
Concept explainers
(a)
To Find:Coefficient of friction between the beam and the wall.
(a)
Answer to Problem 58P
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Weight of steel beam
Length of the beam,
Length of the cable,
Formula used:
For translational and
Calculation:
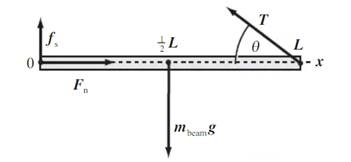
Horizontal component of net force
Vertical component of net force
From
Where,
Equation
Conclusion:
Thus, the coefficient of friction between the beam and the wall is
(b)
To Find:Tension in the cable.
(b)
Answer to Problem 58P
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Formula used:
From part (a):
Calculation:
Substitute the values and solve:
Conclusion:
Thus, the tension in the cable is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
- Two rods, one made of copper and the other of steel, have the same dimensions. If the copper rod stretches by 0.15mm under some stress, how much does the steel rod stretch under the same stress?arrow_forwardAlarge uniform cylindrical steel rod of density =7.8g/cm3 is 2.0 m long and has a diameter of 5.0 cm. the rod is fastened to a concrete floor with its long axis vertical.what is the normal stress in the rod at the cross-section located at (a)1.0 mfrom its lower end?(b)1.5 m from the lower end?arrow_forwardA copper wire is 1.0 m long and it diameter is 1.0 mm. if the wire hangs vertically how much weight must be added to its free end in order to stretch it 3.0mm?arrow_forward
- A suspender rod of a suspension bridge is 25.0 m long. If the rod is made of steel, what must its diameter be so that it does not stretch more than 1.0 cm when a 2.5104kg tuck passes by it? Assume that the rod supports all of the weight of the truck.arrow_forwardCan compress stress be applied to a rubber band?arrow_forwardReview the relationship between stress and strain. Can you find any similarities between the two quantities?arrow_forward
- An aluminium (=2.7g/cm3) wire is suspended from the ceiling and hangs vertically. How long must the wire be before the stress at its upper end reaches the proportionality limit, which is 8.0107N/m2 ?arrow_forwardWhen the structure shown below is supported at point P, it is in equilibrium. Find the magnitude .of force F and the force applied at P. the weight of the structure is negligible.arrow_forwardA 100-N weight is attached to a free end of a metallic wire that hangs from the ceiling. When a second 100-N weight is added to the wire, it stretches 3.0 mm. The diameter and the length of the wire are 1.0 mm and2.0 m, respectively. What is Young’s modulus of the metal used to manufacture the wire?arrow_forward
- Á brass wire (Y = 10" N/m²) and a steel %3D wire (Y = 2 x 10" N/m²) of equal length and diameter are suspended from a common rigid support. The free ends A of brass and B of steel at a distance of 75 cm are connected by a %3D horizontal bar, with both the wires vertical and parallel. Calculate the distance of a point from B, at which a load may be attached so that the bar remains horizontal. 75cm (75-x) P,arrow_forwardA cable used to lift heavy materials like steel I-beams must be strong enough to resist breaking even under a load of 1.7 106 N. For safety, the cable must support twice that load. (a) What cross-sectional area should the cable have if it's to be made of steel? (b) By how much will a 7.0-m length of this cable stretch when subject to the 1.7 106-N load?arrow_forwardIf the same force F pulls on two cylindrical rods of the same material, which has a greater change in length: a rod of radius 2r and length L, or a rod of radius 4r and length 5L? Select one: the rod of radius 4r and length 5L not enough informationg given. it depends if the force is tensile or compressive. the rod of radius 2r and length L both rods have the same change in length.arrow_forward
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

