
Foundations of Materials Science and Engineering
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696558
Author: SMITH
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 4.8, Problem 1KCP
To determine
Describe and illustrate the solidification process of a pure metal in terms of the nucleation and growth of crystals.
Expert Solution & Answer
Explanation of Solution
Show the solidification process of a pure metal as in Figure (1).
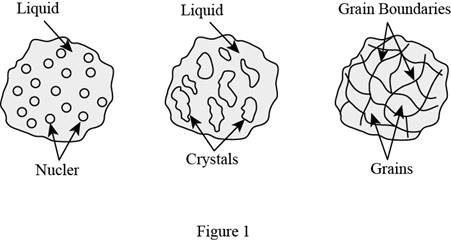
In general, the solidification process of a pure metal involves three stages in terms of the nucleation and growth of crystals. The first stage involves the development of stable nuclei in the fluid melt. The second stage involves the development of these cores or nuclei into stable crystals in the fluid melt and the last stage involves the development solidified structure enclosing grains formed from the crystals.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Subscribe now to access step-by-step solutions to millions of textbook problems written by subject matter experts!
Students have asked these similar questions
(b) Determine the Miller indices of the cubic crystal plane that intersects the following position
coordinates: (0, 0, 1/2); (1, 0, 0); (1/2, 1/4, 0).
(c) Describe and illustrate the solidification process of a pure metal in terms of the nucleation
and growth of crystals.
Given that the expression for the equilibrium concentration of point defects are similar for pure metals, will there be identical amount of vacancies and (self-) interstitial atoms at room temperature? Justify your answer
4. Johnston and Gilman reported that in a grown LiF crystal that has been subjected to a constantstress of 10.8 MPa, the dislocation velocity at 249.1 K was 6×10-3 cm/s and at 227.3 K thevelocity was 10-6 cm/s. They also observed that their data suggested an Arrhenius relationshipbetween the dislocation velocity and the absolute temperature so that we can write? = ?exp ( ― ?/??)where v is the dislocation velocity, A is a constant of proportionality, Q an effective activationenergy in J/mol, and R is the universal gas constant (8.314 J/mol.K). Determine Q and A usingthe given data and the above equation.
5. A typical cross-head speed in a tensile testing machine is 0.2 in./min.
(a) What is thenominal/engineering strain rate imposed by this cross-head speed on a typical engineering tensilespecimen with a 2 inch gauge length?
(b) Estimate the average dislocation velocity that would be obtained at this strain rate in analpha-iron specimen with a total dislocation density of 1010 cm-2 of…
Chapter 4 Solutions
Foundations of Materials Science and Engineering
Ch. 4.8 - Prob. 1KCPCh. 4.8 - Define the homogeneous nucleation process for the...Ch. 4.8 - In the solidification of a pure metal, what are...Ch. 4.8 - In the solidification of a metal, what is the...Ch. 4.8 - During solidification, how does the degree of...Ch. 4.8 - Distinguish between homogeneous and heterogeneous...Ch. 4.8 - Describe the grain structure of a metal ingot that...Ch. 4.8 - Distinguish between equiaxed and columnar grains...Ch. 4.8 - How can the grain size of a cast ingot be refined?...Ch. 4.8 - Prob. 10KCP
Ch. 4.8 - Prob. 11KCPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 12KCPCh. 4.8 - Distinguish between a substitutional solid...Ch. 4.8 - What are the conditions that are favorable for...Ch. 4.8 - Prob. 15KCPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 16KCPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 17KCPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 18KCPCh. 4.8 - Describe the structure of a grain boundary. Why...Ch. 4.8 - Describe and illustrate the following planar...Ch. 4.8 - Prob. 21KCPCh. 4.8 - Describe the optical metallography technique. What...Ch. 4.8 - Prob. 23KCPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 24KCPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 25KCPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 26KCPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 27KCPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 28KCPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 29KCPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 30KCPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 31KCPCh. 4.8 - Calculate the size (radius) of the critically...Ch. 4.8 - Prob. 33AAPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 34AAPCh. 4.8 - Calculate the number of atoms in a critically...Ch. 4.8 - Prob. 36AAPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 37AAPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 38AAPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 39AAPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 40AAPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 41AAPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 42AAPCh. 4.8 - Determine, by counting, the ASTM grain-size number...Ch. 4.8 - Prob. 44AAPCh. 4.8 - For the grain structure in Problem 4.43, estimate...Ch. 4.8 - Prob. 46AAPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 47SEPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 48SEPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 49SEPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 50SEPCh. 4.8 - In Chapter 3 (Example Problem 3.11), we calculated...Ch. 4.8 - Prob. 52SEPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 53SEPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 54SEPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 55SEPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 56SEPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 57SEPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 58SEPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 59SEPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 60SEPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 61SEPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 62SEPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 63SEPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 64SEPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 65SEPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 66SEP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 30% ethylene glycol solution in water is gradually cooled. At what temperature in degree celsius does crystallization begin?arrow_forwardDescribe the cooling of a peritectic alloy with the concentration CO and sketch the microstructure during solidification. T S+α 8 S S+B a+ß В сarrow_forwardExplain the concept of formation and stability of metal-complexes and its application for the quantitative determination of hardness in water. 1arrow_forward
- (a) Describe with illustration, TWO (2) possible point defects that can occur in metal alloying elements. (b) Nickel and boron are to be diffused into an FCC iron metal during surface treatment. The diffusion process begins at the same time for both nickel and boron atoms. Identify with justification which metal atom diffused at a higher rate during the process. Table 2: Atom and crystal characteristic Atomic radius Crystal Structure Electronegativity Element Ni 0.1246 FCC +2 0.085 Rhombohedral +3 Fe 0.124 FCC +2 C 0.071 НСР +4arrow_forwarda) Sketch and label tensile stress-strain curves for a typical BCC and FCC metal and explain the salient differences from a slip system perspective Explain the Fick’s two laws of diffusion and discuss their common uses. What atomic factors govern the extent of solid solubility?arrow_forward(d) Given that the grain size in a solid solution is determined according to the following expression: = 22-1 where Ny is the average number of grains per square inch at a magnification of M, and n is the ASTM grain size number. Carry out the following: i. Determine the ASTM grain size if 30 grains per square inch are measured at a magnificatio 100X. ii. Calculate the number of grains per square inch at a magnification of 75X.arrow_forward
- How phases grow in alloys during crystal growtharrow_forward(a) Explain the fotlowing teminologies: i. Crystallinity ii. Allotropy iii. Polymorphism iv. Coordination number 31Page (b) Copper crystallises as FCC (face centred cubic). Given that the atomic radius and density of a given copper sample are 1.28 x 1010 m and 8.98 x 10' kg/m' respectively, carry out the following: Calculate the mass of the copper sample. Take Avogadro's number, NA = 6.023 x 1023 atoms/mole. (i) If the interatomic planar spacing, d, in the sample above is 2.96 x 1010 m, determine the angle at which the first Bragg reflection will occur from the (111) plane if x-radiation of wavelength 1.52 x 1010 m is used for the analysis. (ii) (c) Give two uses of pure copper and two commercial applications of copper alloys.arrow_forwardQ1/ In a homogeneous solidification process, assume molten metal solidifies into a spherical nucleus with a BCC structure. The given data are; lattice parameter (0.292 nm), the heat of fusion energy (1.85×10-9 J/m³), latent surface free energy (0.204 J/m²), critical radius (1-35 nm), equilibrium melting temperature (1516 K), and room temperature (27 °C). Calculate the following for this metal; (a) supercooling value temperature (b) activation tree energy (c) number of atoms in a nucleus of critical size.arrow_forward
- Questions: Considering that the steel contains 0.1 – 0.8 wt% carbon by weight, how can you account for the high percentage of pearlite in the microstructure? (1) Hint: See Figure 3, the enlarged picture of pearlite and consider differences in atomic weight (Fe;C), and overall composition of pearlite. 20 μη From Metals Handbook, Vol.9, 9th edition, Metallography and Micrestructures, 1985. Heproduced by permission of ASM International, Materials Park, OH. Figure 3 High magnification micrograph of pearlitearrow_forward2. (a) Nickel-based alloys are used for gas turbine blades in aerospace engines. Briefly discuss the characteristics that make these alloys the choice for this application. (b) Single-crystal technology is applied to nickel alloys that are used as gas turbine blades in aerospace engines. With the aid of sketches describe how a single-crystal casting can be manufactured and explain why a single-crystal casting is likely to have superior creep resistance than a directly-solidified one. (c) Demonstrate the application of the Ten-percent Rule by calculating the approximate tensile strength and elastic modulus in the 0˚ direction of a carbon-fibre reinforced polymer composite if the strength and elastic modulus in the 0˚ single ply are 3620 MPa and 143 GPa respectively. The lay-up sequence of the composite is [02/+45/-45/902]s.arrow_forwardDetermine values for the constants n and k for the recrystallization of copper at 119°C. Enter your results in the questions belowarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY