
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130970695
Author: Peter S. Shaffer, Lillian C. McDermott
Publisher: Addison Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 26.1, Problem 2TH
A W-shaped piece of glassware is partially filled with water as shown. Point X is at the same height as the water level in the center of the tube.
For each of the following points, slate whether the pressure is greater than, less than, or equal to atmospheric pressure. Explain your reasoning.
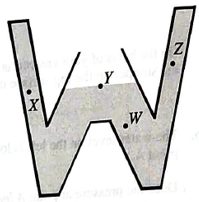
• pointW
• pointX
• pointY
• pointZ
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
(c) Summary of displaced volume
When the block is completely submerged, how does the volume of the block compare to
the volume of liquid displaced? The volume of the block can be found in the upper left-
i.
hand side of the screen in the video.
What determines the volume of liquid displaced by a submerged object? (Does it depend
on the object's mass, its volume, or its depth?)
ii.
PREDICT: How would the volumes of liquids displaced compare if you submerged one
aluminum block in water and an identical aluminum block in a liquid with a different
density than water (e.g oil)? Explain.
iii.
A vertical U-shaped tube is filled with a liquid of density ρ and the right end of the tube is sealed with a stopper, as shown in the left figure. Some of the liquid is removed from the left column with a syringe and the left column descends a distance d, while the right column remains as it was. Refer to the right figure.
1)
Three students are debating:
Student A: The pressure at level C must now be greater than the atmospheric pressure because liquid there is being pushed up against the stopper.
Student B: I think the pressure at level B must be the same as at level A, because they are at the same level. Both are at atmospheric pressure. So the pressure at level C must be lower than atmospheric, because pressure decreases as you ascend.
Student C: But the liquid is denser than air, so the pressure at C cannot be less than atmospheric pressure.
With which student(s) should you agree?
2
Looking at the figure below, a small parallelepiped of fluid centered on the point, explain why the pressure will be independent of x and z? And what will you need to know to determine the pressure in y?
Chapter 26 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Ch. 26.1 - Prob. 1aTHCh. 26.1 - 1. A U-tube filled with water is closed on one...Ch. 26.1 - 1. A U-tube filled with water is closed on one...Ch. 26.1 - 1. A U-tube filled with water is closed on one...Ch. 26.1 - 1. A U-tube filled with water is closed on one...Ch. 26.1 - A W-shaped piece of glassware is partially filled...Ch. 26.1 - Prob. 3aTHCh. 26.1 - A U-tube is partly filled with water. Oil is then...Ch. 26.1 - Prob. 3cTHCh. 26.2 - 1. Three objects are at rest in three beakers of...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
In Fig. 25.36, the switch is initially open and both capacitors are initially uncharged. All resistors have the...
Essential University Physics: Volume 2 (3rd Edition)
A projectile has horizontal range R on level ground and reaches maximum height h. Find an expression for its in...
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
14. A constant force applied to object A causes it to accelerate at 5 m/s2. The same force applied to object B ...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Explain all answers clearly, with complete sentences and proper essay structure, if needed. An asterisk (*) des...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Pseudoscience. Choose a pseudoscientific claim that has been in the news recently, and learn more about it and ...
Life in the Universe (4th Edition)
If the velocity of blood flow in the aorta is normally about 0.32 m/s, what beat frequency would you expect if ...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- can you pls help me solve this.. a hydraulic lift raises a 2000kg automobile when a 500N force is applied to the smaller piston. If the smaller piston has an area of 10 square centimeter, what is the cross sectional area of the larger piston? •Pls answer with complete solution (3 dec places) •Sketch an illustration/diagram with labels (this is a must; for a better understanding) Thank you I will give your answer a LIKE for helping me...arrow_forwardPlease answer them ALL for an Upvote. Thanksyou. Given: Pi constant to be used: 3.14159 Capillary tube: radius = 0.02 cm; length = 9 cm; pressure = 0.7 mmHg Liquid sample: density = 4 ml; time of flow = 4.5 seconds •What is the pressure in MKS unit? •What is the pressure in CGS unit? •What is the viscosity of the liquid? •If the weight was given as 8.5 grams, what will be the density of the liquid? •What is the kinematic viscosity of the liquid? •What is the fluidity of the liquid?arrow_forwardA water droplet evaporates before they reach the ground. ond ord Figure 1: Water droplets [source] In this situation, a few assumptions are made: a) At initial point, a typical water droplet is in sphere shape with radius r and remain spherical while evaporating. b) The rate of evaporation (when it loses mass (m)) is proportional to the surface area, S. There is no air-resistance and downward direction is the positive direction. quat To describe this problem, given that p is the mass density of water, rois the radius of water before it drops, m is the water mass, V is the water volume andk is the constant of proportionality. QUESTION: (1) From assumption (b), show that the radius of the water droplet at time t is or r(t) = (=)t+ro- %3D (Hint: m = pV,V =tr³, S = 4nr²). 4 TTr 3arrow_forward
- The brake piston consists of a full circular part. Its cross section is shown in. Suppose that a = 16 mm, Part A b=90 mm, c = 55 mm, d=45 mm, e = 35 mm. f = 40 mm. 29 μA e Submit a Determine the interior surface area of the brake piston. Express your answer to four significant figures and include the appropriate units. ▸ View Available Hint(s) Value Units C ?arrow_forwardTRUE OR FALSE. On the answer sheet, shade the circle for Letter A if the statement is correct. Otherwise, shade the circle for Letter E. I. 1. Boat floats because there is a force that is pushing it up. 2. Only the weight of the object determines if the object will sink or float. 3. If I change the shape of the clay, its weight and volume also change. 4. Cutting a wood in half will also make its density half of the original density. 5. The pressure exerted by the fluid at rest on an object is directly proportional to the density of the liquid and depth and is sometimes called as gauge pressure.arrow_forwardPLEASE SOLVE THE PRESSURE AT A AND Barrow_forward
- A large tank has a tube coming out of it like a straw, as shown in the picture below. The tube of water is entirely full and closed at the end on the right, while the tank is open to the air. Rank the pressures at points N, U, C, L, E, A, and R (using <, >, and =). Explain your reasoning. How does the pressure at point R compare with the atmospheric pressure immediately outside of the straw? Explain your reasoning. Describe what would happen if you held the right end of the straw (near point R) in place and poked a hole in the end of it. (This is how a siphon works.) Explain your reasoning. (A video of you doing this experiment yourself could be submitted as evidence of your reasoning.)arrow_forwarda. Determine the work done ON a fluid that expands from 1 to 4 as indicated in the figure at the right.b. How much work is done ON the fluid if it is compressed from 4 to 1 along the same path? * For part (a), provide a derivation equation in terms of variables for initial andfinal pressure and volume.arrow_forwardLiquid A is known to have a lower surface tension and lower viscosity than Liquid B. Use these facts to predict the result of each experiment in the table below, if you can. experiment 35.0 mL each of Liquid A and Liquid B are poured through a funnel, and the times t and the needed to pour each liquid through the funnel are measured. Identical wire loops are dipped into Liquid A and Liquid B, so that a film of liquid forms across the loops (like the bubble solution on a child's bubble blowing wand). The width of each loop is increased slowly and the forces F and FB needed to make the loops 5% wider are measured. will be greater than t will be less than f Ot will be equal to f predicted outcome It's impossible to predict whether or fB will be greater without more information. F will be greater than FB will be less than FB OFA will be equal to FB O A It's impossible to predict whether For FB will be greater without more information. Xarrow_forward
- Figure 1 of 1 Gas 18 cmarrow_forwardAn oil drop with the diameter of 1mm, is in the contact with the air with the pressure of 80 KN/m2. i. Find the dimension of surface tension in MLT system ii. If the surface tension of the drop be 42.27x103 N/m, find the pressure difference of the drop. iii. Calculate the internal pressure of the drop. iv. Explain briefly, if the oil drop replace by oil bubble, what changes will happen in internal pressure?arrow_forwarding.pearson.com/?courseld=12521655&key=322254521541138373232024#/ In the event of an emergency, a nuclear reactor is shut down by dropping the control rod R, having a weight of 20 lb, into the reactor core C, as shown in (Figure 1). A If the rod is immersed in "heavy" water, which offers a drag resistance to downward motion of FD = (0.25v) lb, where v is the velocity of the rod in ft/s, determine the distance s it must descend into the reactor core when it attains a speed of 14 ft/s. The rod is released from rest when s = 0. Neglect the effects of buoyancy. Express your answer in feet to three significant figures. Figure R Search FD 1 of 1 > V = VAΣ ΜΕ ΑΣΦ JA vec 20 ? Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ft Next > 3:41 PM 4/23/2024arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON
The Laws of Thermodynamics, Entropy, and Gibbs Free Energy; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8N1BxHgsoOw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY