
Concept explainers
A magnet is supported by another magnet as shown at right.
1. Draw a free-body diagram for magnet 2. The label for each of the forces on your diagram should indicate:
• the type of force (e.g., gravitational, normal),
• the object on which the force is exerted, and
• the object exerting the force.
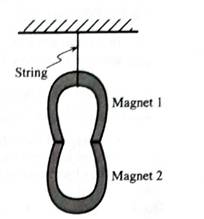
2. Suppose that the magnets were replaced by stronger magnets of the same mass.
If this changes the free-body diagram for magnet 2, sketch the new free-body diagram and describe how the diagram changes. (Label the forces you did in part I above.) If the free-body diagram for magnet 2 does not change, explain why it does not.
3. Can a magnet exert a non-contact force on another object?
Can a magnet exert a contact force on another object?
Describe how you can use a magnet to exert both a contact force and a non-contact force on another magnet.
4. To ensure that you have accounted for all the forces acting on magnet 2 in parts 1 and 2:
List all the non-contact forces acting on magnet 2.
List all the contact forces acting on magnet 2. (Hint: Which objects are in contact with magnet 2?)
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 2 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Applied Physics (11th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Conceptual Physics (12th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
- Please explain and show your solution. Choose from the choices below. Thank you.arrow_forwardAnswer the each of the following show your Complete Solution. Answers is already provided I just need the Solution.arrow_forwardMODIFIED TRUE OR FALSE Directions: Write TRUE if the statement is right. Otherwise, change the underlined word/s to make the statement Correct. Write your answer on the space provided before each item. 1. The acceleration of an object is independent upon the value of its mass. 2. A less massive object has more inertia than a more massive object. 3. A force is a push or pulI exerted upon an object which results from the interaction of that object with its environment. 4. Action and reaction forces are acting on only one body or object. 5. It wou!d take an unbalanced force to cause an object to accelerate from rest. 6. If an object's speed does not change, no net force is acting on the object. 7. Action and reaction forces are equal in magnitude and come in the same direction. 8. Newton's first law of motion is applicable to both moving and non-moving objects. 9. The acceleration of an object is independent upon the magnitude of force exerted. 10. An object can experience two or more…arrow_forward
- Study Area Student Workbook Document Sharing User Settings For help with math skills, you may want to review: Rearrangement of Equations Involving Multiplication and Division For general problem-solving tips and strategies for this topic, you may want to view a Video Tutor Solution of The working of a speaker. Figure 3 d 2.0 cm 2.0 cm I 1 of 1 Part A What is the force on the first wire in (Figure 1)? Assume that I = 9.0 A and d = 56 cm O Fon 1 = (2.3 × 10-4 N, up) O Fon 1 = (2.3 × 10-4 N, down) Fon 1 Fon 1 = (4.5 × 10-4 N, up) Submit 1 = O Fon 1 = 0 N Part B O Fon 2 (6.8 x 10-4 N, down) What is the force on the second wire in the figure? Request Answer O Fon 2 2 = (2.3 × 10−4 N, up) = (2.3 x 10-4 N, down) Fon 2 = (4.5 x 10-4 N, up) Fon 2 = (4.5 × 10-4 N, down) O Fon2=ON + + ☐arrow_forwardPlease help me on seventh question according table and figure. Solve it using vectors. 7) What should be the power of the voltage supply that we will use in the acceleration region?arrow_forwardSOLVE THE FOLLOWING AND SHOW YOUR COMPLETE SOLUTION. EXPRESS YOUR ANSWER IN POLAR FORM.arrow_forward
- Analyze the problem below then answer the following questions B. What is the magnitude of the Torce in standard form? The following force vectors are acting on an object from different directions. A = (101 – 50k)N, B = (301 + 25/)N, and ĉ = (-15) + 20k)N. .Roundoff at three decimal places, e.g. "233.401N"No space between characters and if answer A.What is the resultant vector in unit vector form? is whole number, no need to add decimal places. If answer is too large or too smallI (more than 1,000,000 or less than 0.0001) .Write answers without the express answer as Scientific "hat", refer to exact example notation in exact sample format "3.2€23N" or "3.2e-15N" or format "(-7i+2j-3k)N" No spaces "-3.2€15N". This format means between characters. If result is 3.2x102"N etc. "Ik", omit the number “1". If the component is zero, no need to Your answer write. Your answer (c.What is the angle and direction of the vector along the x-y plane? DWhat is the angle and direction of the vector along…arrow_forwardA soccer ball is kicked from point P, at an angle above a horizontal field. The ball follows an ideal path before landing on the field at point P. Ball P Horizontal field P, 12. On the diagram below, draw an arrow to represent the direction of the net force on the ball when it is at position X. Label the arrow F [Neglect friction.] Y Ball Pi Horizontal field P, 13. On the diagram above, draw an arrow to represent the direction of the acceleration of the ball at position Y. Label the arrow a. [Neglect friction.]arrow_forwardAn object moves clockwise along the trajectory shown in the top-view diagram below. The acceleration varies, but is always directed toward point K. a. Draw and label arrows on the diagram at points A–G to indicate: the direction of the velocity of the object, and the direction of the net force on the object. C F Top view diagram Explain how you knew to draw the arrows as you did. b. For points B, D, and G, determine whether the object is speeding up, slowing down, or moving at constant speed. Explain your reasoning. Base your answers on the work- energy theorem. B G Top view diagramarrow_forward
- Show your solutions. 1. A total distance of travel of 2,000 km breaks every 200 km of a pattern of East-South-East-South continuously up to the end. The time of travel was recorded 5 hours. Find the average velocity of the travel and neglect the turning impact. a. 240 kph b. 300 kph c. 350 kph d. 400 kph e. 440 kph 2. Which of the following is correct if a helicopter flies from the same origin, what will be its average velocity in an hour travel? a. 1,212.20 kph b. 1,500 kph c. 1,000 kph d. 1,414.20 kph e. 800 kpharrow_forwardBriefly explain and show your complete solution. Choose only from the choices below. Thank you.arrow_forwardA physics teacher ties an eraser to the end of a string and then whirls it in a counter-clockwise circle. If the teacher lets go of the string, then the eraser hits a student (or several students) in the classroom. If the string is let go when the eraser is at point X on the diagram at the right, then which student(s) in the class will the eraser hit? Write the initials in this space: ________________arrow_forward
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
