
Concept explainers
To review:
The rate of photosynthesis increases in the leaf exposed to higher light intensities.
Given:
The graphs representing the rate of photosynthesis as a function of the intensity of light.
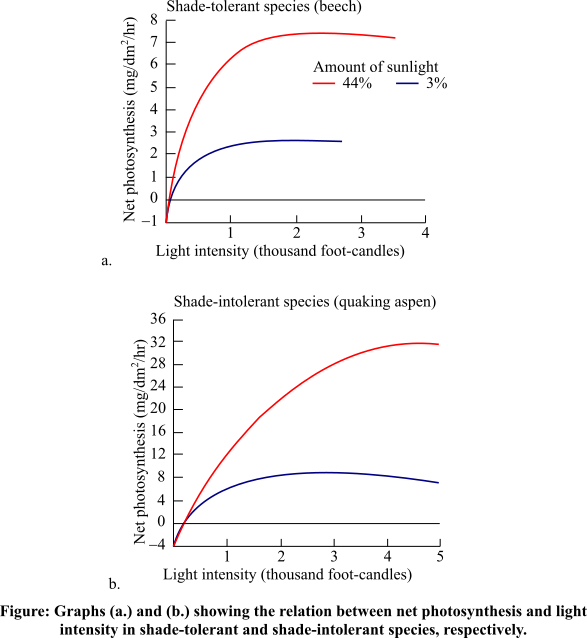
Introduction:
The process of photosynthesis is light dependent. Photosynthesis converts light energy into chemical energy. The rate of photosynthesis will increase if the leaves are exposed to the higher intensity of light.
Explanation of Solution
Photosynthesis is a light-dependent process. This process uses light energy to produce carbohydrate and provide energy to plant for various
The rate of photosynthesis increases when there are higher light intensities. The leaves, which are exposed to the higher intensity of light, show high rate of photosynthesis. At low light intensity, the leaves will show a decrease in the rate of photosynthesis. The leaves with the larger surface area and high density of chlorophyll will show a high rate of photosynthesis as they can absorb more light.
From the given graphs, it is clearly visible that both the plants show increasing rate of photosynthesis in high intensity of light (shown by orange line) and rate of photosynthesis is low in low intensity of light (shown by purple line). The photosynthesis is directly proportional to the intensity of light, so the curves of photosynthesis increase with increasing light intensities.
This occurs because of the increase in the rate of light-dependent reactions, which in turn results in the increase in photosynthesis rate. However, the rate of photosynthesis is dependent on other factors like temperature and carbon dioxide concentration. Therefore, with further increase in light intensity, the photosynthesis rate does not rise further and eventually plateaus.
Thus, it can be concluded that photosynthesis is a light-dependent process. The rate of photosynthesis is directly proportional to the intensity of the light but to a certain extent only, as photosynthesis is controlled by various other factors also.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Life: The Science of Biology
- What are the two places where light energy is required in the light reaction of photosynthesis? Why must energy be supplied at precisely these points?arrow_forwardDiagram 41 The Light Reactions of Photosynthesis STROMA Poteyte Potayate mples HAD Light HLARO ACE (high ir Carto Thylakold membrane ATP ynthase STROMA ow N concentration) ADP Diagram 4 shows a single thylakoid membrane taken from a chloroplast inside of a leaf cell. The events of the light dependent cycle that take place along the thylakoid membrane are shown. Identify an energy transfer that takes place n Diagram 4. Light energy is directly transferred into the chemical bonds of sugar. O Light energy is directly transferred into the chemical bonds of ATP The energy of the bonds of water are transferred into the chemical bonds of ATP. The energy from an excited electron is transferred into the chemical bonds of NADPH.arrow_forwardWhat is the overall outcome of the light reactions in photosynthesis? NADPH and ATP molecules are produced during the light reactions and are used to power the light independent reactions. NADPH and ATP molecules are produced during the light reactions, which are used to power the light dependent reactions. Sugar and ATP are produced during the light reactions, which are used to power the light independent reactions. Carbon dioxide and NADPH are produced during the light reactions, which are used to power the light dependent reactions.arrow_forward
- What is the relationship between light intensity and the rate of photosynthesis. Make a prediction about this relationship, and identify both independent and dependent variables in the prediction. What will be a suitable hypothesis predict answers for the following: A) what is the rate of germinating peas versus non-germinating peas. B) what is the effect of temperature on germinating peas?arrow_forwardWhich of the following is in the correct order from smallest to largest? Thylakoid disk, Photosystem I, mesophyll cell, chloroplast, leaf Photosystem II, Chloroplast, thylakoid disk, mesophyll cell, leaf Thylakoid disk, Photosystem II, chloroplast, mesophyll cell, leaf Photosystem II, Thylakoid disk, chloroplast, mesophyll cell, leafarrow_forwardWould a higher leaf area index always increase the amount of photosynthesis? Explain.arrow_forward
- The distinctly blue shade of a blue spruce results from the scattering of light by small waxy particles that coat the leaves. Explain how this scattering can protect the leaves from damage by short-wavelength ultraviolet light while still permitting the passage of longer wavelengths of light for photosynthesis.arrow_forwardAn experiment was done to determine how color of light and distance affects photosynthetic activity of the pond weed. Pond weed was placed in a test tube containing a solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate, and had its end cut; light was placed 50 cm away and four colors were tested (clear, red, blue, and green). After placing the light, the pondweed was given a certain amount of time to adjust before counting the bubbles, bubbles were counted for 1, 3, and 5 minutes. Only the bubbles that came out of the cut end was counted to represent the rate of photosynthesis. Below is the tabulated results. What are the possible factors or errors that could have affected clear/white light to have lower photosynthetic activity? In theory this should have the highest rate.arrow_forwardWhat are the products of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis? 1) production of ATP, oxygen, and NADPH O 2) production of ATP, water, and NADH 3) regeneration of NAD+ O 4) Production of G3P and ATP O 5) production of oxygen and NAD+arrow_forward
- What stages of the light-dependent reactions occur prior to the buildup of hydrogen ions in the thylakoid compartment? Select all that apply. Energy emitted by the electron transport chain triggered by PSII generates a hydrogen ion gradient across the thylakoid membrane. PSII pulls replacement electrons from water molecules, which then break apart into oxygen atoms and hydrogen ions. A photosystem II (PSII) absorbs light energy and releases an electron. Electrons released from PSII enter an electron transport chain in the thylakoid membrane. A flow of hydrogen ions causes ATP synthase to phosphorylate ATP.arrow_forwardUnder what environmental conditions does photorespiration “outcompete" that of the CC? Specifically, what mechanism is responsible for committing the cell to photorespiration and what type of plant does not have any "safeguards" to ensure that the CC is performed rather than photorespiration?arrow_forwardIndicate whether each of the following is produced during thelight-independent or light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis:O2, ATP, NADPH, and glucose.arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





