
Concept explainers
(a)
Toprove: The maximum height of a projectile is,
(a)
Answer to Problem 18P
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
When a projectile motion happens at an angle ? from the horizontal, the initial velocity of the projectile will have a vertical and a horizontal component.
To determine the maximum height reached by a projectile during its flight, the vertical component of its motion is needed.
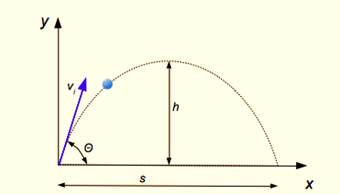
The movement of the projectile is influenced by gravity, vertically. This implies that the vertical portion of the initial velocity will be zero at maximum height.
On its way to maximum height, the projectile must decelerate, come to a complete stop at maximum height, and begin its free fall downward to the earth. The vertical portion of its initial velocity is,
 0
0
This equals to,
Hence, the maximum height reached by the projectile will be,
Conclusion:
The maximum height of a projectile is,
(b)
To prove: The time it takes a projectile to reach its maximum height is,
(b)
Answer to Problem 18P
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
The time it takes for a projectile to be projected from a point and landed is named as flight time. This depends on the projectile’s initial velocity and projection angle. The optimum projectile height is if the projectile exceeds a vertical velocity of zero.
In a projectile motion to determine how long an object will remain airborne ,the vertical and horizontal components of the flight path should be considered separately.
The time will take to reach its maximum height in a projectile motion.
Here,
Hence,
Conclusion: The time takes a projectile to reach its maximum height is,
(c)
To prove: The time it takes for a projectile to descend from its maximum height to its original elevation is the same as the time to ascend ,which is,
(c)
Answer to Problem 18P
Time of ascent = Time of descent =
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:The time that takes a projectile to descend from its maximum height to its original elevation is the same as the time to ascend.
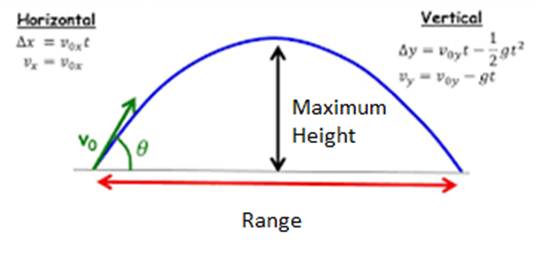
The components of a projectile to ascend to its maximum height are as follows.
The time taken to reach its maximum is,
The components of a projectile to descend from its maximum height are as follows.
The time taken to descend from its maximum is,
Since
Conclusion:
Time of ascent = Time of descent
(d)
To prove: The y component of velocity is reversed when a projectile descend to its original elevation
(d)
Answer to Problem 18P
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:The x component is the projectile’s horizontal motion and the y component represents the projectile’s vertical motion. The units for expressing the distance horizontal and vertical are meters
The time interval between the projectile that reaches the point and is at the maximum height is the same. The magnitude of the velocity on the upward and downward motion at the same point will be the same; the direction will be reversed.
Hence, the y component of velocity is equals when a projectile descends to its original elevation. But its reverse in sign.
Conclusion:
The y component of velocity is equals when a projectile descends to its original elevation. But its reverse in sign.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Physics Fundamentals
- A cannon ball is fired with an initial speed of 123 m/s at angle of 60 degrees from the horizontal. Express the initial velocity as a linear combination of its unit vector components. Vo - ( mis) 7 + m/s) ? At the maximum height, the speed of the cannon ball is v= m/s and the magnitude of its acceleration is a- m/s?. The time needed to reach maximum height is t- S. The maximum height reached by the cannon ball is H= m.arrow_forwardThe initial velocity of a car, v i is 45 km/hr in the positive x-direction. The final velocity of the car, vf is 66 km/hr in a direction that points 750 above the positive x-axis. Sketch the vectors v = v f − v i . Find the magnitude of the change in velocity v. Find the direction of the change in velocity v.arrow_forwardA golf ball is hit off a tee at the edge of a cliff. Its x and y coordinates as functions of time are given by the following expressions: x = (18.0 m/s)t y = (4.00 m/s)t – (4.90 m/s²)t² (a) Express the position of the ball as function of time in terms of unit vectors. (b) In terms of unit vectors, calculate for the position, velocity, and acceleration of the golf ball at t = 3.00 s.arrow_forward
- If the initial velocity of a projectile has a magnitude of 28.562 m/s, with a direction angle of 37.851 degrees above horizontal, what is the x component of its velocity in unit of m/s?arrow_forwardA batted baseball is hit with a velocity of 40.9 m/s, starting from an initial height of 10 m. Find how high the ball travels in two cases: (a) a ball hit directly upward and (b) a ball hit at an angle of 68° with respect to the horizontal. Also find how long the ball stays in the air in each case (from right after the ball is launched until right before it lands). case a? case b?arrow_forwardDuring the siege of Constantinople that led to its conquest by the Ottomans in 1453, the Hungarian engineer Orban built a set of bombards (primitive cannon) to throw enormous stones at the city to breach its walls. The largest of these could throw a 300 kg stone a distance x = 2 km. Assume that the stone was launched at an angle of 0 = 45 degrees above the horizontal; in the absence of air resistance, this gives the largest range. a) What speed did the stone have to be launched at to achieve this range? b) How long was the ball in the air? c) How fast was the ball traveling at the apex of its flight?arrow_forward
- A projectile is fired horizontally into a resisting medium with a velocity vo = 5.3 m/s and the resulting deceleration is equal to cv³, where c = 0.039 m ²s ¹, and v is the velocity within the medium. Find the velocity v of the projectile at time t = 7.0 s after penetration. Answer: v= m/sarrow_forwardAlaskan rescue plane drops a package of emergency rations to stranded hikers. The plane is traveling horizontally at 40.0 m/s at a height of 100 m above the ground. Neglect air resistance. (a) Where does the package strike the ground relative to the point at which it was released? (b) What are the horizontal and vertical components of the velocity of the package just before it hits the ground? (c) What is the angle of the impact?arrow_forwardA projectile is launched vertically upward with initial velocity vo. Assume that the resistance of air is proportional to the square of the velocity. Calculate the maximum height it reaches and the velocity of the projectile when it hits the ground on its return. Ymáx = in (1 + ), kví v = vove//v3 + v Ve = /mg/c Утӑх 2k Ans.arrow_forward
- A projectile is launched vertically upward with initial velocity v0. Assume that the resistance of air is proportional to the square of the velocity. Calculate the maximum height it reaches and the velocity of the projectile when it hits the ground on its return. Ymáx = -v;t In (v:/Vvž + v? za + gar/?a°a = a Ve = /mg/c T = /m/gcarrow_forwardIf a projectile is fired with an initial speed of vo ft/s at an angle a above the horizontal, then its position after t seconds is given by the parametric equations x = (Vo cos(a))t y = (vo sin(æ))t – 16t2 (where x and y are measured in feet). Suppose a gun fires a bullet into the air with an initial speed of 1856 ft/s at an angle of 30° to the horizontal. (a) After how many seconds will the bullet hit the ground? (b) How far from the gun will the bullet hit the ground? (Round your answer to one decimal place.) mi (c) What is the maximum height attained by the bullet? (Round your answer to one decimal place.) miarrow_forwardAn object has an initial velocity of 29.0 m/s at 95.0° and an acceleration of 1.90 m/s2 at 200.0°. Assume that all angles are measured with respect to the positive x-axis. (a) Write the initial velocity vector and the acceleration vector in unit vector notation. (b) If the object maintains this acceleration for 12.0 seconds, determine the average velocity vector over the time interval. Express your answer in your unit vector notation.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





