
(a)
The magnitude and direction of the resultant velocity vector
Answer to Problem 39QAP
The resultant velocity vector
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The magnitude and the directions of the velocity vectors
Formula used:
If
The magnitude of the vector
The angle the vector makes with the x axis is given by,
Calculation:
Assume the +x axis to be directed along the East and the +yaxis along the North.
Draw a vector diagram for the velocities.
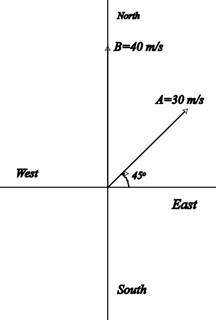
The vector
The velocity vector
Calculate the x and y components of the vector
Calculate the magnitude of the resultant velocity vector
Calculate the angle made by the vector with the +x axis (East).
Conclusion:
The resultant velocity vector
(b)
The magnitude and direction of the resultant velocity vector
Answer to Problem 39QAP
The resultant velocity vector
Explanation of Solution
Given:
From part (a), the components of the vectors
Formula used:
If
The magnitude of the vector
The angle made by the vector with the x axis is given by,
Calculation:
Calculate the x and y components of the vector
Calculate the magnitude of the vector
Calculate the angle made by the vector
Since the y component of
Conclusion:
The resultant velocity vector
(c)
The magnitude and the direction of the resultant velocity vector
Answer to Problem 39QAP
The resultant velocity vector
Explanation of Solution
Given:
From part (a), the components of the vectors
Formula used:
If
The magnitude of the vector
The angle made by the vector with the x axis is given by,
Calculation:
Calculate the x and y components of the vector
Calculate the magnitude of the vector
Calculate the angle made by the vector
Conclusion:
The resultant velocity vector
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS
- Suppose you take two steps A and B (that is, two nonzero displacements). Under what circumstances can you end up at your starting point? More generally, under what circumstances can two nonzero vectors add to give zero? Is the maximum distance you can end up from the starting point A+B the sum of the lengths of the two steps?arrow_forwardSuppose you first walk 12.0 m in a direction 20° west of north and then 20.0 m in a direction 40.0° south of west. How far are you from your starting point, and what is the compass direction of a line connecting your starting point to your final position? (If you represent the two legs of the walk as vector displacements A and B, as in Figure 3.56, then this problem finds their sum R=A+B. )arrow_forward(a) Repeat the problem two problems prior, but for the second leg you walk 20.0 m in a direction 40.0° north of east (which is equivalent to subtracting B from A that is, to finding R=AB ). (b) Repeat the problem two problems prior, but now you first walk 20.0 m in a direction 40.0° south of west and then 12.0 m in a direction 20.0° east of south (which is equivalent to subtracting A from B that is, to finding R=BA=R ). Show that this is the case.arrow_forward
- At time t = 0, a package is released from an airplane 12) flying horizontally at a height of 500.0 m above the ground with a constant speed of 100.0 m/s. Five seconds later, another package is released. 9=100.0 m/s a) When does the first package hit the ground? b) What is the velocity vector of the first package just before it hits the ground? c) What is the position vector of the second package at the instant the first one hits the ground? h=500.0 m d) How far away are the packages when both hit the ground? ground Answers: a) t = 10.1 s, b) i = (100î – 98.99ĵ) m/s, c) ř, = (1010î + 372.6j) m, d) Ax = 500marrow_forwardif three vectors with magnitude 30, 40, 50 are added together, which of the following cannot represent the magnitude of the resultant? a. 0 b. 30 c. 50 d. 150 e. None of a, b, c and darrow_forwardV₂ = 12 units 60° y V₁ = 10 units 4 PROBLEM 1/2 3 -x SS For the given vectors V₁ and V₂ of Prob. 1/2, de- termine the magnitude of the vector difference V' = V₂ - V₁ and the angle, which V' makes with the positive x-axis. Complete both graphical and algebraic solutions.arrow_forward
- abäi 25 Q3) Let vector A = 5i +2j, Vector B = %3D -3i -5j, and vector C = A+ B. (a) Write %3D vector C in component form. (b) Draw a coordinate system and on it show the all vectors. (c) What are the ?magnitude and direction of vector Carrow_forwardQ3) Consider an arbitrary vector A = A,â, + A¸âp + A,â, in cylindrical coordinates and express in Cartesian coordinatesarrow_forward18) The ball hits point A which is horizontally 100 m away as indicated. a) Find the height of point A. b) What is its speed when it hits the point A? c) What is its displacement vector 1.5 s after it is fired? Figure shows a ball that is fired with an initial speed of 40 m/s at an angle of 37° above the horizontal. 40 m/s h 37° 100 marrow_forward
- 25 DI Example -8- A hiker begins a trip by first walking 25.0 km southeast from her car. She stops and sets up her tent for the night. On the second day, she walks 40.0 km in a direction 60.0° north of east, at which point she discovers a forest ranger's tower. (A) Determine the components of the hiker's displacement for each day. (B) Determine the components of the hiker's resultant displacement R for the trip. Find an expression for R in terms of unit vectors.arrow_forwardQUESTION 3 Problem An explorer in Antarctica leaves his shelter during a whiteout. He takes 50 m northeast, next 180 m at 72° north of west, and then 150 m due south. Save the explorer from becoming hopelessly lost by giving him the displacement, calculated by using the method of components, that will return him to his shelter. Solution By vector-component approach, we list down the given in a table as follows: Given X-component (w/ sign direction) y-component (w/ sign direction) A = 50 m NE m m B = 180 m 72° NW C = 150 m S m Resultant m Thus, the magnitude of the resultant vector is R = With a direction of e = O NW Therefore, the vector needed for him to successfully get back home is Rhome = O SE E E E E Earrow_forward8- Chapter 3- questn-10 What are the x-and y-components of the vector E? E, (+) E, (+) Option 1 Option 2 Option 3 Option 4 Option 5 E, E cos B, E, = E sin B, E, = -E cos B, E, = -E sin B. E, = -E cos B, !! %3! E, = E sin ß E, = E cos B E, = -E sin ß E, = -E cos B E, = E sin B %3D %3Darrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





