
Shown here are condensed income statements for two different companies (both are organized as LLCs and pay no income taxes).
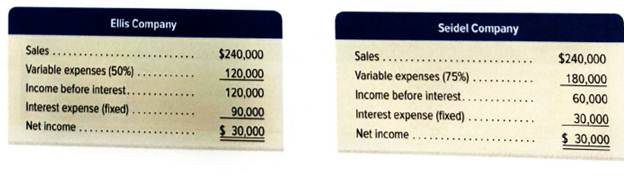
Required
- Compute times interest earned for Ellis Company.
- Compute times interest earned for Seidel Company.
- What happens to each company’s net income if sales increase by 10%?
- What happens to each company’s net income if sales increase by 40%?
- What happens to each company’s net income if sales increase by 90%?
- What happens to each company’s net income if sales decrease by 20%?
- What happens to each company’s net income if sales decrease by 50%?
- What happens to each company’s net income if sales decrease by 80%? Analysis Component
- Comment on the results from parts 3 through 8 in relation to the fixed-cost strategies of the two companies and the ratio values you computed in parts 1 and 2.
1.
Introduction: The times interest earned refer to the ratio of income before interest and taxes to interest earned.
To calculate: Times interest earned for company E.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of times interest earned for company E:
2.
Introduction: The times interest earned refer to the ratio of income before interest and taxes to interest earned.
To calculate: Times interest earned for company S.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of times interest earned for company S:
3.
Introduction: The net income refers to that part of income which is generated after subtracting all expenses such as cost of goods sold and other non-operating expenses, depreciation and taxes.
To calculate: The net income of each company if the sales increased by 10%.
Explanation of Solution
If sales increased by 10% for each company,
For company E;
For company S:
Computing net income for company E:
| Particular | Amount |
| Sales | $264,000 |
| Less: variable expense (50%) | (132,000) |
| Income before interest | 132,000 |
| Less: Interest expense(fixed) | (90,000) |
| Net income | $42,000 |
Computing net income for company S:
| Particular | Amount |
| Sales | $264,000 |
| Less: variable expense (75%) | (180,000) |
| Income before interest | 84,000 |
| Less: Interest expense(fixed) | (30,000) |
| Net income | $54,000 |
4.
Introduction: The net income refers to that part of income which is generated after subtracting all expenses such as cost of goods sold and other non-operating expenses, depreciation and taxes.
To calculate: The net income of each company if the sales increased by 40%.
Explanation of Solution
If sales increased by 40% for each company,
For company E;
For company S:
Computing net income for company E:
| Particular | Amount |
| Sales | $336,000 |
| Less: variable expense (50%) | (168,000) |
| Income before interest | 168,000 |
| Less: Interest expense(fixed) | (90,000) |
| Net income | $78,000 |
Computing net income for company S:
| Particular | Amount |
| Sales | $336,000 |
| Less: variable expense (75%) | (252,000) |
| Income before interest | 84,000 |
| Less: Interest expense(fixed) | (30,000) |
| Net income | $54,000 |
5.
Introduction: The net income refers to that part of income which is generated after subtracting all expenses such as cost of goods sold and other non-operating expenses, depreciation and taxes.
To calculate: The net income of each company if the sales increased by 90%.
Explanation of Solution
If sales increased by 90% for each company,
For company E;
For company S:
Computing net income for company E:
| Particular | Amount |
| Sales | $456,000 |
| Less: variable expense (50%) | (228,000) |
| Income before interest | 228,000 |
| Less: Interest expense(fixed) | (90,000) |
| Net income | $138,000 |
Computing net income for company S:
| Particular | Amount |
| Sales | $456,000 |
| Less: variable expense (75%) | (342,000) |
| Income before interest | 114,000 |
| Less: Interest expense(fixed) | (30,000) |
| Net income | $84,000 |
6.
Introduction: The net income refers to that part of income which is generated after subtracting all expenses such as cost of goods sold and other non-operating expenses, depreciation and taxes.
To calculate: The net income of each company if the sales decreased by 20%.
Explanation of Solution
If sales decreased by 20% for each company,
For company E;
For company S:
Computing net income for company E:
| Particular | Amount |
| Sales | $192,000 |
| Less: variable expense (50%) | (96,000) |
| Income before interest | 96,000 |
| Less: Interest expense(fixed) | (90,000) |
| Net income | $6,000 |
Computing net income for company W:
| Particular | Amount |
| Sales | $192,000 |
| Less: variable expense (75%) | (144,000) |
| Income before interest | 48,000 |
| Less: Interest expense(fixed) | (30,000) |
| Net income | $18,000 |
7.
Introduction: The net income refers to that part of income which is generated after subtracting all expenses such as cost of goods sold and other non-operating expenses, depreciation and taxes.
To calculate: The net income of each company if the sales decreased by 50%.
Explanation of Solution
If sales decreased by 50% for each company,
For company E;
For company S:
Computing net income for company E:
| Particular | Amount |
| Sales | $120,000 |
| Less: variable expense (50%) | (60,000) |
| Income before interest | 60,000 |
| Less: Interest expense(fixed) | (90,000) |
| Net income | ($30,000) |
Computing net income for company S:
| Particular | Amount |
| Sales | $120,000 |
| Less: variable expense (75%) | (90,000) |
| Income before interest | 30,000 |
| Less: Interest expense(fixed) | (30,000) |
| Net income | $0 |
8.
Introduction: The net income refers to that part of income which is generated after subtracting all expenses such as cost of goods sold and other non-operating expenses, depreciation and taxes.
To calculate: The net income of each company if the sales decreased by 80%.
Explanation of Solution
If sales decreased by 80% for each company,
For company E;
For company S:
Computing net income for company M:
| Particular | Amount |
| Sales | $48,000 |
| Less: variable expense (50%) | (24,000) |
| Income before interest | 24,000 |
| Less: Interest expense(fixed) | (90,000) |
| Net income | ($74,000) |
Computing net income for company W:
| Particular | Amount |
| Sales | $48,000 |
| Less: variable expense (75%) | (36,000) |
| Income before interest | 12,000 |
| Less: Interest expense(fixed) | (30,000) |
| Net loss | ($18,000) |
9.
Introduction: The net income refers to that part of income which is generated after subtracting all expenses such as cost of goods sold and other non-operating expenses, depreciation and taxes.
The time's interest earned refers to the ratio of income before interest and taxes to interest earned.
To comment: On the result for interest earned by both the companies and for part 3 to 8.
Explanation of Solution
Comments on times interest earned by both the companies are:
For company E:
The time's interest earned by company E is 1.3 times which is lesser than 2.5 times this indicates that it is difficult for the company to meet its debt and to invest in the company is riskier from the investor's point of view.
For company S:
The time's interest earned by company E is 2times which lesser than 2.5 times but the situation is better than company S, this indicates the riskier to invest in the company from an investor point of view.
Comments on the fixed cost strategies for the company The company fixed cost does not affect the net income as the sales increase but when sales start decreasing the net income is falling down and lead to losses for the company. Thus the company should increase sales or maintain sales to generate profit for the firm.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Financial Accounting: Information for Decisions
- Use the following income statement of Elliott Game Theory Consulting to determine its net operating profit after taxes (NOPAT). Use 25% as the tax rate. Elliott Game Theory Consulting Income Statement for Year Ending December 31arrow_forwardTwo companies have the financial information shown below. Requirements: Calculate the Gross Margin Percentage for each company. Calculate the Net Income Percentage for each company. From these ratios, what type of business do you think Yuri and Zuri might be? Yuri Zuri Net Sales 450,000 785,000 Cost of Goods Sold 261,000 698,000 Operating Expenses 67,500 45,200arrow_forwardThe net profit margin tells how much profit a company makes for every dollar it generates in revenue. If N is the net income (income after taxes have been paid) and R is the total revenue, then the net profit margin M is M (N,R) =N/R. This company pays a tax rate of 35% on its income. A) let I represent the company’s income before taxes. Express N as a function of I. (n is the part of I left after taxes) B) express M in terms of I and Rarrow_forward
- Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Shown here are condensed income statements for two different companies (assume no income taxes). Miller Company Sales Variable expenses (80%) Income before interest Interest expense (fixed) Net income Weaver Company Sales Variable expenses (608) Income before interest Interest expense (fixed) Net income Required: 1. Compute times interest earned for Miller Company and for Weaver Company. Choose Numerator: Times interest earned for Miller Company and Weaver Company. Choose Denominator: = 1 $ 1,100,000 880,000 220,000 78,000 $ 142,000 1 $ 1,100,000 660,000 440,000 298,000 $ 142,000 " = = Times interest earned Times interest earned 0 0arrow_forwardRefer again to the income statements for Cover-to-Cover Company and Biblio Files Company on their respective Income Statement panels. Note that both companies have the same sales and net income. Answer questions (1) - (3) that follow, assuming that all data for the coming year is the same as the current year, except for the amount of sales. 1. If Cover-to-Cover Company wants to increase its profit by $20,000 in the coming year, what must their amount of sales be? 2. If Biblio Files Company wants to increase its profit by $20,000 in the coming year, what must their amount of sales be? 3. What would explain the difference between your answers for (1) and (2)? The answers are not different; each company has the same required sales amount for the coming year to achieve the desired target profit. The companies have goals that are not in the relevant range. Biblio Files Company has a higher contribution margin ratio, and so more of each sales dollar is…arrow_forwardUsing Table 6–13, create a pro forma balance sheet using the percentage of sales method. If net income next year is $50,000, answer the following: How much did the owners take out of the business? What is the profit margin for next year?arrow_forward
- Consider the following income statement for the Heir Jordan Corporation: HEIR JORDAN CORPORATIONIncome Statement Sales $ 42,900 Costs 33,900 Taxable income $ 9,000 Taxes (21%) 1,890 Net income $ 7,110 Dividends $ 3,400 Addition to retained earnings 3,710 The balance sheet for the Heir Jordan Corporation follows. Based on this information and the income statement, supply the missing information using the percentage of sales approach. Assume that accounts payable vary with sales, whereas notes payable do not. (Leave no cells blank - be certain to enter "0" whenever the item is not a constant percentage of sales. Enter each answer as a percent rounded 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) HEIR JORDAN CORPORATION Balance Sheet Percentage of Sales Percentage of Sales Assets…arrow_forwardCompute profit margin for each of the 3 separate companies. Which company is the most profitable based on the profit margin ratio? Net income Net sales Total assets Kerr $ 6,450 43,000 48,000 Jax $ 1,640 41,000 45,000 Profit Margin Conclusion Bron $ 3,420 38,000 43,000 Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Compute profit margin for each of the 3 separate companies. Company Profit Margin (%) Kerr Jax Bronarrow_forwardRequired: Based on the information in the table below, prepare an income statement for Windswept Woodworks, Incorporated for year 2. Assume that the company pays a flat tax rate of 21% on its taxable income. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) Windswept Woodworks, Incorporated Input Data (millions of dollars) Accounts payable Accounts receivable Accumulated depreciation Cash & equivalents Common stock Cost of goods sold Depreciation expense Common stock dividends paid Interest expense Inventory Addition to retained earnings Long-term debt Notes payable Gross plant & equipment Retained earnings Sales Other current liabilities Tax rate Market price per share - year end Number of shares outstanding Windswept Woodworks, Incorporated Income Statement for the period ending December 31, Year 2 (millions of dollars) Sales Cost of goods sold Gross profit on sales Depreciation expense Earnings before interest and taxes Interest expense Taxable income Taxes (@21%) Net income Year 2 Year 1…arrow_forward
- Preparing common-size income statement Data for Connor Inc and Alto Corp follow: Requirements Prepare common-size income statements. Which company earns more net income? Which company’s net income is a higher percentage or its net sales revenue?arrow_forwardIf the following financial information related to XYZ Company. Total Revenues last year $870, depreciation expenses $40, costs of goods sold $350, and interest expenses $50. At the end of the year, current assets were $100 and current liabilities were $105. The company has an average tax rate of 30%. Calculate the net income for XYZ Company by setting up an income statement.arrow_forwardA company has the following income statement. What is its net operating profit after taxes (NOPAT)? Round it to a whole dollar. Will need to find EBIT first. Sales $ 1,050 Costs 600 Depreciation 170 EBIT $ ? Interest expense 50 EBT $ ? Taxes (24%) ? Net income $ ?arrow_forward
 Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning

