
Concept explainers
Shown at right is a side-view diagram of the displacement,
1. Suppose instead that a hand pushes with a force of the same magnitude,
Explain how you used the definition of work to obtain your answer.
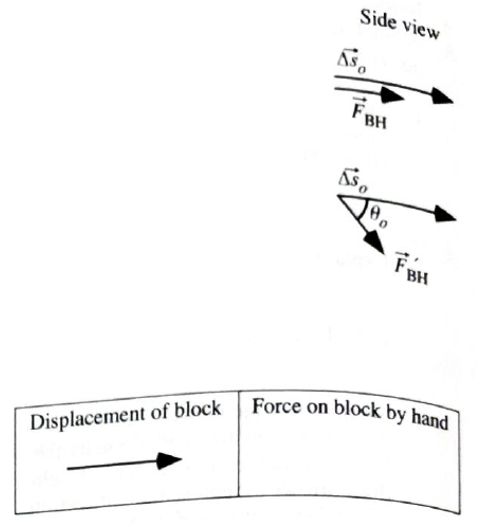
Suppose instead that a hand pushes with a force of the same magnitude,
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics: Principles with Applications
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
The Cosmic Perspective
Conceptual Physical Science (6th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
- Two blocks are connected by a very light string passing over a massless and frictionless pulley (Figure 1). Traveling at constant speed, the 20.0 N block moves 80.0 cm to the right and the 12.0 N block moves 80.0 cm downward. Part E During this process, how much work is done on the 20.0 N block by friction? Express your answer with the appropriate units. HẢ ? Wf, 20.0 N = Value Units Figure 1 of 1 Submit Request Answer Part F 20.0 During this process, how much work is done on the 20.0 N block by the normal force? N Express your answer with the appropriate units. ? 12.0 N Wn, 20.0 N = Value Unitsarrow_forwardmar Mech HW-60 Conservation of energy Just before 5. A spring is used to launch a block up a frictionless ramp as shown at right. At time t, the spring is compressed and the block is released from point A. The block moves up the ramp, losing contact with the spring at point B. When it passes point C, the block has a velocity vc directed up the ramp. t = t, Imagine a system that includes the block and possibly one or more additional objects. Is it possible to choose a system whose total energy is constant during the interval from t, to t,? If so, state which object(s) must be included in the system. Explain. a. tiner ods vd Anloe C BA b. Is it possible to choose a system so that the total energy is not constant during the interval from t, to t,? If so, what is the system containing the fewest possible objects for which the energy is not constant during this interval? Explain. pe ebtm by te re be.old A oold lonitaen2 e noool n o vd onob bow Jon o dem gaiwollol edsbi 2 msta di ve lodst…arrow_forwardUsing a cable with a tension of 1270 N, a tow truck pulls a car 5.00 km along a horizontal roadway. You do not have to show your work. Part A How much work does the cable do on the car if it pulls horizontally? Part B How much work does the cable do on the car if it pulls at 35.0∘ above the horizontal? Part C How much work does the cable do on the tow truck if it pulls horizontally? Part D How much work does the cable do on the tow truck if it pulls at 35.0∘ above the horizontal? Part E How much work does gravity do on the car in part A?arrow_forward
- A process occurs in which a system's potential energy decreases while the system does work on the environment. Does the system's kinetic energy increase, decrease, or stay the same? Or is there not enough information to tell? Explain. Match the words in the left column to the appropriate blanks in the sentences on the right.arrow_forwardWrite an expression for the net external work done on the block as it moves from the bottom of the block) and H (the height of the ramp). Show your work. to the top of the ramp in terms of the following quantities: mg (the magnitude of the weight| Name Work and changes in kinetic energy Me HL Free-body diagram for block H . In the space provided, draw and label a free-body diagram for the block as it moves un the ramp. h. For each force on the block, determine the angle between the displacement of the block and the force as the block moves up the ramp. Write an expression for the work done on the block by each force as the block moves up the I6 Express your answer in terms of any or all of the following: sin 0, cos 0, m, g, and d. the k done by any force is zero, state so explicitly. Show your work. You may need to use the angle addition formula cos (a + B) = cos a cos B- sin a sin p.arrow_forwardA force F is applied to a 2.0 kg, radio-controlled model car parallel to the x-axis as it moves along a straight track. The x-component of the force varies with the x-coordinate of the car as shown in the figure (Figure 1). Part A Calculate the work done by the force F when the car moves from x = 0 to x = 3.0 m. Express your answer with the appropriate units. Wo-3.0 = Value Units Figure 1 of 1 Part B F, (N) Calculate the work done by the force F when the car moves from x = 3.0 m to x = 4.0 m. 2 Express your answer with the appropriate units. 1 x (m) ? 1 2 3 4 5 -1 W3.0–4.0 = Value Units -2arrow_forward
- Use Diagram 1 below to answer the following questions. Assume the speed at Position 1 is 10 m/s, the mass of the roller coaster car is 250 kg, the track is frictionless, and that no work is done by air resistance. Position 3 is higher than Position 4, but lower than Position 1. 3 35 m 15 m 2. hat is the kinetic energy of the roller coaster car at Position 2? 三 三 DELLarrow_forwardA force of 8 N will stretch a rubber band 4 cm (0.04 m). Assuming that Hooke's law applies, how far will a 12-N force stretch the rubber band? How much work does it take to stretch the rubber band this far? How far will a 12-N force stretch the rubber band? m (Simplify your answer.) How much work does it take to stretch the rubber band this far? J (Simplify your answer.)arrow_forwardIn a physics lab, a Hot Wheels car starts at an elevated position, moves down an incline to the level ground, strikes a box and skids to a stop. Consider three states for the car: state A is the top of the incline; state B is the bottom of the incline before striking the box; state C is after the car has been brought to a stop. Use the diagram above (Image #4) and your understanding of the work-energy theorem to construct bar charts for the motion from A to B and from B to C. please help!arrow_forward
- Suppose you lift a 25 kg box by a height of 1.0 m. How much work do you do in lifting the box? Instead of lifting the box straight up, suppose you push it up a 1.0 m high ramp that makes a 30 degree angle with the horizontal, as shown in (Figure 1). Being clever, you choose a ramp with no friction. How much force is required to push the box straight up the slope at a constant speed? How long is the ramp? Use your force and distance results to calculate the work you do in pushing the box up the ramp.arrow_forwardUse the diagram and the information given to answer the following questions: The diagram shows a roller coaster of mass m=200 kg starting at Point A with a speed of v = 4.00 m/s and a height h = 30m. There is no work being done by a non-conservative force. a.Considering the ground (the upper surface of the shaded region in the diagram) as h=0, what is the cart’s gravitational potential energy at Point A,What is the cart’s kinetic energy ay Point A? and What is the cart’s Total Mechanical Energy at Point A? b.Using Conservation of Energy, determine the cart’s kinetic energy at Point B? and What is the cart’s speed at Point? c.Use Conservation of Energy to find the cart’s speed at Point C? and also Use Conservation of Energy to determine how high up the slope at Point D the cart would reach before stopping. Please answer it completelyarrow_forwardThe diagram below shows the potential energy U of a particle (in joules) as a function of its position æ. U 4 ir D 3 2 A 1 -1 -2+ B A particle is initially at point B. It is moving to the right, and its total energy is 4 J. Which of the following most accurately describes the motion of the particle? Ignore friction. O The particle will move between A and C indefinitely. The particle will eventually come to rest at B. The particle will come to rest at C. O The particle will come to rest at D. O The particle will move past D and continue to the right. O Something else will happen.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





