
Concept explainers
The image distance for a plane mirror.
Answer to Problem 1RQ
The image distance for a plane mirror is equals the object distance.
Explanation of Solution
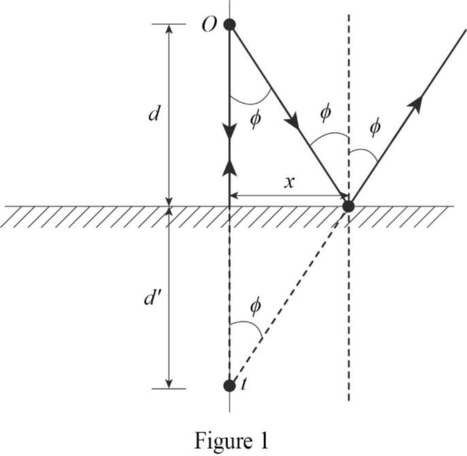
The ray incident along normally to the mirror gets reflected directly back along the normal. So it appears to have originated behind the mirror on the normal. The light ray that strikes the mirror at an angle
The two projected paths cross behind the mirror at point
Conclusion:
Therefore, the image distance for a plane mirror is equals the object distance.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
General Physics, 2nd Edition
- The radius of curvature of the left-hand face of a flint glass biconvex lens (n = 1.60) has a magnitude of 8.00 cm, and the radius of curvature of the right-hand face has a magnitude of 11.0 cm. The incident surface of a biconvex lens is convex regardless of which side is the incident side. What is the focal length of the lens if light is incident on the lens from the left?arrow_forwardThe disk of the Sun subtends an angle of 0.533 at the Earth. What are (a) the position and (b) the diameter of the solar image formed by a concave spherical mirror with a radius of curvature of magnitude 3.00 m?arrow_forwardWhat is the focal length of a pane of window glass? (a) zero (b) infinity (c) the thickness of the glass (d) impossible to determinearrow_forward
- A light bulb is placed 10 cm from a plane mirror, which faces a convex mirror of radius of curvature 8 cm. The plane mirror is located at a distance of 30 cm from the vertex of the convex mirror. Find the location of two images in the convex mirror. Are there other images? If so, where are they located?arrow_forwardcm bottle is standing a distance from a convex mirror and the focal-length is 5 m, find the radius of curvature, image distance, magnification, and image height from a distanċe of 4. 8. and am away, Determine if the image is real or virtual, upright or upside down, or smaller or larger.arrow_forwardThe left end of a long glass rod, 8.00 cm in diameter, has a convex hemispherical surface 4.00 cm in radius. The refractive index of the glass is 1.60.arrow_forward
- Light is incident on a plane mirror at an angle of 29° relative to the normal. What is the angle of reflection?=__________ °arrow_forwardWhich of the following is true for mirrors? A concave mirror can form a virtual image if the object distance is less than its radius. ]A plane mirror can only form virtual images. The focal length of a spherical mirror is twice its radius. A convex mirror can form real images if the object is placed behind it.arrow_forwardCONCAVE AND CONVEX MIRROR. TRUE OR FALSE A. Both statements are TRUE B. Both statements are FALSE C. Statement 1 is TRUE and Statement 2 is FALSE D. Statement 1 is FALSE and Statement 2 is TRUE 1. An object was placed 1 cm from a convex lens. The focal point is at 5 cm. ___________STATEMENT 1: The image location is in front of the lens. ___________STATEMENT 2: The image is inverted. 2. A 16.0 cm tall box is placed 0.50 m in front of the concave mirror. The focal point is located 1.00 m from the mirror. By making a ray diagram, we will know that __________STATEMENT 1: The orientation of the image is downright STATEMENT 2: The image is larger than the object. For items 3&4: A magnifies, inverted image is located at a distance of 30.0 cm from a concave mirror with a focal length of 15 cm. __________3. STATEMENT 1: The object distance from the mirror is 20 cm. STATEMENT 2: The image formed is real. __________4. STATEMENT 1: If the mirror was changed…arrow_forward
- PLEASE ANSWER D, E, AND F An object is placed 11.0 cm in front of a concave mirror with radius of curvature of 30.0 cm. a. What is the focal length of the mirror? ________________________ b. What is the image distance? ________________________ c. What is the magnification? ________________________ d. Is the image (circle the answer): real or virtual? upright or inverted? enlarged or reduced in size? e. Draw a ray diagram. f. If a different object, 10.0 cm tall, is placed in front of the mirror and the image appears inverted and 2.00 cm tall, how far from the mirror was that object placed? ___________________arrow_forwardLight is incident on a plane mirror at an angle of 32° relative to its surface. What is the angle of reflection? =__________°arrow_forwardA concave spherical mirror forms a real image on the principal axis 18 cm from the mirror. If the magnification is 2.0, what is the position of the object_______ and the radius of curvature of the mirror?arrow_forward
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning



