
Concept explainers
To review:
The relationship between genotype of patients and concentration as well as
Given:
In the given study, the drug calm was administered to people whose SNPs were known and after 12 hours, blood samples were drawn to find the concentration of the drug. The three different SNPs with genotypes are: SNP 5689 (AA, AG, and GG), SNP 8835 (AA, AC, and CC), and SNP 11286 (TT, TG, and GG) as shown in Figure below. The letters (A, T, G, and C) stand for the type of nucleotide on the two homologous chromosomes.
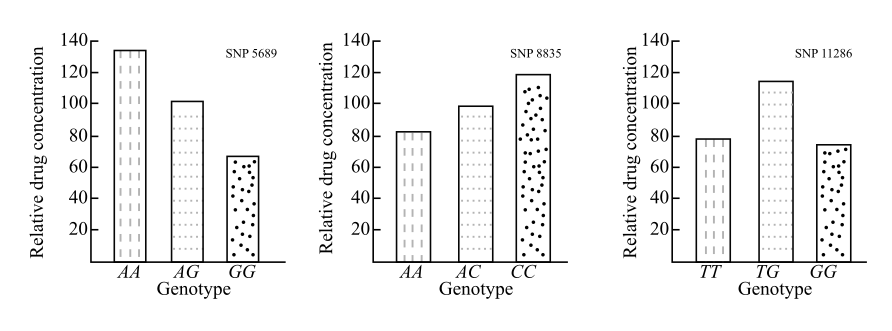
Introduction:
The study of effectiveness of the drug based on information about individual genome or SNPs is called pharmacogenomics. The metabolism of calm depends on the genotype or SNP present in each individual.
Explanation of Solution
SNP 5869: The rate of metabolism and drug concentration after 12 hours of administration is correlated with different genotypes of SNP 5869. The metabolism of the drug is efficient in the people with genotype GG where the drug concentration in the blood is around 70. On the other hand, the drug concentration for the genotype AG is around 100 and it is around 130 for AA genotype. So, the genotype GG of SNP 5869 is associated with metabolizing the drug, calm efficiently.
SNP 8835: The rate of metabolism is high in the case of the genotype AA where the drug concentration is less, which is around 80. On the other hand, the rate of drug metabolism is less in the case of the genotype CC with drug concentration of around 120 and genotype AC where the concentration is around 100. So, the genotype AA of SNP 8835 is associated with metabolizing the drug, calm efficiently.
SNP 11286: The rate of metabolism is efficient for the genotype TT where the drug concentration is around 80. The rate of metabolism is less for the genotypes GG and TG where the drug concentration is 90 and 110, respectively. So, the genotype TT of SNP 11286 is associated with metabolizing the drug, calm efficiently.
Thus, efficiency and rate of drug metabolism depend on the genotypes where drug concentration is inversely proportional to the rate of metabolism.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Life: The Science of Biology
- Based on the sensitivity of DNA to DNase I, as illustrated in Figure , which type of chicken hemoglobin (embryonic or adult) is likely to be produced in the highest quantity in the following tissues and developmental stages? Q. Erythroblasts at day 5arrow_forwardDetermine the isoelectric point of the peptide product of the mutated sequence: 5' - AUG UCC AUG AUU CUG GAA AUU ACC UCC AUC AUG AAG CGC UGA CCC AUU AUU AA - 3'arrow_forward>mutant1…arrow_forward
- Determine the responsiveness of the wild-type protein to maltose, the way by which mutation affects the function of the protein, and the most probable nature of the mutation in the gene at the molecular level.arrow_forwardLS1-1 Which of the following best represents the amino acid sequence found in normal adults with the HBB gene? O His, Gly, Asp, Gly, Gin, Leu, Leu Val, His, Leu, Thr, Pro, Glu, Glu O Val, Gly, Asp, Thr, Pro, Glu, Glu O Leu, Glu, Asp, Gly, Gin, Leu, Leuarrow_forwardQ11. One of the two genes known to be mutated in cases of Hypokalemic periodic paralysis (which is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern but known to affect males more often than females) is the calcium voltage-gated channel subunit alpha1 S (CACNA1S). What is known about the gene is recorded here: https://www.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Gene/Summary?db=core;g=ENSG00000081248;r=1:201039512-201112451 Please navigate to the link above and ensure that you click to reveal the transcript table. Then use the information in the table to answer the following question. What is the NCBI accession number (including the version) of the RefSeq Match for the first transcript (CACNA1S-201)? Answer: NCBI accession number (including the version) of the RefSeq Match for the first transcript (CACNA1S-201) is ...arrow_forward
- 66 Where is the promoter ? 3 5. 7 Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. a 2. 3 4.arrow_forwardThrough GWAS explorations, scientists have identified several SNPs linked to obesity in people who livein the United States. One of these SNPs was within agene called FTO. Interestingly, a common FTO variant is associated with obesity, but only in people bornafter 1945. Moreover, the later the birth year, thehigher the risk for obesity associated with this variantof FTO. Why would a genetic risk factor for obesityvary by birth year?arrow_forwardExercise Ill: For this lab exercise, you will evaluate a human pedigree for a particular disease, Huntington disease. Huntington disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. The disease presents around the age of 40, although there are juvenile onset forms of the disease. Suppose that there is a SNP closely linked to the Huntington gene, so close that there is little crossing over between the SNP and the Huntington gene. Consider the following family: Velma's father, now deceased, had Huntington Disease, but neither of his parents had the disease; therefore, it was a new mutation that caused his disease. Velma's mother does not have the disease. Before his death, Velma's father was genotyped for the SNP marker that is linked to the Huntington gene, and it was determined that he has alleles A1 and A2. Velma's mother was also genotyped and has alleles A1 and A3. Velma has one brother (age 45) who has Huntington Disease, and…arrow_forward

