
a)
To determine: The theoretical minimum number of workstations.
a)
Answer to Problem 23P
The theoretical minimum number of workstations is 5 workstations.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Task | Time (seconds) | Immediate predecessors |
| A | 40 | - |
| B | 30 | A |
| C | 50 | A |
| D | 40 | B |
| E | 6 | B |
| F | 25 | C |
| G | 15 | C |
| H | 20 | D, E |
| I | 18 | F, G |
| J | 30 | H, I |
| Total | 274 |
- Output is 60 iStars / hour
Calculation of cycle time:
The requirement is to produce 60 iStars / hour. Hence, the cycle time for one iStar will be:
Formula to calculate theoretical minimum number of workstations:
Calculation of theoretical minimum number of workstations:
The theoretical minimum number of workstations is 5 workstations.
b)
To balance: The assembly line.
b)
Explanation of Solution
Precedence diagram:
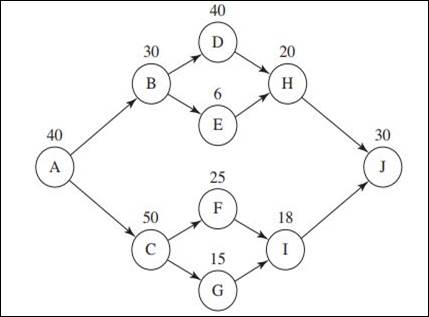
List of most following tasks:
| Tasks | Following tasks |
| A | 9 |
| B | 4 |
| C | 4 |
| D | 2 |
| E | 2 |
| F | 2 |
| G | 2 |
| H | 1 |
| I | 1 |
| J | 0 |
Assignment of different tasks to different workstations:
| Workstation | Elligible tasks | Selected tasks | Task time (seconds) | Available cycle time (seconds) | Remarks |
| 1 | 60 | ||||
| A | A | 40 | 20 | ||
| B,C | 20 (Idle time) | Cycle time is less than task time | |||
| 2 | 60 | ||||
| B, C | C | 7 | 50 | Tie broken randomnly | |
| B, F, G | 10 (Idle time) | Cycle time is less than task time | |||
| 3 | 60 | ||||
| B, F, G | B | 30 | 30 | Task B has most following tasks. | |
| D, E, F, G | F | 25 | 24 | Tie broken randomnly | |
| D, E, G | 1 (Idle time) | Cycle time is less than task time | |||
| 4 | 60 | ||||
| D, E, G | D | 40 | 20 | Tie broken randomnly | |
| E, G | G | 15 | 5 | Tie broken randomnly | |
| E,I | 5 (Idle time) | Cycle time is less than task time | |||
| 5 | 60 | ||||
| E, I | E | 6 | 54 | Task E has most following tasks. | |
| I, H | H | 20 | 34 | Tie broken randomnly | |
| I | I | 18 | 2 | Task I is only elligible task | |
| 2 (Idle time) | |||||
| 6 | 60 | ||||
| J | J | 30 | 30 | Task J is the remaining task | |
| 30 (Idle time) |
| Workstation | Task assigned | Idle time |
| 1 | A | 20 |
| 2 | C | 10 |
| 3 | B, F | 1 |
| 4 | D, G | 5 |
| 5 | E, H, I | 2 |
| 6 | J | 30 |
| Total | 68 |
c)
To determine: The actual number of workstations.
c)
Answer to Problem 23P
The actual number of workstations is 6.
Explanation of Solution
| Workstation | Task assigned | Idle time |
| 1 | A | 20 |
| 2 | C | 10 |
| 3 | B, F | 1 |
| 4 | D, G | 5 |
| 5 | E, H, I | 2 |
| 6 | J | 30 |
| Total | 68 |
The actual number of workstations is 6.
d)
To determine: The efficiency.
Introduction:
Efficiency:
Efficiency is the measure of what is actually produced as opposed to what can be theoretically produced with the same amount of resources.
d)
Answer to Problem 23P
The efficiency is 76.11%.
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate efficiency:
Calculation of efficiency:
The efficiency is 76.11%.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Principles Of Operations Management
- Stanford Rosenberg Computing wants to establish anassembly line for producing a new product, the Personal DigitalAssistant (PDA). The tasks, task times, and immediate predecessorsfor the tasks are as follows: Rosenberg's goal is to produce 180 PDAs per hour.a) What is the cycle time?b) What is the theoretical minimum for the number of workstations that Rosenberg can achieve in this assembly line?c) Can the theoretical minimum actually be reached when workstations are assigned?arrow_forwardSmart Manufacturing's production engineers are reviewing the layout of their assembly line for their leading product. The line will operate eight hours a day with a desired output of 240 units per day. The following table contains information about this product's task times and precedence relationships: TASK Task Time (seconds) Immediate Precedent A 60 -- B 80 A C 20 A D 50 A E 90 B,C F 30 C,D G 30 E, F H 60 G Determine: a) Network of activities (precedence diagram) b) Cycle time c) The required number of workstations d) Evaluate the solution by the appropriate line balance heuristicarrow_forwardThe desired daily output for an assembly line is 480 units. This assembly line will operate 760 minutes per day. The following table contains information on this product's task times and precedence relationships: TASK А ABCDEFGH 58 48 28 25 38 78 58 18 TASK TIME (SECONDS) Work Station I II III 50 IV 40 20 Efficiency 30 50 10 b. What is the workstation cycle time? Workstation cycle time 95 seconds per unit IMMEDIATE PREDECESSOR c. Balance this line using the largest number of following tasks. Use the longest task time as a secondary criterion. (Leave no cells blank - be certain to enter "0" wherever required.) Task IAAUI A-C-D E-G B-D F А А 77.6 % B с D-F E-G Idle Time d. What is the efficiency of your line balance? (Round your answer to 1 decimal place.) 5 5 55 20arrow_forward
- Amelio Rodriguez Computing wants to establish an assembly line for producing a new product, the Personal Digital Assistant (PDA). The tasks, task times, and immediate predecessors for the tasks are as follows: Task A BCDE Time (sec) 12 14 Workstation # 1 8 5 20 Amelio's goal is to produce 180 PDAs per hour. a) The cycle time for the production of a PDA = 20 seconds (round your response to two decimal places). Immediate Predecessor A A B, C D b) The theoretical minimum number of workstations that Amelio can achieve in this assembly line = 3 (round your response up to the next whole number). c) For one to assign the tasks to the actual workstations and be able to use the "theoretical minimum" number, the activity assignment should be: Tasks Assigned to Workstation Aarrow_forwardA company needs to rebalance a product layout for producing new plastic license plates. They plan to use the assembly line six hours in order to meet projected demand of 2,160 license plates each day. The following table describes the tasks involved in the production of this product: Without regard to projected demand, what is the maximum possible cycle time for this assembly line? Task Time (secs) Immediate Predecessor a 3 none b 4 none c 5 a,b d 7 none e 9 c,darrow_forwardDefine layout planning and explain its importance.arrow_forward
- An assembly line is to operate eight hours per day with a desired output of 240 units perday. The following table contains information on this product’s task times and precedencerelationships: Task Task Time (Seconds) Immediate Predecessor A 60 — B 80 A C 20 A D 50 A E 90…arrow_forwardAssembly Line Problem A shop works a 400-minute day. The manager of the shop wants an output of 200 units per day for the assembly line that has the elemental tasks shown in the following table. Task Immediate Predecessor Task(s) Task Time (minutes) a --- 0.5 b a 1.4 c a 1.2 d a 0.7 e b,c 0.5 f d g e 0.4 h g 0.3 i F 0.5 j e, I 0.8 k h, j 0.9 l k 0.3 d)Compute the efficiency of the assembly linearrow_forwardThe desired daily output for an assembly line is 240 units. This assembly line will operate 8 hours per day. The following table contains information on the product's task times and precedence relationships: Task 1 2 345678 Time (s) 60 80 20 50 90 30 30 60 a. Draw the precedence diagram. b. What is the workstation cycle time? c. Balance this line using the longest task time. d. What is the efficiency of your balanced line? Predecessor 1 1 1 2,3 3,4 5,6 7arrow_forward
- The desired daily ouput for an assembly line is 420 units. This assembly line will operate 595 minutes per day. The following table contains information on the products task times and precedence relationships Task. Task time-seconds Immediate predecessor A. 35 - B. 40 A C 30 A D 40 B E 20 C F 70 C G 45 E-F H 30 D-G The required workstation cycle time to meet the desired output time is 85 seconds Balance this line using the largest number of following tasks. Use the longest task time as a secondary criterion The answer gives only 4 workstations as option Have to fill out following Workstation. Task Idle time 1 ?? ?? 2 ?? ?? 3…arrow_forwardWhat is DESIGNING PROCESS LAYOUTS?arrow_forwardThe desired daily output for an assembly line is 540 units. This assembly line will operate 720 minutes per day. The following table contains information on this product's task times and precedence relationships: TASK TASK TIME(SECONDS) IMMEDIATEPREDECESSOR A 35 — B 25 A C 35 A D 55 B E 5 B F 15 C G 30 E-D H 5 F-G b. What is the workstation cycle time? c. Balance this line using the largest number of following tasks. Use the longest task time as a secondary criterion. (Leave no cells blank - be certain to enter "0" wherever required.)arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.
Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.





