
(a)
The IS-LM curve of the economy.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The IS-LM curves of the economy can be calculated from the given details. It is given that the value of
Similarly, the LM curve of the economy can be obtained by equating the money market as follows:
Mundell - Fleming model: The Mundell Fleming model is the extended version of the IS-LM model of the economy that incorporates the BOP into the equilibrium. Thus, it is the model that portrays the short run relationship between the nominal exchange rate of the economy, interest rate and the output.
(b)
The equilibrium exchange rate, income, and net exports.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The equilibrium exchange rate of the economy can be calculated by equating the output (Y) from both the IS curve and the LM curve as follows:
Thus, the equilibrium exchange rate in the economy is 2. The equilibrium income in the economy can be calculated by substituting the value of net exports in the equation above as follows:
Thus, the equilibrium income in the economy is equal to 1,200. The net exports in the economy can be calculated by substituting the value of the exchange rate in the net exports as follows:
Thus, the net exports in the economy is equal to 100.
(c)
The IS and LM curves when the government spending increases by 50.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
When there is an increase in the government spending by 50, the new IS curve can be derived as follows:
Since the economy has the floating exchange rate, the LM curve of the economy remains unchanged. As a result, there will be no change in the income and output of the economy. Thus, the income remains at 1,200. Therefore, the new exchange rate can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the exchange rate is 3. A higher exchange rate decreases the exports as the domestic currency appreciates and becomes costly to the foreign countries. Thus, the increased government spending will be matched by a lower net exports. This can be illustrated as follows:
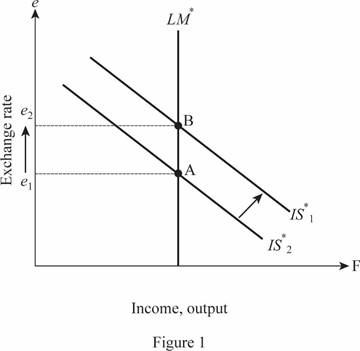
Thus, the IS curve shifts toward the right graphically, whereas the exchange rate increases.
(d)
The IS and LM curves when the government spending increases by 50 under fixed exchange rate.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
When there is an increase in the government spending by 50, the new IS equation becomes
Thus, when the exchange rate is fixed at 2, the equilibrium income should increase to 1,400. As a result, the money supply must be increased by the monetary authority to keep the exchange rate fixed at 2. Therefore, M would increase to 3,600 due to the rightward shift in the LM curve and it can be illustrated as follows:
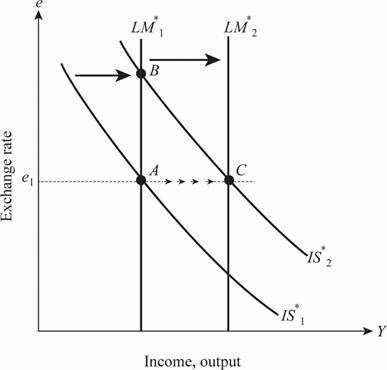
Thus, the IS curve shifts toward the right increases the exchange rate, whereas the increase in the money supply leads to the rightward shift in the LM curve which brings the exchange rate back to the original position with increased output and income.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- For an open economy, which of the following expressions represents private saving (S)?investment plus tax revenues less government expenditure plus net exports, I + T – G + NXI + T – G – NXI + G + NXG – T + NX – Inone of the abovearrow_forwardconsumption and investment: C = 1,000 + (2/3)*(Y – T) and I = 1,200 – 100*r. Furthermore, Y = 8,000, G = 2500, T = 2,000. Calculate the national saving.arrow_forwardConsider the following equations for a small open economy C = 2500 + 0.85Yd; T = 700 + 0.25Y; G = 8000; TR = 800; I = 4000 + 0.2Y; M = 3000 + 0.25Y; X = 2000 Use the reduced form equation to compute equilibrium national income. Compute the values of disposable income, consumption expenditure, tax revenue, and net exports. Using a measure, you are familiar with, demonstrate if the economy is operating a balanced budget.arrow_forward
- Consider the following economy C=1000+0.4(Y-T) 1=500 T=400 G=300 What is the investment of equilibrium?arrow_forwardSolve for the following a) investment: b) Private saving: c) public savingarrow_forwardHow does investment as defined by economists differ from investment as defined by the general public?arrow_forward
- The following information is provided about an open economy with a government. Use the information to answer the questions that follow: C = 450 + 0.4Y I = 350G = 150X = 70 Z = 35 + 0.1Y T = 0.15YYf = 155 Before the government decreased the tax rate, how much of government spending was required to bring the economy to full employment?arrow_forwardGiven the following on a closed economy, determine the following The level of Private savings The level of Public savings The level of national savingarrow_forwardIf the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is adjusted for the PPP (Purchasing Power Parity, or what a U.S. dollar can buy in each country), what would be the correct ordering of the economies if we order them from the highest to the lowest - in terms of the GDP by PPP? Please choose your answer from the below list of countries - ranked correctly from highest to the lowest, as per the 2020 IMF estimates Group of answer choices China, Germany, United States, Japan and United Kingdom. United States, China, Germany, United Kingdom, and Japan. China, United States, India, Japan and Germany.arrow_forward
- In a closed economy, saving and investment must be equal, but this is not the case in an open economy. In the following problem, you will explore how saving and investment are connected to the international flow of capital and goods in an economy. Before delving into the relationship between these various components of an economy, you will be asked to recall some relationships between aggregate variables that will be useful in your analysis. Recall the components that make up GDP. National income (Y) equals total expenditure on the economy's output of goods and services. Thus, where C = consumption, I = investment, G = government purchases, X = exports, M = imports, and NX = net exports: Y = Also, national saving is the income of the nation that is left after paying for Therefore, national saving (S) is defined as: Rearranging the previous equation and solving for Y yields Y = . Plugging this into the original equation showing the various components of GDP results in the following…arrow_forwardWhat is % of all the Investment in total GDParrow_forwardIncome (Y = ?) Transfer Payments = $300,000 Households Taxes = $300,000 Capital Market Private Savings = $900,000 Government Government Deficit = $300,000 Business Private Investment Gov't Purchase of G&S = $300,000 Firms = $600,000 Consumption Expenditures = $2,400,000 Employing the data from the figure above and assuming a closed economy, what is income Y equal to?arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





