
(a)
The relation between the three currents
(a)
Answer to Problem 60P
The three currents are related by the equation
Explanation of Solution
Figure.1 shows the flow of currents in the circuit.
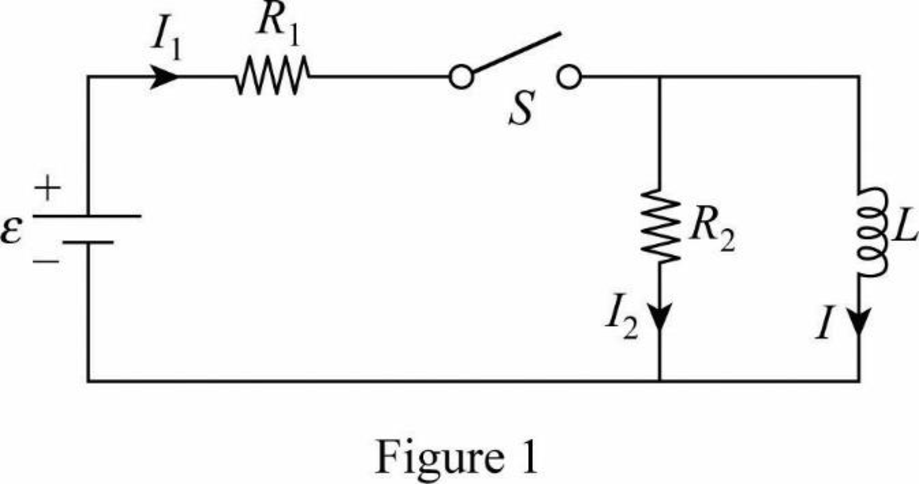
From figure.1,
The current through the resistor
Conclusion:
Therefore, the equation relating the three currents in the circuit is
(b)
The relation using the loop in the left hand side
(b)
Answer to Problem 60P
The relation obtained from the left hand side loop is
Explanation of Solution
According to Kirchhoff’s voltage rule, the algebraic sum of all the voltages in any closed loop in a circuit is zero.
Consider the direction of current from positive terminal of battery to the negative terminal to write the Kirchhoff’s voltage rule using figure.1.
The equation for the voltage across the resistor
Conclusion:
Write the algebraic sum of each of the voltages to obtain the required equation.
Therefore, the relation obtained from the left hand side loop is
(c)
The relation using the outer loop
(c)
Answer to Problem 60P
The relation obtained from the outer loop is
Explanation of Solution
According to Kirchhoff’s voltage rule, the algebraic sum of all the voltages in any closed loop in a circuit is zero.
Consider the direction of current from positive terminal of battery to the negative terminal to write the Kirchhoff’s voltage rule using figure.1.
The equation for the voltage across the resistor
Conclusion:
Write the algebraic sum of each of the voltages to obtain the required equation.
Therefore, the relation obtained from the outer loop is
(d)
An equation having only
(d)
Answer to Problem 60P
The relation having only
Explanation of Solution
Substitute equation (I) in equation (II).
Substitute equation (I) in equation (III).
Compare equation (III) and equation (IV).
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the relation having only
(e)
The equation of current with respect to time
(e)
Answer to Problem 60P
The equation of current with respect to time is
Explanation of Solution
The Kirchhoff’s loop rule for the reference equation is
Write the equation for the solution of equation (VI).
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute equation (VIII) in equation (VII0.
Here,
Therefore, equation of current with respect to time is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
- Show that Equation 32.28 in the text Ls Kirchhoffs loop rule as applied to the circuit in Figure P32.56 with the switch thrown to position b.arrow_forwardConsider the circuit in Figure P32.18, taking = 6.00 V, L = 8.00 mH, and R = 4.00 . (a) What is the inductive time constant of the circuit? (b) Calculate the current in the circuit 250 s after the switch is closed. (c) What is the value of the final steady-state current? (d) After what time interval does the current reach 80.0% of its maximum value?arrow_forwardA coil with a self-inductance of 3.0 H and a resistance of 100 2 carries a steady current of 2.0 A. (a) What is the energy stored in the magnetic field of the coil? (b) What is the energy per second dissipated in the resistance of the coil?arrow_forward
- Design a current loop that, when rotated in a uniform magnetic field of strength 0.10 T, will produce an emf =0 sin t. where 0=110V and 0=110V .arrow_forwardConsider the circuit shown in the figure below where L = 5.10 mH and R₂ = 410 N. L voo 24.0 V + a S ob R₁ R₂ (a) When the switch is in position a, for what value of R₁ will the circuit have a time constant of 14.9 µs? ΚΩ (b) What is the current in the inductor at the instant the switch is thrown to position b? mAarrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning





