
Concept explainers
A body is projected downward at an angle of
striking the ground? (b) How far from the foot of the building will it strike? (c) At what angle with the horizontal will it strike?
(a)
The time taken by the body to hit the ground if it is projected downward at an angle of
Answer to Problem 45SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The downward angle made by the body with the horizontal is
The initial speed of body is
The height of the building from the ground is
Formula used:
The expression for the vertical component of the initial velocity is written as,
Here,
The expression for the vertical displacement of the object in horizontal motion is written as,
Here,
Explanation:
Draw the diagram according to the problem.
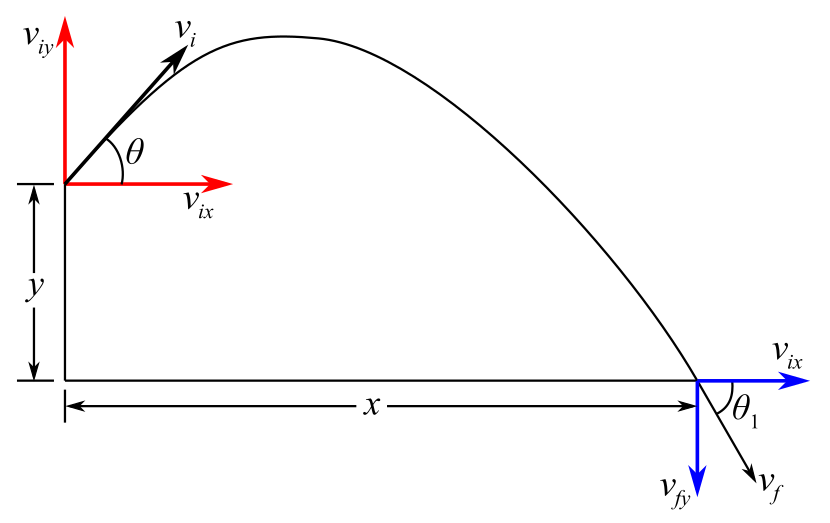
Here,
Recall the expression for the vertical component of the initial velocity.
Substitute
Recall the expression for the vertical displacement of the object.
Substitute
Solve the quadratic equation for
Or,
Understand that, the time cannot be negative. So, the time of flight will be
Conclusion:
Hence, the time taken by the body to hit the ground is
(b)
The horizontal distance traveled by the body from the foot of the building to striking point, if it is projected downward from the building of height
Answer to Problem 45SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The downward angle made by the body with the horizontal is
The initial speed of body is
The height of the building from the ground is
Formula used:
The expression for the horizontal component of the initial velocity is written as,
Here,
The expression for the horizontal displacement of the body which follows projectile motion is written as,
Here,
Explanation:
Recall the expression for the horizontal component of the initial velocity.
Substitute
Recall the expression for the horizontal displacement of the body which follows projectile motion.
Substitute
Conclusion:
Hence, the distance traveled by the body from the foot of the building to striking point is
(c)
The angle made by the body with horizontal when it will strike the groundif it is projected downward at an angle of
Answer to Problem 45SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The downward angle made by the body with the horizontal is
The initial speed of body is
The height of the building from the ground is
Formula used:
The expression for the horizontal component of the initial velocity is written as,
Here,
The expression for the vertical component of the initial velocity is written as,
The expression for the
Here,
The expression for the
Here,
Explanation:
Redraw the diagram according to problem.

Recall the expression for the horizontal component of the initial velocity.
Substitute
Recall the expression for the vertical component of the initial velocity.
Substitute
Recall the expression for the
Substitute
Write the expression for the angle made by the body with the horizontal when it strikes the ground.
Or,
Substitute
Understand that, the velocity along the horizontal remains constant throughout the given projectile motion but the vertical component of the velocity changes.
Conclusion:
Hence, the angle made by the body with horizontal when it will strike is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Schaum's Outline of College Physics, Twelfth Edition (Schaum's Outlines)
- Olympus Mons on Mars is the largest volcano in the solar system, at a height of 25 km and with a radius of 312 km. If you are standing on the summit, with what Initial velocity would you have to fire a projectile from a cannon horizontally to clear the volcano and land on the surface of Mars? Note that Mars has an acceleration of gravity of 3.7m/s2 .arrow_forwardFigure OQ3.3 shows a birds-eye view of a car going around a highway curve. As the car moves from point 1 to point 2, its speed doubles. Which of the vectors (a) through (e) shows the direction of the cars average acceleration between these two points?arrow_forwardA stone is thrown from the top of a building upward at an angle of 60.0* to the horizontal and with an initial speed of 24.0 m/s. If the height of the building is 45.0 m. (a) how long is it before the stone hits the ground?(b) What is the speed of the stone just before it strikes the ground?(c) Where ?does the stone strike the groundarrow_forward
- A ball is thrown horizontally from a height of 5.50 m with an initial velocity of 25m/s. (A) how long will it take the ball to reach the ground? (B) at what horizontal distance from the point of release will it strike the ground? (C) what will be the magnitude of its velocity when it takes the ground?arrow_forwardA projectile is thrown from the top of a cliff with an initial speed of 25 m/s at an angle of 600 up from the horizontal. If the projectile lands 100 m from the base of the cliff how tall is the cliff?arrow_forwardA stone is thrown from the top of a building upward at an angle of 30.0° to the horizontal with an initial speed of 20.0 m/s as shown. The height from which the stone is thrown is 45.0 m above the ground.(A) How long does it take the stone to reach the ground? (B) What is the speed of the stone just before it strikes the ground?arrow_forward
- An object is thrown off the top of a building with velocity 28 m/s at an angle of 32° with respect to the horizontal. It takes 6.2 s for the object to land. (a) How high is the building in meters? (b) What is the horizontal distance that the object travels in meters?arrow_forwardA rock is thrown from the top of a building 94 m high, with a speed of 14 m/s at an angle 33 degrees above the horizontal. When it hits the ground, what is the magnitude of its velocity (i.e. its speed).arrow_forwardA golfer tees off from the top of a rise, giving the golf ball an initial velocity of 44 m/s at an angle of 28° above the horizontal. The ball strikes the fairway a horizontal distance of 190 m from the tee. Assume the fairway is level. (a) How high is the rise above the fairway? (b) What is the speed of the ball as it strikes the fairway?arrow_forward
- A batter hits a baseball 3 ft above the ground, so that the ball leaves the bat with a speed of 120 ft/s and at an angle 60° above horizontal. (a) How far will the baseball travel until it first hits the ground? (b) What will be the maximum height of the baseball? (c) What is the speed that the baseball is traveling at when it first hits the ground?arrow_forwardA stone is thrown from the edge of a tower at an angle of 35 degrees above the horizontal and hits the ground 5.3 s later, 84 m away from the base of the tower. (a) What is the initial speed of the stone? (b) What is the magnitude and direction of the stone’s velocity just before hitting the ground?arrow_forwardA rock is thrown from the rooftop of a building. The initial velocity of the rock is 7.3 m/s at an angle of 25° below the horizontal. It strikes the ground 4.2 s later. (a) How far horizontally from the base of the building does the rock strike the ground? (b) Find the height from which the rock was thrown. (c) How long does it take the rock to reach a point 10 m below the level of launching?arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University

