
Concept explainers
A block on a frictionless table is connected to a spring as shown. The spring is initially unstretched. The block is displaced to the right of point R and is then released.
1. When the block passes point R, is the spring compressed or stretched?
Does your answer depend on the direction in which the block is moving? Explain.
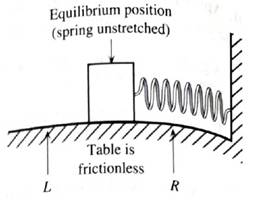
2. In the space provided, draw a free-body diagram for the block at the instant the block passes point R moving to the left. Draw arrows to represent the directions of the velocity, the acceleration, and the net force on the block, all at that instant. If any quantity is zero, state so explicitly.

Is the net work done on the block from point of release to point R, positive, negative, or zero? Explain.
At some instant, the block passes point L moving to the left. Draw a free-body diagram for the block at that instant. Also, draw arrows to represent the direction of the velocity, the net force, and the acceleration, all at that instant. If any quantity is zero, state so explicitly.

During a small displacement of the block from the right of point L to take the left of point L:
Is the net work done on the block positive, negative, or zero? Explain.
Does the speed of the block increase, decrease, or remain the same? Explain how your answer is consistent with the work-energy theorem.
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 3 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics (5th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
University Physics Volume 2
An Introduction to Thermal Physics
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
- please answer all 4 parts and type answer please You have a massless spring with a relaxed length of 13.8 cm. (Draw a picture and a free body diagram for the object for parts A and B situation below.) A. If you hang the spring vertically with a 0.92 kg weight on it, the spring is now 17.6 cm long. What is the spring constant k? B. If you set the spring on the ground in a vertical position and set a 1.2 kg weight on top of it, how far is the spring compressed? What is the length of the spring when the weight is on it? C. If you hold the spring in a horizontal orientation, how much would you need to compress it to create a restoring force of 18 N from the spring? D. How much would you need to stretch the spring to get the same 18 N restoring force? Explain.arrow_forwardA rollercoaster cart of mass 450.0 kg is traveling in a loop of radius of 15.0m. Its speed at point A is 28.0m/s and its speed at point B is 14.0 m/s. Assume that at A the cart is already moving with circular motion. 1. Draw free body diagrams for the cart at points A and B (two separate free body diagrams). 2. Calculate the acceleration of the cart at points A and B (magnitude and direction). 3. Calculate the magnitude of the normal force exerted by the tracks on the cart at point A. 4. Calculate the magnitude of the normal force exerted by the tracks on the cart at point B.arrow_forwardShow transcribed image text a) Refer to Figure #1. A wagon is moving in a straight line with constant acceleration ax and its kinematics is measured with respect to inertial coordinates (X1, Y1). A ball inside the wagon is acted upon by a force F (components F7 and Fy) and gravity force Mg. The coordinate (x2. Y2) is moving with the wagon. Determine the acceleration of the ball measured in the (X2. Y2) coordinate frame. In other words, compute the acceleration of the ball relative to the wagon. (a) Answer: a(M/W)x = FX/M - ax; a(M/W)y = Fy/M - garrow_forward
- Constants The figure(Figure 1) shows a block (mass ma ) on a smooth horizontal surface, connected by a thin cord that passes over a pulley to a second block (mB), which hangs vertically. Part B Draw a free-body diagram for block B, showing the force of gravity on it, the force (tension) exerted by the cord, and any normal force. Draw the vectors starting at the black dot. The location and orientation of the vectors will be graded. The exact length of your vectors will not be graded but the relative length of one to the other will be graded. Figure (1 of 1 mB No elements selectedarrow_forwardA block with mass m = 1.34 kg has a speed of 6.79 m/s at point A on the path shown below. The path is frictionless until point C. The coefficient of kinetic friction between points C and D is 0.780. The labeled vertical distances are h₁ = 5.68 m and h₂ = 2.45 m. The block comes to rest after sliding a distance L past point C. a. Draw a complete free-body diagram for the block moving from point C to D.arrow_forwarde) A crate being pushed and pulled by the forces while moving to the right with acceleration a on a surface as in the figure below (friction present) f) A pulley system as we have seen in the class demo. Assume that the force F is able to lift the mass at a constant rate. 2. Write Newton's 2nd law for both x and y axes for the case e) and for the mass of case f) of problem 1.;arrow_forward
- Problem Solving: Show your solutions completely and neatly. 1. Two blocks A and B are lying on a frictionless surface as shown in Figure below, are connected by a cord passing over a small frictionless pulley. a. Draw an FBD for each block. b. What is the tension in the cord? 10 Kg A 30° 45° c. Calculate the mass of block B which slides down the plane that keeps the system moving at a constant speed.arrow_forwardM Assume M=500g, 0=60 degrees, the co-efficient of static friction is 0.5, and the co-efficient of kinetic friction is 0.1. 1. Will the box slide down the ramp or not move at all? Show your work. 2. If the box slides down the ramp find the acceleration of the box 3. How fast will the box be moving when it reaches the bottom of the ramp if the box was dropped from rest from an initial height of 2m above the ground?arrow_forwardProblem 3 A ball of mass m, slides over a ey sliding inclined plane of mass M and angle a. Denote by X, the coordinate of O' with re- spect to 0, and by (x.y) the Coordinate of m with respect 1. a O' to O'(see figure below) 1. Calculate the degree of freedom of the system 2. Find the velocity of m with respect to O. 3. Write the expression of the Lagrangian function 4. Derive the Euler Lagrange equations 5. Find r" and X" in terms of the masses (m.M), angle a and garrow_forward
- e1 A double incline is setup with two ramps as shown. The left block has a mass m1, and the right block has a mass m2. The left ramp is rough with kinetic friction coefficient uy and an angle 01. The ramp on the right is frictionless with an angle 02. The pulley is massless and frictionless. Assume the system starts accelerating to the right on initial release. a) In the Space below draw a set of free body diagrams (or a single one if taking that method which is fine) to fully describe all forces in this problem. b) Find an equation for the acceleration of the system.arrow_forwardWrite the given, find, solution and final answer. 1. A woman pushes a 2.0 kg cart initially cart initially at rest with a force of 350 N along a horizontal surface. The cart moves a distance of 4.0 m. What is the final speed of the cart assuming it starts from rest? 2. A force F= (3i+2j-4k) N acts on a particle. Because of this, the particle undergoes a displacement d= (5i+4j-8k) m. Find the work done by this force.arrow_forwardIn the picture below a block is at a height, h above point B with an initial velocity of 1.33m/s to the right. At point C the height is h/3 above B and a frictional force begins acting on the block at C. If the block stops 4.58 meters from point C and the kinetic coefficient of friction on the block was 0.313, what was the initial height of the block?arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





