
Return to Figure 9.2. Suppose
Suppose a new firm with the same LRAC curve as the incumbent tries to bleak into the market by selling
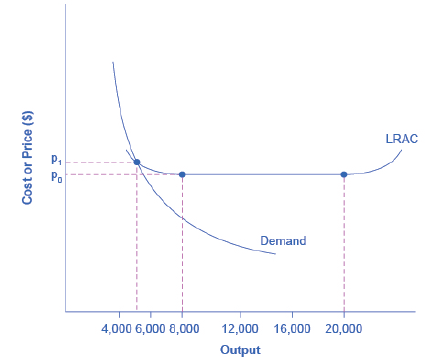
Figure 9.2 Economics of Scale and Natural Monoploy
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 9 Solutions
Principles of Economics 2e
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Principles of Management
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Cost Accounting (15th Edition)
Financial Accounting (12th Edition) (What's New in Accounting)
Managerial Accounting (5th Edition)
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
- A firm in a perfectly competitive industry has patented a newprocess for making widgets. The new process lowers the firm’saverage cost, meaning that this firm alone (although still aprice taker) can earn real economic profits in the long run. a. If the market price is $20 per widget and the firm’s marginalcost is given by MC=0.4q , where q is the dailywidget production for the firm, how many widgets willthe firm produce? b. Suppose a government study has found that the firm’snew process is polluting the air and estimates the socialmarginal cost of widget production by this firm to be. If the market price is still $20, what is thesocially optimal level of production for the firm? Whatshould be the rate of a government-imposed excise tax tobring about this optimal level of production? c. Graph your results.arrow_forwardSuppose that the market demand for a product is given by ( A > 0 and B > 0). Suppose QABP=-also that in a competitive industry the typical firm’s cost function is given by (k > 2()Cqkaqbq=++0, a > 0 and b > 0).(a) Calculate the long-run equilibrium market price and the output for the typical firm. (b) Calculate the equilibrium number of firms in the market.(c) Describe how changes in the demand parameters A and B affect the equilibrium number of firms in this market. Explain your results intuitively.arrow_forwardConsider a set of 1000 companies operating in a competitive market. The supply curve for this market is given by O = 20+2P and the demand curve is given by D = 280-4P, where quantity Q is measured in millions of tons and Price P is measured in monetary units. Considering that the marginal cost of the individual firm is given by 2Q, the quantity Q being measured in thousands of tons, we ask: a) Sketch the market equilibrium and the equilibrium of an individual firm. b) What is the situation of this market at that particular moment. c) Make considerations about the long-run equilibrium trend of this market.arrow_forward
- Suppose that each firm in a competitive industry has the following costs: Total cost: TC = 50 + 1/2q2 Marginal cost: MC = q where q is an individual firm's quantity produced. The market demand curve for this product is Demand: QD where P is the price and Q is the total quantity of the good. Currently, there are 9 firms in the market. = 120 – P а. What is each firm’s fixed cost? What is its variable cost? Give the equation for average total cost. b. Graph average-total-cost curve and the marginal-cost curve for q from 5 to 15. At what quantity is average-total-cost curve at its minimum? What is marginal cost and average total cost at that quantity? с. Give the equation for each firm's supply curve. d. Give the equation for the market supply curve for the short run in which the number of firms is fixed. е. What is the equilibrium price and quantity for this market in the short run? In this equilibrium, how much does each firm produce? Calculate each firm's profit or ^ loss. Is there…arrow_forwardSuppose that a competitive firm's marginal cost of producing output q (MC) is given by Assume that the market price (P) of the firm's product is $15. What level of output (q) will the firm produce? The firm will produce units of output. (Enter your response rounded to two decimal places.) What is the firm's producer surplus? Producer surplus (PS) is $ (Enter your response rounded to two decimal places.) Suppose that the average variable cost of the firm (AVC) is given by MC(q)=3+2q. AVC(q)=3+1q. Suppose that the firm's fixed costs (FC) are known to be $50. Will the firm be eaming a positive, negative, or zero profit in the short run? In the short run, the firm's profit will be positive Enter your answer in each of the answer boxes.arrow_forwardSuppose there are in total 3 firms in the market. Firm 1 decides its output first, then Firm 2 and Firm 3 decide their outputs simultaneously. The inverse demand function is p = 14 – 3q, where q = q1 + q2 + 43, and each firm's cost function is c(q.) = 2q?. What is the quantity that Firm 1 produces? Round your answer to 2 decimal points. Answer: The correct answer is: 1.04arrow_forward
- Suppose Razor is the only pharmaceutical firm that sells a flu vaccine in an economy. It faces the following demand, marginal revenue, marginal cost and total cost functions. P = 70 – Q MR = 70 – 2Q MC = 10 + Q Demand: Marginal revenue: Marginal cost: Total cost: TC = 20 + 10Q + 2 Find the profit maximizing output and the price of the vaccine for the firm. Show your steps. а. b. Derive the average cost function. Show your workings. Use the result of part a and b, find the profit level of the firm. Show your workings. с. d. Suppose the government is considering a price ceiling 10 percent below the price derived in part a. I. Suggest one reason for the imposition of the price ceiling. II. i) With the price ceiling, what is the price for the vaccine? ii) Given the price in part i, how many vaccines will be purchased in the vaccine market? With the price ceiling, is there any shortage in the vaccine market? Explain your answer. iii)arrow_forwardMondi Company produces party boxes that are sold in bundles of 1000 boxes. The market is highly competitive, with boxes currently selling for R100 per thousand. The company has a total and marginal cost curve given by: TC = 3,000,000 + 0.001Q2 MC = 0.002Q Q is measured in thousand box bundles per year. [5] a. Determine Mondi's profit maximizing quantity. b. Calculate if the firm is earning a profit or a loss? c. Based on the analysis above, should Mondi Company operate or shut down in the shortrun?arrow_forwardSuppose we have two identical fırms A and B, selling identical products. They are the only firms in the market and compete by choosing quantities at the same time. The Market demand curve is given by P=287-Q. The only cost is a constant marginal cost of $13. If Firm A produces a quantity of 60 and Firm B produces a quantity of 33, what is market price? Enter a number only, no $ sign. 194arrow_forward
- There are only two driveway paving companies in a small town, Asphalt, Inc. and Blacktop Bros. The inverse demand curve for paving services is ?= 2040 ―20? where quantity is measured in pave jobs per month and price is measured in dollars per job. Assume Asphalt, Inc. has a marginal cost of $100 per driveway and Blacktop Bros. has a marginal cost of $150. Answer the following questions: Determine each firm’s reaction curve and graph it. How many paving jobs will each firm produce in Cournot equilibrium? What will the market price of a pave job be? How much profit does each firm earn?arrow_forwardSuppose that each firm in a competitive industry has the following costs: Total cost: TC = 50 + 1/2q2 Marginal cost: MC = q Where q is an individual firm’s quantity produced. The market demand curve for the product is: Demand: QD = 120 – P Where P is the price and Q is the total quantity of the good. Currently there are 9 firms in the market. What is each firm’s fixed cost? What is its variable cost? Give the equation for average total cost. Graph the average-total-cost curve and the marginal-cost curve for q from 5 to 15. At what quantity is the average-total-cost curve at its minimum? What is the marginal cost and average total cost at that quantity? Give the equation for each firm’s supply curve. Give the equation for the market supply curve for the short run in which the number of firms is fixed. What is the equilibrium price and quantity for the market in the short run? In this equilibrium, how much does each firm produce? Calculate the firm’s profit and loss. Do firms have…arrow_forwardWakanda is a firm that solely supplies vibranium to Marley and Paradis. The demand function of the Marley market is given as QM=110-PM , and the demand function of the Paradis market is QP=30-PP . Wakanda’s total cost in producing vibranium is given as TC=100+10Q , where represents a ton of vibranium. 3. How much is the total cost of production? 4. Assuming that Wakanda can price discriminate between Marley and Paradis market, calculate its total profits.arrow_forward

