIONS PLEASE.
Synthesis of Diphenylacetylene
This synthesis requires two reactions. The first results in the debromination of trans-stilbene. In the first reaction, glacial acetic acid will be used as the solvent.
What is glacial acetic acid?
Why are we using pyridinium hydrobromide perbromide instead of bromine in this experiment?
What is the name of this reaction and what intermediate is formed?
In the second reaction, we are going to see stilbene dibromide undergo two eliminations to form the alkene. Provide the structure of diphenylacetylene. In each elimination the starting material will lose HBr. What is the name of this type of reaction?
Assuming you began this reaction with 1.035 g of trans-stilbene, and your final weight of diphenylacetylene is 0.377g, what is your percent yield? Which spectrometry would you use to verify that your product no longer contained any bromine, and had been completely converted to the alkyne? Sketch the spectrum of your…
The question is: "Draw the curved arrow mechanism for the reaction between pentan-2-one and (CH3)3O– in t-butanol to form an enolate. Draw all electrons and charges on both resonance structures. Then answer the question about the reaction."
I got the initial arrows correct, but am not entirely sure what the carbanion intermediate would look like and then what the curved arrows would be to convert it to its final oxanion form
Chapter 9 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The product in this reaction is basic enough to be protonated by a dilute HCl solution. Draw the protonated species, clearly showing where protonation occurs. Draw all possible resonance structures of the conjugate acid of the product, and use these to explain why the product is so much more basic than a typical ester, like ethyl acetate.arrow_forwardThis reaction does not follow the expected theory. Given what you know about substitution/elimination, what is the expected mechanism this reaction should follow? Suggest why that is not what happens and give the actual product of the reaction. Br ткон sarrow_forwardThe above reaction proceeds to yield only a single product. Draw the structure(s) of the carbocation intermediate, including resonance contributors, to show why this is the case.arrow_forward
- This is the reaction I was referring to, I have no idea of what reagents can lead me to the products.arrow_forwardRank these substrates in order of increasing ability to undergo a nucleophilic substitution aromatic (SNAr) reaction.arrow_forwardWhat is the slow (rate-determining) step in any electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction? Please provide a detailed explanation.arrow_forward
- Predict the product of the reaction. Draw all hydrogen atoms.arrow_forwardFor the following reaction explain why the unexpected products form, while the two theoretical products below are not formed.arrow_forwardWrite the main product(s) that will be formed as a result of the following reaction, together with its mechanism.arrow_forward
- Fill in the appropriate reagent or starting material in each of the following reactions.arrow_forwardThe reaction of an amine with an alkyl halide gives an ammonium salt. The rate of this SN2 reaction is sensitive to the polarity of the solvent. Draw an energy diagram for this reaction in a nonpolar solvent and another in a polar solvent. Consider the nature of the transition state, and explain why this reaction should be sensitive to the polarity of the solvent. Predict whether it will be faster or slower in a more polar solvent.arrow_forwardwhat is the product and mechanism used in this reaction?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning