
Concept explainers
(a)
The reading on the scale in an elevator when elevator accelerates at
Answer to Problem 87QAP
The reading on the scale is
Explanation of Solution
Givendata:
Formula Used:
Newton's second law:
Calculation:
We are interested in calculating the reading on the scale for accelerationof the elevator, at
together as one object.
The reading on the scale is equal in magnitude to the normalforce acting on the dog. Gravity also acts on the dog.
We can use Newton's second law tocalculate N as a function of the acceleration.
We'll define up to be positive y throughout ourcalculation.
Free-body diagram of the dog:
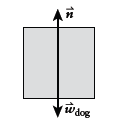
Conclusion:
Thus, we have the reading on the scale in an elevator when elevator accelerates at
(b)
The reading on the scale in an elevator when elevator cruises down at a steady speed.
Answer to Problem 87QAP
The reading on the scale is
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Formula Used:
Newton's second law:
Calculation:
We are interested in calculating the reading on the scale for elevator cruises down at a steady speed., which is equal to the acceleration of the scale and dog since they traveltogether as one object.
The reading on the scale is equal in magnitude to the normal force acting on the dog. Gravity also acts on the dog.
We can use Newton's second law to calculate N as a function of the acceleration.
We'll define up to be positive y throughout our calculation.
Free-body diagram of the dog:
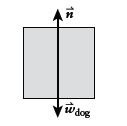
Conclusion:
Thus, we have the reading on the scale in an elevator
(c)
The reading on the scale in an elevator when elevator accelerates at
Answer to Problem 87QAP
The reading on the scale is
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Formula Used:
Newton's second law:
Calculation:
We are interested in calculating the reading on the scale for acceleration as
of the elevator, which are equal to the accelerations of the scale and dog since they travel
together as one object.
The reading on the scale is equal in magnitude to the normal force acting on the dog. Gravity also acts on the dog.
We can use Newton's second law to calculate N as a function of the acceleration.
We'll define up to be positive y throughout our calculation.
Free-body diagram of the dog:
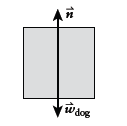
Conclusion:
The reading on the scale in an elevator when elevator accelerates at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS
- An automobile driver traveling down an 8% grade slams on his brakes and skids 30 m before hitting a parked car. A lawyer hires an expert who measures the coefficient of kinetic friction between the tires and road to be k = 0.45. Is the lawyer correct to accuse the driver of exceeding the 25-MPH speed limit? Explain.arrow_forward1) Listen When a 54.0-kg crate is pushed across a frictionless horizontal floor with a force of 240.0 N, directed 20.0° below the horizontal, the magnitude of the aceleration of the crate is m/s². 20.0arrow_forward25 - A diver with a mass of 70 kg jumps from the 10.0 meter high tower for a direct-vertical dive. Its movement ends at 2.50 meters below the water level. Find the average drag force exerted by the water on the diver. A) 1.50 kN B) 4.12 kN C) 3.09 kN D) 5.34 kN E) 1.05 kNarrow_forward
- 3. • A baseball player slides into third base with an initial speed of 4.0 m/s. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the player and the ground is 0.46, how far does the player slide before coming to rest?arrow_forward30 Physics 1 Chapter 6: Force and Motion II Example A raindrop with radius R= 1.5 mm falls from a cloud that is at height h the ground. The drag coefficient C for the drop is 0.60. Assume that the drop is spherical throughout its fall. The density of water) Pw is 1000 kg/m³, and the density of air pa 1S 1.2 kg/m³) If you know that the raindrop reaches terminal speed after falling just a few meters. What is the terminal speed? = 1200 m above Solutionarrow_forward•9:EV %VO 4G N Question 10 The SI unit of coefficient of friction is a. no units b. N/m c. N m/s d. m/Narrow_forward
- 6) Problem 1: A 76-kg man stands on a bathroom scale in an elevator that accelerates upwards from rest to 11 m/s in 2.00 s. Calculate the scale reading, in newtons, during this process (The scale exerts an upward force on him equal to its reading.)arrow_forwarda) "A swimmer pushing off from the side of a pool. She pushes against the pool wall with her feet and accelerates in the direction opposite to her push" What is the concept of above situation and explain.arrow_forwardA 1300-kg car is skidding to a stop along a horizontal surface. The car decelerates from 27 m/s to a rest position in 3 seconds. Assuming negligible air resistance, determine the friction between the car tires and the road surface. a) -1700 N b) -12740 N c) -11700 Narrow_forward
- Q2) A hockey puck having a mass of 0.3 kg slides on the horizontal, frictionless surfuce of an ice rink. Two hockey sticks strike the puck simultaneously, exerting the forces on the puck shown in Figure 2. The force Fi has a magnitude of 5 N, and the force F: has a magnitude of 8 N. Determine both the magnitude and the direction of the puck's acceleration. - 5ON - KON Fig 2arrow_forwardA soft tennis ball is dropped onto a hard floor from a height of 1.50 m and rebounds to a height of 1.10 m. (a) Calculate its velocity just before it strikes the floor. (b) Calculate its velocity just after It leaves the floor on its way back up. (c) Calculate its acceleration during contact with the floor if that contact lasts 3.50 ms (3.50103s) (d) How much did the ball compress during its collision with the floor, assuming the floor is absolutely rigid?arrow_forwardAs a fish jumps vertically out of the water, assume that only two significant forces act on it: an upward force F exerted by the tail fin and the downward force due to gravity. A record Chinook salmon has a length of 1.50 m and a mass of 61.0 kg. If this fish is moving upward at 3.00 m/s as its head first breaks the surface and has an upward speed of 6.00 m/s after two-thirds of its length has left the surface, assume constant acceleration and determine (a) the salmons acceleration and (b) the magnitude of the force F during this interval.arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College





