
(a)
Interpretation:
The validation corresponding to the fact that aspartame is chiral is to be stated. If aspartame is chiral, then the possible number of stereoisomers for aspartame is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
A compound that contains a chiral carbon is known as chiral compound. Carbon atom that contains all the four different atoms or group of atoms attached to it is referred as the chiral atom. This carbon is also known as stereocenter.
The possible number of stereoisomers is calculated by the expression
Answer to Problem 10P
Aspartame is a chiral compound. The possible number of stereoisomers for aspartame is
Explanation of Solution
The aspartame is a chiral compound. The structure of aspartame which contains chiral carbon atoms is shown as,
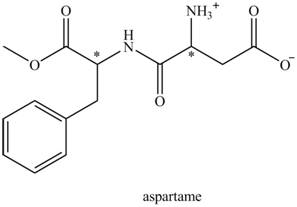
There are two chiral carbon atoms present in aspartame which are marked with asterisk sign. In the structure of aspartame, one carbon atom is directly bonded to
Thus, the possible number of stereoisomers in aspartame is,
Where,
- is the number of stereocenter.
Thus, the possible stereoisomers of aspartame is
(b)
Interpretation:
The name of each functional group present in aspartame is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
An atom or a group of atoms that shows characteristic physical and chemical properties are collectively known as
Answer to Problem 10P
The name of each functional group present in aspartame is ester group
Explanation of Solution
According to the structure of aspartame shown in Figure 1, there are four functional groups present in the structure of aspartame.
The name of all the functional group of aspartame is ester group
(c)
Interpretation:
The net charge on aspartame molecule in an aqueous solution at
Concept Introduction:
The negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration of the solution is known as
Answer to Problem 10P
The net charge on aspartame molecule in an aqueous solution at
Explanation of Solution
In an aqueous solution of
Hence, there is no change of charge takes place in aspartame and it possesses zero net charge.
(d)
Interpretation:
The validation corresponding to the fact that aspartame is whether soluble in water or not is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
According to the concept of solubility, it is mentioned that like dissolves like. Generally, polar compound can only be dissolved in polar solvents and non-polar or weakly polar compounds can only be dissolved in non-polar solvents or weakly polar solvents.
Answer to Problem 10P
Aspartame is soluble in water.
Explanation of Solution
The given structure of asparatame is present in zwitterion form which suggests that it is a polar molecule. According to the concept of like dissolves like, aspartame is soluble in water because water is also a polar molecule.
(e)
Interpretation:
The structural formulas for the products that are obtained by the complete hydrolysis of aspartame in aqueous
Concept Introduction:
An atom or a group of atoms that shows characteristic physical and chemical properties are collectively known as functional groups. The functional group is the most reactive part present in the molecule. The main functional groups are
The addition of water molecule to the compound is known as hydrolysis that compound.
Answer to Problem 10P
The structural formulas for the products that are obtained by the complete hydrolysis of aspartame in aqueous
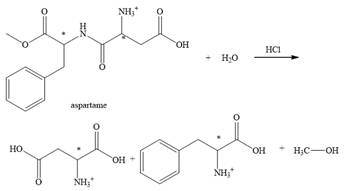
Explanation of Solution
The hydrolysis of aspartame in the presence of aqueous
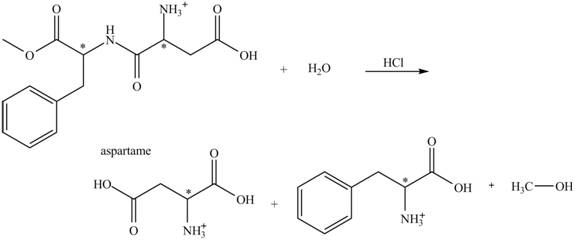
Figure 2.
The reaction of aspartame with aqueous
(f)
Interpretation:
The structural formulas for the products that are obtained by the complete hydrolysis of aspartame in aqueous
Concept Introduction:
An atom or a group of atoms that shows characteristic physical and chemical properties are collectively known as functional groups. The functional group is the most reactive part present in the molecule. The main functional groups are
The addition of water molecule to the compound is known as hydrolysis that compound.
Answer to Problem 10P
The structural formulas for the products that are obtained by the complete hydrolysis of aspartame in aqueous
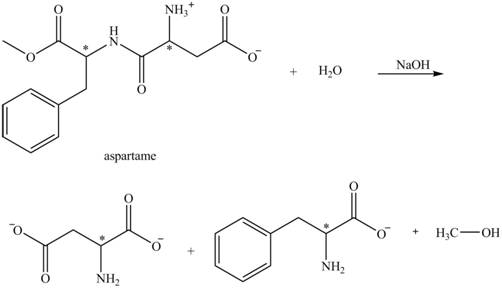
Explanation of Solution
The hydrolysis of aspartame in the presence of aqueous
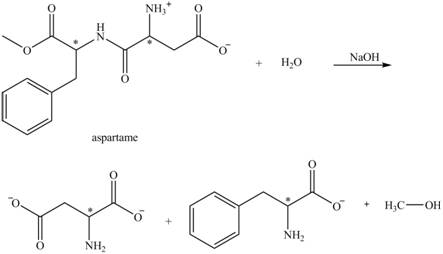
Figure 3.
The reaction of aspartame with aqueous
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Introduction To General, Organic, And Biochemistry
- Some of the most important organic compounds in biochemistry are the α-amino acids, represented by the general formula shown.Write structural formulas for the following α-amino acids.(a) Alanine (R = methyl)(b) Valine (R = isopropyl)(c) Leucine (R = isobutyl)(d) Isoleucine (R = sec-butyl)(e) Serine (R = XCH2, where X is the functional group that characterizes alcohols)(f) Cysteine (R = XCH2, where X is the functional group that characterizes thiols)(g) Aspartic acid (R = XCH2, where X is the functional group that characterizes carboxylic acids)arrow_forward(a) Consider structure Y. OH CH3 C-0-CH3 Structure Y i. Redraw structure Y, circle and name all the functional groups that exist in Y. ii. Label the chiral carbons in asterisks(*).arrow_forwardHexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride, CH3(CH2)15N(CH3)+3 Cl-, is one of a class of cationic detergents, commonly used inshampoos and as “clothes rinses.”(a) Identify the hydrophilic head group and the hydrophobic tail.(b) Draw a depiction of a micelle that would form if this compound were dissolved in water.(c) What are the intermolecular forces that are primarily responsible for the micelle’s solubility in water?arrow_forward
- (a) Which of the common amino acids have more than one carboxyl group?arrow_forward(a) What is the empirical formula of cellulose? (b) Whatis the monomer that forms the basis of the cellulose polymer?(c) What bond connects the monomer units in cellulose:amide, acid, ether, ester, or alcohol?arrow_forwardIndicate whether each statement is true or false: (a)Disaccharides are a type of carbohydrate. (b) Sucrose is amonosaccharide. (c) All carbohydrates have the formulaCnH2mOm.arrow_forward
- (a) Why can’t two purine bases (A and G) form a base pair and hydrogen bond to each other on two strands of DNA in the double helix? (b) Why is hydrogen bonding between guanine and cytosine more favorable than hydrogen bonding between guanine and thymine?arrow_forwardHow many chiral centers are in each of the following molecules? Mark each one with an asterisk. (a) OH (b) (c) OH OH OH он (d) (e) (f) (g) OH HN ON CIarrow_forwardWhich statements are true about constitutional isomers? (a) They have the same molecular formula. (b) They have the same molecular weight. (c) They have the same order of attachment of atoms. (d) They have the same physical propertiesarrow_forward
- Q3: Use arrows to match the terms (A) column with (B) column. Some may be used more than once and others not at all. B a- contain glycerol backbone b- glucose é- amino acids d- esters of fatty acids e- octapeptide f- disaccharide 6- Proteins g- polysaccharide k- compound lipids i- steroid-like j- lipids k- polar lipids + glucose storage in animals 7- Cholesterol 8- Lactose 9- Waxes 10AngiotensinlI ((T.O.P)) ((1-2))arrow_forward(i) Which one of the following is a disaccharide : Starch, Maltose, Fructose, Glucose?(ii) What is the difference between fibrous protein and globular protein?(iii) Write the name of vitamin whose deficiency causes bones deformities in children.arrow_forwardIndicate whether each statement is true or false: (a) Disaccharides are a type of carbohydrate. (b) Sucrose is a monosaccharide. (c) All carbohydrates have the formula CnH2mOm.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





