
Concept explainers
To determine: The suitable outsourcing provider based on cultural risk factors using factor- rating method.
Introduction:
Factor-rating method:
The factor-rating method is a quantitative approach to make a decision from various alternatives such that the decision is beneficial to the firm involved. This method is utilized to decide on new layout, new locations, best supplier, outsourcing providers etc.
Answer to Problem 9P
Ranga should select Mexico.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
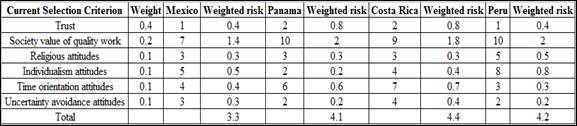
| Current Selection Criterion | Weight | Mexico | Panama | Costa Rica | Peru |
| Trust | 0.4 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Society value of quality work | 0.2 | 7 | 10 | 9 | 10 |
| Religious attitudes | 0.1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 5 |
| Individualism attitudes | 0.1 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 8 |
| Time orientation attitudes | 0.1 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 3 |
| Uncertainty avoidance attitudes | 0.1 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 2 |
Low Risk = 1
High Risk = 10
Formula to calculate weighted risk:
Formula to calculate Total weighted risk:
Excel Formula:
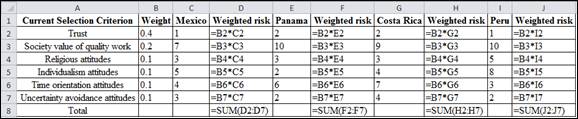
Excel Explanation:
Calculation of weighted risk for Mexico:
The weighted risk is calculated my multiplying the weights with risk rating of each criteria.
The weighted risk is calculated as follows:
Trust:
The weighted risk for Trust is 0.4.
Society value of quality work:
The weighted risk for society value of quality work is 1.4.
Religious attitudes:
The weighted risk for Religious attitudes is 0.3.
Individualism attitudes:
The weighted risk for Individualism attitudes is 0.5.
Time orientation attitudes:
The weighted risk for Time orientation attitudes is 0.4.
Uncertainty avoidance attitudes:
The weighted risk for Uncertainty avoidance attitudes is 0.3.
Calculation of Total weighted risk:
The total weighted risk is calculated be summing all the weighted risk values.
The total weighted risk for Mexico is 3.3.
Calculation of weighted risk for Panama:
The weighted risk is calculated my multiplying the weights with risk rating of each criteria.
The weighted risk is calculated as follows:
Trust:
The weighted risk for Trust is 0.8.
Society value of quality work:
The weighted risk for society value of quality work is 2.
Religious attitudes:
The weighted risk for Religious attitudes is 0.3.
Individualism attitudes:
The weighted risk for Individualism attitudes is 0.2.
Time orientation attitudes:
The weighted risk for Time orientation attitudes is 0.6.
Uncertainty avoidance attitudes:
The weighted risk for Uncertainty avoidance attitudes is 0.2.
Calculation of Total weighted risk:
The total weighted risk is calculated be summing all the weighted risk values.
The total weighted risk for Panama is 4.1.
Calculation of weighted risk for Costa Rica:
The weighted risk is calculated my multiplying the weights with risk rating of each criteria.
The weighted risk is calculated as follows:
Trust:
The weighted risk for Trust is 0.8.
Society value of quality work:
The weighted risk for society value of quality work is 1.8.
Religious attitudes:
The weighted risk for Religious attitudes is 0.3.
Individualism attitudes:
The weighted risk for Individualism attitudes is 0.4.
Time orientation attitudes:
The weighted risk for Time orientation attitudes is 0.7.
Uncertainty avoidance attitudes:
The weighted risk for Uncertainty avoidance attitudes is 0.4.
Calculation of Total weighted risk:
The total weighted risk is calculated be summing all the weighted risk values.
The total weighted risk for Costa Rica is 4.4.
Calculation of weighted risk for Peru:
The weighted risk is calculated my multiplying the weights with risk rating of each criteria.
The weighted risk is calculated as follows:
Trust:
The weighted risk for Trust is 0.4.
Society value of quality work:
The weighted risk for society value of quality work is 2.
Religious attitudes:
The weighted risk for Religious attitudes is 0.5.
Individualism attitudes:
The weighted risk for Individualism attitudes is 0.8.
Time orientation attitudes:
The weighted risk for Time orientation attitudes is 0.3.
Uncertainty avoidance attitudes:
The weighted risk for Uncertainty avoidance attitudes is 0.2.
Calculation of Total weighted risk:
The total weighted risk is calculated be summing all the weighted risk values.
The total weighted risk for Peru is 4.2.
The weighted risk value for Mexico is 3.3. The weighted risk value for Panama is 4.1. The weighted risk value for Costa Rica is 4.4. The weighted risk value for Peru is 4.2. Since, the risk value for Mexico is less (3.3 < 4.1, 4.4, 4.2), Mexico is selected.
Hence, Ranga should select Mexico.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Principles Of Operations Management
- Mr. Rajesh Kumar approached your consulting firm for advice regarding international expansion. His hotels and resorts company does not have any experience at all in venturing into business overseas. Amir, your manager will explain to Mr. Rajesh on the entry methods for international expansion, however he asked you to advise Mr. Rajesh first on the three basic entry decisions that he must consider before choosing the entry methods. Discussarrow_forwardRanga Ramasesh is the operations manager fora firm that is trying to decide which one of four countries itshould research for possible outsourcing providers. The firststep is to select a country based on cultural risk factors, whichare critical to eventual business success with the provider.Ranga has reviewed outsourcing provider directories andfound that the four countries in the table that follows have anample number of providers from which they can choose. Toaid in the country selection step, he has enlisted the aid of acultural expert, John Wang, who has provided ratings of thevarious criteria in the table. The resulting ratings are on a 1 to10 scale, where 1 is a low risk and 10 is a high risk. John has also determined six criteria weightings: Trust,with a weight of 0.4; Quality, with 0.2; Religious, with 0.1;Individualism, with 0.1; Time, with 0.1; and Uncertainty,with 0.1. Using the factor-rating method, which countryshould Ranga select?arrow_forwardWhen a small-medium firm seeks to enter a foreign market through exporting they must consider the following points 1. Identify opportunities 2. Unanticipated problems associated with doing business in a foreign market 3. Method for international transaction 4. How to deal with foreign exchange risk 5. Further expansion/ another appropriate mode of entering Stylo one of the most recognized names in Pakistani footwear industry wants to enter foreign market through exporting. Here you are directed to assist Stylo in investigating with the help of above-mentioned pointsarrow_forward
- Many computer hardware manufacturers rely on foreign companies to provide raw materials; build computer parts; and assemble hard drives, monitors, keyboards, and other components. While there are many advantages to dealing with foreign suppliers, hardware manufacturers may find certain aspects of their business (such as quality and cost control, shipping, and communication) more complicated when dealing with a supplier in another country. In addition to these fairly common business problems, hardware manufacturers are sometimes faced with serious ethical issues relating to their foreign suppliers. Two such issues that have recently surfaced involve (1) suppliers who run their factories in a manner that is unsafe or unfair to their workers and (2) raw materials suppliers who funnel money to groups engaged in armed conflict, including some that commit crimes and human rights abuses. In February 2009, alarming information came to light about the Meitai Plastics and Electronics factory in…arrow_forwardMany computer hardware manufacturers rely on foreign companies to provide raw materials; build computer parts; and assemble hard drives, monitors, keyboards, and other components. While there are many advantages to dealing with foreign suppliers, hardware manufacturers may find certain aspects of their business (such as quality and cost control, shipping, and communication) more complicated when dealing with a supplier in another country. In addition to these fairly common business problems, hardware manufacturers are sometimes faced with serious ethical issues relating to their foreign suppliers. Two such issues that have recently surfaced involve (1) suppliers who run their factories in a manner that is unsafe or unfair to their workers and (2) raw materials suppliers who funnel money to groups engaged in armed conflict, including some that commit crimes and human rights abuses. In February 2009, alarming information came to light about the Meitai Plastics and Electronics factory in…arrow_forwardYou are operating in Trinidad and want to market your Petroleum Gas to Brazil. Conduct an assessment of the mode of entry you will utilize based on the 5 modes discussed in the course (exporting, licensing arrangements, partnering and strategic alliances, acquisitions, establishing new, wholly-owned subsidiaries). Discuss two (2) potential advantages and two (2) disadvantages of the mode of entry selected. Conduct research on two (2) companies that failed when using the mode of entry you have selected for your product. Company names must be stated and what led to the failure must be clearly identified.arrow_forward
- You are required to select a company that markets its consumer products in Singapore. (You are to choose a product-based business and not a service-based business). The company you have chosen should be a manufacturer and not a distributor.2. Identify a new product that you think this company might find suitable to launch and market in Singapore (i.e. it must be a product that is related to its line of business and it must also be new and not marketed before by the company). For example, if you choose Nokia, then the product you might come up with a phone that monitors blood pressure.arrow_forwardYou work for a company that designs and manufactures personal computers. Your company’s R&D centre is in Michigan. The computers are manufactured under contract in Taiwan. Marketing strategy is delegated to the heads of three regional groups: a North American group (based in Chicago), a European group (based in Paris), and an Asian group (based in Singapore). Each regional group develops the marketing approach within its region. In order of importance, the largest markets for your products are North America, Germany, Great Britain, China and Australia. Your company is experiencing problems in its product development and commercialization process. Products are late to market, the manufacturing quality is poor, costs are higher than projected, and market acceptance of new products is less than hoped for. What might be the source of these problems? How would you fix them?arrow_forwardTesco relies heavily on, ‘localization’ in Japan. Based on the international business strategies discussed in the course, clearly state by name, the international business strategy which TESCO is utilizing in Japan. Discuss the benefits and risks associated with this strategy. What alternative international business strategy will you suggest for Tesco in Japan and why? You are to discuss all other international business strategies as addressed in the course before indicating your suggestion.arrow_forward
- Instructions: Analyze and answer the following questions A US Company plans to sell farm equipment in a country in Asia. This country traditionally had not conducted business with companies outside of its geographic region. Answer these questions for the US company. What geographic factors might influence the company's international business activities?Kindly elaborate your answer. Thank you so much!arrow_forwardDiscuss the effect of destination marketing practices in tourism industry in the covid-19 pandemic development in Sri Lanka. Here the discussion should be based on but not limited to the following- -Government established tourism promotional organizations in Sri Lanka. -Practices of your mentioned organizations in promoting Sri Lankan tourism industry. -Private sector involvement on promoting Sri Lanka as a tourism destination, and the sustainability of practices promoted.arrow_forwardDiscuss why you would recommend to X Company of your choice that wants to enter Pietermaritzburg - Kwazulu-Natal South African market, to use the Michael Porter’s Model.arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.
Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.





