
Concept explainers
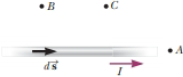
Consider the magnetic field due to the current in the wire shown in Figure 29.2. Rank the points A, B, and C in terms of magnitude of the magnetic field that is due to the current in just the length element
Figure 29.2 (Quick Quiz 29.1) Where is the magnetic field due to the current element the greatest?
Answer to Problem 30.1QQ
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate the magnetic field due to the current flow through a small length element is,
Here,
From the equation (1), it is clear that the magnetic field due to the current flow is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the point to the small length element and directly proportional to the cross product of the vectors
The point A lies in the direction of the small length element of the wire. So, the angle between the vectors
The distance between the point
Thus, from the greatest to least order the magnetic field is maximum at point
Conclusion:
Therefore, the rank of the points
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 30 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
- + min130.acellus.com/StudentFunctions/Interface/acellus_engine.html?Class... C in a B Field A mass spectrometer shoots a 7.35 x 10-26 kg molecule with a charge of +2e (3.20 x 10-19 C) at a speed of 23.4 m/s through a magnetic field, and it moves in a circular arc of radius 0.0706 m. What is the magnetic field? [? ] × 10²) T Connal Coefficient (green) onal Academy of Science. All Rights Reserved. Exponent (yellow) Enter huluarrow_forward1. Consider a long, thick current-carrying wire with radius R. A. Find the magnetic field at z=R from the wire. B. How much current is enclosed (Ienc) at 0 < z <R? Note: the answers are in formula form.arrow_forwardAnswer the following questions from the given photo: 1. Find x component of the magnetic field at p. 2. Find y component of the magnetic field at p. 3. Find z component of the magnetic field at p.arrow_forward
- Answer the problem using the GRESA format. Also, kindly please include an illustration or diagram. A hypothetical charge -0.47 pC with a mass 38 fg moves in a circular path perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field with a magnitude of 47 mT and is directed into the page. If the speed of the hypothetical charge is 27 km/s: Determine the radius of the circular path. Determine the time interval required to complete one revolution.arrow_forwardAn infinite straight wire has a current of 4 = 9.00 A. Figure 2.2 shows that a circular conducting loop of wire is placed immediately to the right of the straight wire, and both sit on the xy-plane. The loop has a radius of R = 0.030 m and has a current of 12 = 1.00 A. a. Calculate the magnitude of the net magnetic field at the center C of the loop. b. What is the direction of the net magnetic field? Is it upward or downward? Figure 2.2 Carrow_forwardAn infinite straight wire has a current of I = 9.00 A. Figure 2.2 shows that a circular conducting loop of wire is placed immediately to the right of the straight wire, and both sit on the xy-plane. The loop has a radius of R = 0.030 m and has a current of 12 = 1.00 A. a. Calculate the magnitude of the net magnetic field at the center C of the loop. b. What is the direction of the net magnetic field? Is it upward or downward? Figure 2.2 12arrow_forward
- Figure 1: CRT with coils in Helmholtz configuration. The hot cathode emits electrons which are then accelerated through potential difference Vacc. When the electrons enter the magnetic field B, which is perpendicular to their velocity, they move on a circular path with radius r. The magnetic field is due to coils in Helmholtz configuration (2 coils separated distance that equals their radius). The magnetic field due to one of the coils with radius R, at a point on the axis distance z away from the center of the coil, was found using the Biot-Savart law: HOIR?N B1 2(R2 + z2)žarrow_forwardWe lay a copper wire in the shape of a 10 cm square loop square. The wire has a diameter of 1 mm and a current of 5 A flows through it. This loop is then used as a motor and can rotate around an axis that passes through its center and in the plane of the loop. What is the magnetic moment of this loop? If I place it in a magnetic field of 0.05 T, what will be the maximum torque exerted on the loop? be the maximum torque exerted on the loop? (As the density of copper is around 8000 kg/m^3, calculate the loop's the loop's moment of inertia and angular acceleration when the torque is maximum... tau = I alpha... of phy-1026!)arrow_forwardAn electron moves along the z-axis with v₂ = 4.7 x 107 m/s. As it passes the origin, what are the strength and direction of the magnetic field at the following (x, y, z) positions? Part A (1 cm, 0 cm, 0 cm) Express your answers using two significant figures.Enter your answers numerically separated by commas. Br, By, B₂ = Submit Part B VE ΑΣΦ Request Answer Ba, By, B₂ = Submit (0 cm, 0 cm, 1 cm) Express your answers using two significant figures. Enter your answers numerically separated by commas. IVE| ΑΣΦ ? Request Answer T ? Tarrow_forward
- In the plane of the paper, a long straight wire carries a current I in the +x direction. A proton is projected a distance a below the wire with a speed v in the +x direction. a) Derive an expression for F, the magnitude of the magnetic force on the proton b(if any) in terms of the current I in the wire. b) Mark Fin a diagram, or provide the direction in terms of the standard Cartesian directions {x,y,z), including an appropriate sign {+/-}.arrow_forwardExplain how is the magnetic flux through the circle is defined by the path of the electron? And draw a figure that illustrates it? Please write to me with pc text typing because I can't read the handwriting.arrow_forwardFigure 1 shows two long straight wires. What is the direction and magnitude of the total magnetic field at point P.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





