
Concept explainers
Each of the following compounds is characterized by a 1H NMR spectrum that consists of
only a single peak having the chemical shift indicated. Identify each compound.
Interpretation:
The compounds gives only single peak in 1H NMR spectrum as indicated by the chemical shift is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
The information related to the proton in the compound can be deduced by the number of signals in a spectrum.
The proton chemical shift in the compound is due to the environment of the proton.
The signal of a particular proton can be split by the presence of protons in vicinal position.
The NMR spectrum of a compound will consist of a single peak if all protons in the compound are structurally equivalent.
Index of hydrogen deficiency is calculated as
Here
Oxygen atoms do not affect the index of hydrogen deficiency.
Answer to Problem 31P
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
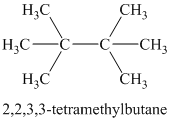
Chemical formula:
A single peak at
Therefore, the structure of the compound is:
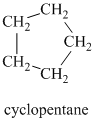
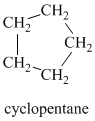
Chemical formula:
A single peak at
Therefore, it must be a symmetric cycloalkane:
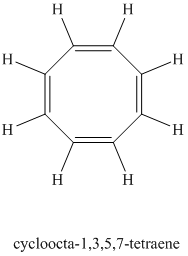
Chemical formula:
A single peak at
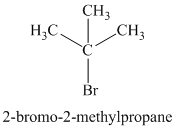
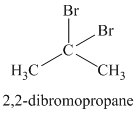
Chemical formula:
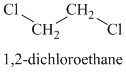
The chemical formula shows it is a saturated alkyl halide. A single peak means that all protons are equivalent. The presence of the bromine atoms accounts for the higher chemical shift of the protons. Therefore, the structure of the compound is:
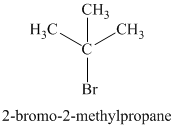
Chemical formula:
A single peak shows all protons to be equivalent. The formula is of a saturated alkyl halide. The presence of two chlorine atoms on the same carbon as the protons will increase the shift to
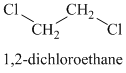
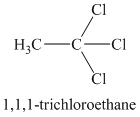
Chemical formula:
A single peak means all protons must be equivalent. The chemical formula shows it to be a saturated alkyl halide. The higher shift of
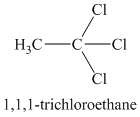
Chemical formula:
A single peak shows all protons to be equivalent. The chemical formula shows it to be a saturated alkyl halide. The high chemical shift of
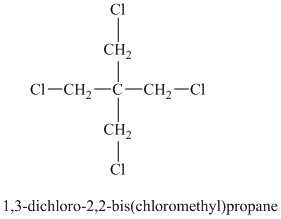
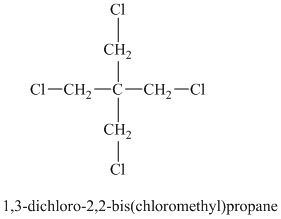
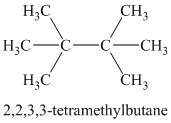
Chemical formula:
A single peak shows all protons are equivalent. The chemical formula shows an index of hydrogen deficiency of four. This, taken together with a chemical shift of
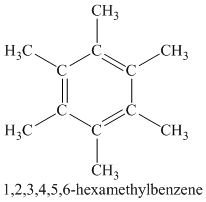
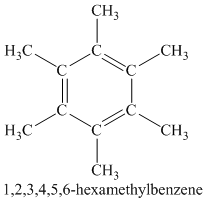
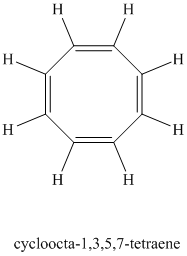
Chemical formula:
A single peak shows all protons are equivalent. The higher chemical shift of
Therefore, the structure of the compound is:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
- The 13C-NMR spectrum of 3-methyl-2-butanol shows signals at 17.88 (CH3), 18.16 (CH3), 20.01 (CH3), 35.04 (carbon-3), and 72.75 (carbon-2). Account for the fact that each methyl group in this molecule gives a different signal.arrow_forwardFollowing are the 'H and 13C NMR spectra for each of three isomeric ketones with formula C7H14O. Determine a structure to each pair of spectra and assign each H and C. Carbon spectrum А C,H140 Carbon spectrum В C;H140 CDCI3 200 150 100 50 Proton spectrum CDC13 A C,H140 200 150 100 50 1.96 2.00 2.91 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 211.04 -44.79 –17.39 – 13.78 -218.40 - 38.85 –18.55arrow_forwardCompound 1 has molecular formula C6H12. It shows three signals in the 1H-NMR spectrum, one at 0.96 ppm, one at 2.03 ppm, and one at 5.33 ppm. The relative integrals of these three signals are 3, 2, and 1, respectively. Compound 2 has molecular formula C7H15Br. It shows two signals in the 1H-NMR spectrum, one at 1.08 ppm and one at 1.59 ppm. The relative integrals of these two signals are 3 and 2, respectively. Propose structures for compounds 1 and 2, explaining how you reach your conclusion.arrow_forward
- Consider carbons x, y, and z in p-methylanisole. One has a chemical shift of δ 20, another has δ 55, and the third δ 157. Match the chemical shifts with the appropriate carbons.arrow_forward2) Compound C gave the following proton NMR signals: a) singlet,1.22 ppm, 6H; b) Triplet, 1.85 ppm, 2H, J = 7 Hz; c) triplet, 2.83 ppm, 2H, J = 7 Hz; d) singlet, 7.02 ppm, 4H. Sketch the proton NMR spectrum of compound C and assign the chemical shifts to the protons of the compounds.arrow_forwardHow many signals will the following compound display in the proton NMR spectrum? Compound: CH3CH2CH2COOCH2CH(CH3)2 O 6 O 7 O 3 O 5 4arrow_forward
- A compound with molecular formula C4H11N has the 'H NMR spectrum shown. Which choices shows the correct number of protons giving rise to each signal? I II III PPM O1- 6H, II - 3H, III - 2H O1- 5H, II - 4H, III - 2H O1- 6H, II - 4H, III - 1H O1- 1H, II - 4H, III – 6Harrow_forwardwhat compound is this cnmr and nmr which is a solid and has a boiling point of 47.8 - 124.3 degrees celsiusarrow_forwardCompound 1 has molecular formula C7H15Cl. It shows two signals in the 1H-NMR spectrum, one at 1.08 ppm and one at 1.59 ppm. The relative integrals of these two signals are 3 and 2, respectively. Propose structures for compound 1, explaining how you reach your conclusion.arrow_forward
- How many signals would you expect to see in the 1H NMR spectrum of each of the five compounds with molecular formula C6H14?arrow_forwardCompound A, with molecular formula C4H9Cl, shows two signals in its 13C NMR spectrum. Compound B, an isomer of compound A, shows foursignals, and in the proton-coupled mode, the signal farthest downfield is a doublet. Identify compounds A and B.arrow_forwardA compound has the molecular formula: C4H8O2 and gives the following C-13 NMR spectrum. Provide the most likely functional groups for each signal. nmrsim presentation 1 1 C:Bruken Topspin3.5pl7 examdata -170.7658 150 100 d 170.8 (O CH3) ; 60.4 (OCH2); 20.8, 14.1 (2 x C=0) 8170.8 (0 CH₂); 60.4 (OCH₂); 20.8, 14.1 (2 x CH3). 8 170.8 (CH3); 60.4 (C-0); 20.8, 14.1 (2 x OCH₂) 8170.8 (C=0); 60.4 (OCH₂); 20.8, 14.1 (2 x CH3). 8170.8 (C) ; 60.4 (O CH2); 20.8, 14.1 (2 x O CH3) -60.4293 50 -20.7902 -14.1385 [ppm] [+]arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
