
Concept explainers
The suspension of an automobile can be approximated by the simplified spring-and-dashpot system shown. (a) Write the differential equation defining the vertical displacement of the mass m when the system moves at a speed v over a road with a sinusoidal cross-section of amplitude δm and wavelength L. (b) Derive an expression for the amplitude of the vertical displacement of the mass m.
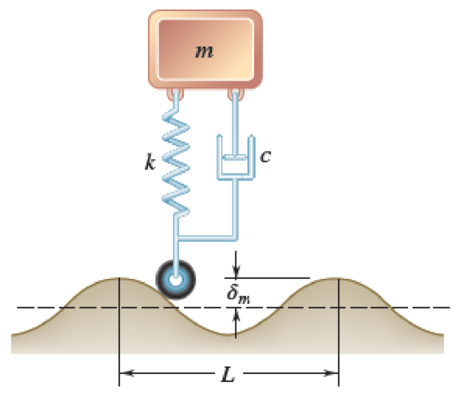
Fig. P19.151
(a)
Write the differential equation defining the vertical displacement of the mass m when the system moves at a speed v over a road with a sinusoidal cross section of amplitude
Answer to Problem 19.151P
The differential equation defining the vertical displacement of the mass m when the system moves at a speed v over a road with a sinusoidal cross section of amplitude
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Show the free body diagram of the system of automobile, spring and dashpot as in Figure (1).
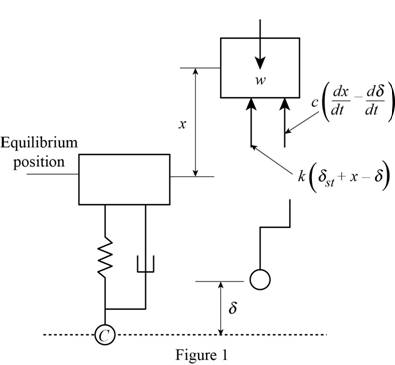
The expression for the weight of the automobile (W) as follows:
Here,
The expression for the acceleration of the automobile (a) as follows:
Refer Figure (1),
The expression for the force by considering the vertical equilibrium condition as follows;
Substitute
Substitute
The expression for the time interval needed to travel
The expression for the forced circular frequency
Substitute
The expression for the motion of the wheel which is sine curve
Differentiate the above equation with respect to time ‘t’.
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the differential equation defining the vertical displacement of the mass m when the system moves at a speed v over a road with a sinusoidal cross section of amplitude
(b)
Derive an expression for the amplitude of the vertical displacement of the mass m.
Answer to Problem 19.151P
The expression for the amplitude of the vertical displacement of the mass m is
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The expression for the general solution from the identity as follows:
Here,
The expression for the force transmitted (F) to the automobile as follows:
Substitute
The expression for the differential equation of the motion for the damped forced vibration as follows:
Compare the equation (3) and (4).
The expression for the steady state of motion of the system as follows:
The expression for the steady state of motion of the system as follows:
Substitute
The expression for the phase angle
The expression for the Eulerian angle
Therefore, the expression for the amplitude of the vertical displacement of the mass m is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- Two springs of constants K1 and K2 are connected in series to a block A that vibrates in simple harmonic motion with a period of 5 s. When the same two springs are connected in parallel to the same block, the block vibrates with a period of 2 s. Determine the ratio K1/K2 of the two spring constants.arrow_forwardA machine of mass 75 kg is mounted on springs and is fitted with a dashpot to damp out vibrations. There are three springs each of stiffness 10 N/mm and it is found that the amplitude of vibration diminishes from 38.4 mm to 6.4 mm in two complete oscillations. Assuming that the damping force varies as the velocity, determine : 1. the resistance of the dash-pot at unit velocity ; 2. the ratio of the frequency of the damped vibration to the frequency of the undamped vibration ; and 3. the periodic time of the damped vibration.arrow_forwardQ.6 The mass of an automobile is 1800 kg, vibrates in a vertical direction while traveling on a rough road having a sinusoidal wave form with an amplitude Y= 0.01 m. Assuming that the automobile can be modeled as a single degree of freedom system with stiffness 250 kN/m and damping ratio š, determine (a) the amplitude of vibration of the automobile and (b) the force transmitted when it is traveling at a speed causing resonance vibration.arrow_forward
- (a) A single cylinder vertical petrol engine of total mass 320 kg is mounted upon a steel chassis and causes a vertical static deflection of 2 mm. The reciprocating parts of the engine have a mass of 24 kg and move through a vertical stroke of 150 mm with simple harmonic motion. A dashpot attached to the system offers a resistance of 490 N at a velocity of 0.3 m/sec. Determine: (i) The speed of the driving shaft at resonance; (ii) The amplitude of steady state vibration when the driving shaft of the engine rotates at 480 rpm. (b) A vibrating system is defined by the following parameters: m=3 kg, k = 100 N/m, C=3 N-sec/m Determine (i) the damping factor, (ii) the natural frequency of damped vibration, (iii) logarithmic decrement, (iv) the ratio of two consecutive amplitudes and (v) the number of cycles after which the original amplitude is reduced to 20 percent.arrow_forward(a) A mass suspended from a helical spring of stiffness s, is displaced by a distance x from its equilibrium position and allowed to vibrate. Show that the motion is simple harmonic. (b) A vertical helical spring having a stiffness of 1540 N/m is clamped at its upper end and carries a mass of 20 kg attached to the lower end. The mass is displaced vertically through a distance of 120 mm and released. Find : 1. Frequency of oscillation ; 2. Maximum velocity reached ; 3. Maximum acceleration; and 4. Maximum value of the inertia force on the mass. (c) A machine of mass 75 kg is mounted on springs and is fitted with a dashpot to damp out vibrations. There are three springs each of stiffness 10 N/mm and it is found that the amplitude of vibration diminishes from 38.4 mm to 6.4 mm in two complete oscillations. Assuming that the damping force varies as the velocity, determine : 1. the resistance of the dashpot at unit velocity ; 2. the ratio of the frequency of the damped vibration to the…arrow_forwardA vehicle is modelled as a combined mass-spring-damper system that oscillates in the vertical direction only. The driver of the vehicle travels along a road whose elevation varies sinusoidally as shown in Figure 2. The mass of the vehicle, which includes the driver, is 2500 kg. The stiffness and damping of the shocks are 40 kN/m and 3000 kg/s respectively. i. Determine the amplitude of vibration of the vehicle when it travels at a constant speed of 90 km/hr along the sinusoidal road. y/m 0.6 ►Velocity of vehicle m 0.4 ► Rigid massless tyre 0.2 distance (m) 20 60 80 -0.2 Figure 2arrow_forward
- A vehicle is modelled as a combined mass-spring-damper system that oscillates in the vertical direction only. The driver of the vehicle travels along a road whose elevation varies sinusoidally as shown in Figure 2. The mass of the vehicle, which includes the driver, is 2500 kg. The stiffness and damping of the shocks are 40 kN/m and 3000 kg/s respectively. i. Determine the amplitude of vibration of the vehicle when it travels at a constant speed of 90 km/hr along the sinusoidal road. ii. If additional load having a combined mass of 1000 kg is placed in the vehicle, determine the travelling speed of the vehicle that would result in a resonant condition. What is the amplitude of the vehicle at resonance? Using an appropriate graph and suitable equations, explain how the oscillations of the vehicle can be significantly reduced when travelling at very high speeds. Please note that a simple graphical sketch with your pen that clearly identifies the key points is acceptable. Your axes must…arrow_forwardAs shown in the Fig. 3, the CM of a cylinder of mass m and radius R is connected to the top of hoop of mass m by a spring. The spring constant is assumed to be known and it is denoted by k. At a given moment the system is slightly compressed and then suddenly released. After the release, both rigid objects roll without slipping. Determine the angular frequency of the resulting oscillation. It is assumed that the spring remains horizontal throughout the motion. Figure 3: Coupled Oscillatorarrow_forward6.25. A 30,000-kg locomotive is coupled to a fully loaded 20,000-kg boxcar and moving at 6.5 m/s. The assembly is coupled to a stationary and empty 5,000-kg cattle car. The stiffness of each coupling is 5.7 x 10' N/m. (a) What are the natural frequencies of the three-car assembly? (b) Mathematically describe the motion of the cattle car after coupling.arrow_forward
- A 11-lb block is attached to the lower end of a spring whose upper end is fixed and vibrates with a period of 7.2 s. Knowing that the constant k of a spring is inversely proportional to its length (e.g., if you cut a 10 lb/in. spring in half, the remaining two springs each have a spring constant of 20 lb/in.), determine the period of a 7-lb block that is attached to the center of the same spring if the upper and lower ends of the spring are fixed.arrow_forwardA 50-kg machine tool is mounted on an elastic foundation. An experiment is run todetermine the stiffness and damping properties of the foundation. When the tool is excitedwith a harmonic force of magnitude 8000 N at a variety of frequencies, the maximumsteady-state amplitude obtained is 2.5 mm, occurring at a frequency of 32 Hz. Use thisinformation to determine the stiffness and damping ratio of the foundation.arrow_forwardΑ Ο CH B d PROBLEM 19.50 A small collar of mass 1 kg is rigidly attached to a 3-kg uniform rod of length L = 750 mm. Determine (a) the distance d to maximize the frequency of oscillation when the rod is given a small initial displacement, (b) the corresponding period of oscillation.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





