
Keep or Drop a Division
Jan Shumard, president and general manager of Danbury Company, was concerned about the future of one of the company’s largest divisions. The division’s most recent quarterly income statement follows:
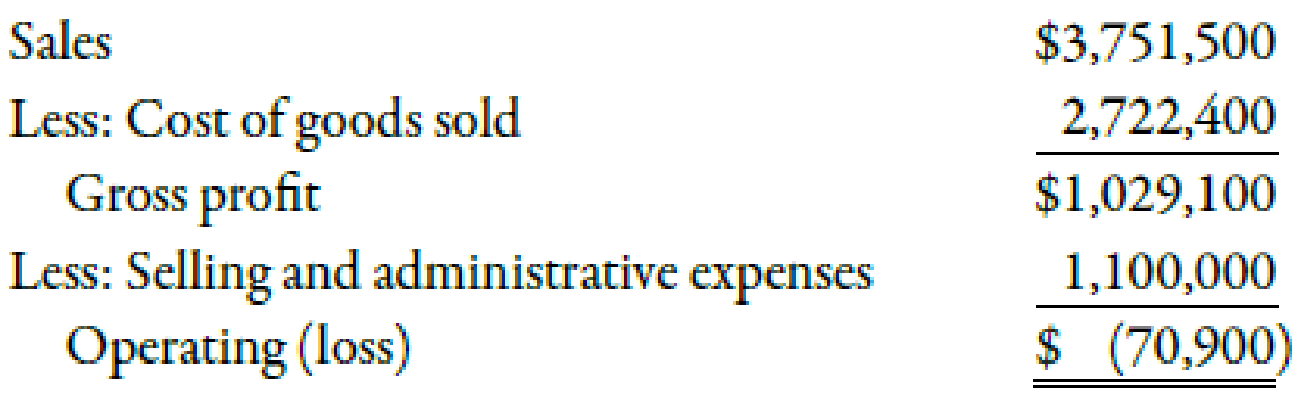
Jan is giving serious consideration to shutting down the division because this is the ninth consecutive quarter that it has shown a loss. To help him in his decision, the following additional information has been gathered:
- The division produces one product at a selling price of $100 to outside parties. The division sells 50% of its output to another division within the company for $83 per unit (full
manufacturing cost plus 25%). The internal price is set by company policy. If the division is shut down, the user division will buy the part externally for $100 per unit. - The fixed overhead assigned per unit is $20.
- There is no alternative use for the facilities if shut down. The facilities and equipment will be sold and the proceeds invested to produce an annuity of $100,000 per year. Of the fixed selling and administrative expenses, 30% represent allocated expenses from corporate headquarters. Variable selling expenses are $5 per unit sold for units sold externally. These expenses are avoided for internal sales. No variable administrative expenses are incurred.
Required:
- 1. Prepare an income statement that more accurately reflects the division’s profit performance.
- 2. Should the president shut down the division? What will be the effect on the company’s profits if the division is closed?
1.
Make an income statement which shows the profit performance of the division.
Explanation of Solution
Income Statement:
The statement that shows revenue and expenses incurred over a period of time (usually one year) is called an income statement. It is used for external financial reporting as it helps the outsiders and investors in evaluating the firm’s financial health.
The following table represents the income statement of Company D:
| Company D | |
| Income Statement | |
| Amount ($) | |
| Sales revenue | 3,751,500 |
| Less: Variable expenses1 | 2,004,900 |
| Contribution margin | 1,746,600 |
| Less: Direct fixed expenses2 | 1,518,250 |
| Divisional margin | 228,350 |
| Less: Common fixed expenses3 | 299,250 |
| Operating income (loss) | (70,900) |
Table (1)
The amount of operating loss for Company D is $70,900.
Working Notes:
1.
First, calculate the number of units:
Hence, the number of units is 20,500 units.
Calculate variable cost per internal unit:
Hence, the variable cost per internal unit is $46.4.
Calculate the variable cost per external unit:
Hence, the variable cost per external unit is $51.4.
Now, calculate the amount of variable cost:
Hence, the amount of variable cost is $2,004,900.
2. First, calculate the fixed selling and administrative expenses in order to calculate direct fixed expenses:
Hence, the amount of fixed selling and administrative expense is $997,500.
Calculate direct fixed selling and administrative expenses:
Hence, the direct fixed selling and administrative expense is $698,250.
Calculate the number of units sold:
Let the number of units sold be x. The division sells 50% of its output to another division for $83 per unit. If the division shut down the part would be purchased externally at $100 per unit. Therefore, the equation is given below:
Hence, the number of units is 41,000 units.
Calculate direct fixed overhead:
Hence, the direct fixed overhead is $820,000.
Now, calculate the amount of total direct fixed expenses:
Hence, the amount of total direct fixed expense is $1,518,250.
3. Calculation of common fixed expense:
Hence, the amount of common fixed expense is $299,250.
2.
Describe whether the president should shut down the division. Also, determine the effect of profit, if the division is closed.
Explanation of Solution
The following table represents the appropriate decision regarding the division:
| Costs | Alternatives | |
| Keep ($) | Drop ($) | |
| Sales | 3,751,500 | |
| Variable cost4 | (2,004,900) | (2,050,000) |
| Direct fixed expenses | (1,518,250) | |
| Annuity | 100,000 | |
| Total | 228,350 | (1,950,000) |
Table (2)
The relevant benefit to keep the division is $228,350 whereas, if the company drops the division, then the relevant benefit will be ($1,950,000). Therefore, the company should keep the division.
Working Note:
4. Calculation of variable cost if the company drops the division:
Hence, the amount of variable cost if the company drops the division is $2,050,000.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Business Decision-Making
- Shannon, Inc., has two divisions. One produces and sells paper party supplies (napkins, paper plates, invitations); the other produces and sells cookware. A segmented income statement for the most recent quarter is given below: On seeing the quarterly statement, Madge Shannon, president of Shannon, Inc., was distressed and discussed her disappointment with Bob Ferguson, the companys vice president of finance. MADGE: The Party Supplies Division is killing us. Its not even covering its own fixed costs. Im beginning to believe that we should shut down that division. This is the seventh consecutive quarter it has failed to provide a positive segment margin. I was certain that Paula Kelly could turn it around. But this is her third quarter, and she hasnt done much better than the previous divisional manager. BOB: Well, before you get too excited about the situation, perhaps you should evaluate Paulas most recent proposals. She wants to spend 10,000 per quarter for the right to use familiar cartoon figures on a new series of invitations, plates, and napkins and at the same time increase the advertising budget by 25,000 per quarter to let the public know about them. According to her marketing people, sales should increase by 10 percent if the right advertising is doneand done quickly. In addition, Paula wants to lease some new production machinery that will increase the rate of production, lower labor costs, and result in less waste of materials. Paula claims that variable costs will be reduced by 30 percent. The cost of the lease is 95,000 per quarter. Upon hearing this news, Madge calmed considerably and, in fact, was somewhat pleased. After all, she was the one who had selected Paula and had a great deal of confidence in Paulas judgment and abilities. Required: 1. Assuming that Paulas proposals are sound, should Madge Shannon be pleased with the prospects for the Party Supplies Division? Prepare a segmented income statement for the next quarter that reflects the implementation of Paulas proposals. Assume that the Cookware Divisions sales increase by 5 percent for the next quarter and that the same cost relationships hold. 2. Suppose that everything materializes as Paula projected except for the 10 percent increase in salesno change in sales revenues takes place. Are the proposals still sound? What if the variable costs are reduced by 40 percent instead of 30 percent with no change in sales?arrow_forwardLinda Mars, a recent graduate of Bell's accounting program, evaluated the operating performance of Cullumber Company's six divisions. Linda made the following presentation to Cullumber's board of directors and suggested the Percy Division be eliminated. "If the Percy Division is eliminated," she said, "our total profits would increase by $26,100." The Other Percy Division Five Divisions Total Sales $1,663,000 $100,900 $1,763,900 Cost of goods sold 977,300 76,800 1,054,100 Gross profit 685,700 24,100 709,800 Operating expenses 528,400 50,200 578,600 Net income $157,300 $ (26,100 ) $131,200 In the Percy Division, cost of goods sold is $59,500 variable and $17,300 fixed, and operating expenses are $31,000 variable and $19,200 fixed. None of the Percy Division's fixed costs will be eliminated if the division is discontinued. Is Linda right about eliminating the Percy Division? Prepare a schedule to support your answer. (Enter negative amounts using either a negative sign preceding the…arrow_forwardSharon Mars, a recent graduate of Bell's accounting program, evaluated the operating performance of Carla Vista Company's six divisions. Sharon made the following presentation to Carla Vista's board of directors and suggested the Percy Division be eliminated. "If the Percy Division is eliminated," she said, "our total profits would increase by $25,300." The Other Five Divisions Percy Division Total Sales $1,663,000 $100,900 $1,763,900 Cost of goods sold 978,400 76,500 1,054,900 Gross profit 684,600 24,400 709,000 Operating expenses 528,500 49,700 578,200 Net income $156,100 $ (25,300) $130,800 In the Percy Division, cost of goods sold is $60,100 variable and $16,400 fixed, and operating expenses are $29,100 variable and $20,600 fixed. None of the Percy Division's fixed costs will be eliminated if the division is discontinued. Is Sharon right about eliminating the Percy Division? Prepare a schedule to support your answer. (Enter negative amounts using either a negative sign preceding…arrow_forward
- Jan Shumard, president and general manager of Danbury Company, was concerned about thefuture of one of the company’s largest divisions. The division’s most recent quarterly incomestatement follows:Sales $3,751,500Less: Cost of goods sold 2,722,400Gross profit $1,029,100Less: Selling and administrative expenses 1,100,000Operating (loss) $ (70,900)Jan is giving serious consideration to shutting down the division because this is the ninth consecutive quarter that it has shown a loss. To help him in his decision, the following additionalinformation has been gathered:• The division produces one product at a selling price of $100 to outside parties. Thedivision sells 50% of its output to another division within the company for $83 per unit(full manufacturing cost plus 25%). The internal price is set by company policy. If thedivision is shut down, the user division will buy the part externally for $100 per unit.• The fixed overhead assigned per unit is $20.• There is no alternative use for…arrow_forwardManuel Inc. produces textiles in many different forms. After recording lower than anticipated profits last year, Manuel has decided to shut down one of its divisions that is not performing well. The accounting manager has compiled the following data on the two divisions being considered for closing and has asked you to evaluate the short-term and long-term effects on profits of closing each division. Which division should be closed if Manuel is most concerned with increasing long-run profits? Winter Outerwear High-End Suits Net revenues $ 1,200,000 $ 5,200,000 Variable costs 660,000 2,160,000 Contribution margin 540,000 3,040,000 Controllable fixed costs 0 2,020,000 Controllable margin 540,000 1,020,000 Noncontrollable fixed costs 770,000 1,540,000 Contribution by division $ (230,000 ) $ (520,000 ) multiple choice Winter Outerwear High-End Suits Closing either would have the same…arrow_forwardThe division manager of Division B received the following operating income data for the past year: The manager of the division is surprised that the T205 product line is not profitable. The division accountant estimates that dropping the T205 product line will decrease fixed cost of goods sold by $75,000 and decrease fixed selling and administrative expenses by $10,000. Prepare a differential analysis to show whether Division B should drop the T205 product line. What is your recommendation to the manager of Division B?arrow_forward
- Anderson Publishing has two divisions: Book Publishing and Magazine Publishing. The Magazine division has been losing money for the last five years and Anderson is considering eliminating that division. Anderson’s information about the two divisions is as follows: Book Division Magazine Division Total Sales Revenue $ 8,160,000 $ 3,452,300 $ 11,612,300 Cost of Goods sold Variable manufacturing costs 2,360,000 1,176,500 3,536,500 Fixed manufacturing costs 1,113,500 1,292,700 2,406,200 Gross Profit $ 4,686,500 $ 983,100 $ 5,669,600 Operating Expenses Variable operating expenses 171,000 250,800 421,800 Fixed operating expenses 2,952,000 1,209,100 4,161,100 Net income $ 1,563,500 $ (476,800) $ 1,086,700 Only 20 percent of the fixed manufacturing costs and 60 percent of the fixed operating expenses are directly attributable to each division. The remaining are common or shared between the two divisions. Required: Compute the contribution margin and the…arrow_forwardAnderson Publishing has two divisions: Book Publishing and Magazine Publishing. The Magazine division has been losing money for the last five years and Anderson is considering eliminating that division. Anderson's information about the two divisions is as follows: Sales Revenue Cost of Goods sold Variable manufacturing costs Fixed manufacturing costs Gross Profit Operating Expenses Variable operating expenses Fixed operating expenses Net income Book Division $ 7,960,000 2,160,000 1,093,500 $4,706,500 151,000 2,932,000 $ 1,623,500 Contribution Margin Segment Margin Book Division Magazine Division $ 3,367,700 Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. 1,076,800 1,241,200 $ 1,049,708 Only 20 percent of the fixed manufacturing costs and 60 percent of the fixed operating expenses are directly attributable to each division. The remaining are common or shared between the two divisions Required: Required 1 Required 2 Compute the contribution margin and segment margin…arrow_forwardSuppose Grainy Day is considering discontinuing its tasty loops product line. Assume that during the past year, the tasty loops' product line income statement showed the following: A B 1 Sales revenue $7,550,000 2 Less: Cost of goods sold 6,400,000 3 Gross profit 1,150,000 4 Less: Operating expenses 1,650,000 5 Operating income (loss) $(500,000) Fixed manufacturing overhead costs account for 40% of the cost of goods, while only 30% of the operating expenses are fixed. Since the tasty loops line is just one of the company's cereal operations, only $780,000 of direct fixed costs (the majority of which is advertising) will be eliminated if the product line is discontinued. The remainder of the fixed costs will still be incurred by the company. If the company decides to discontinue the product line, what will happen to the company's operating income? Should Grainy Day discontinue the tasty loops product line?arrow_forward
- Anderson Publishing has two divisions: Book Publishing and Magazine Publishing. The Magazine division has been losing money for the last five years and Anderson is considering eliminating that division. Anderson’s information about the two divisions is as follows: Book Division Magazine Division Total Sales Revenue $ 7,840,000 $ 3,316,900 $ 11,156,900 Cost of Goods sold Variable manufacturing costs 2,040,000 1,016,900 3,056,900 Fixed manufacturing costs 1,081,500 1,210,300 2,291,800 Gross Profit $ 4,718,500 $ 1,089,700 $ 5,808,200 Operating Expenses Variable operating expenses 139,000 203,900 342,900 Fixed operating expenses 2,920,000 1,191,200 4,111,200 Net income $ 1,659,500 $ (305,400) $ 1,354,100 Only 20 percent of the fixed manufacturing costs and 60 percent of the fixed operating expenses are directly attributable to each division. The remaining are common or shared between the two divisions. Required: Present the financial information in…arrow_forwardReq 1 Req 2A Req 2B Prepare a contributlon format Income statement segmented by dlvislons. Division Total Company East Central West Req 1 Req 2A Req 2B The Marketing Department has proposed increasing the West Division's monthly advertising by $22,000 based on the belief that it would increase that division's sales by 13%. Assuming these estimates are accurate, how much would the company's net operating income increase (decrease) if the proposal is implemented? (Do not round intermediate calculations.) Net operating income will by Req 1 Req 2A Req 2B Would you recommend the increased advertising? OYes Noarrow_forwardGion Company is considering eliminating its windows division, which reported an operating loss for the recent year of $125,000. Division sales for the year were $1,310,000 and its variable costs were $1,175,000. The fixed costs of the division were $270,000. If the windows division is dropped, 60% of the fixed costs allocated to it could be eliminated. The impact on Gion's operating income from eliminating this business segment would be: Multiple Choice $56,700 decrease $27.000 increase $162,000 decrease $162,000 increase $27,000 decreasearrow_forward
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning

