
Concept explainers
The Excel worksheet form that appears below is to be used to recreate Example E and Exhibit 12-8. Download the workbook containing this form from Connect, where you will also receive instructions about how to use this worksheet form.

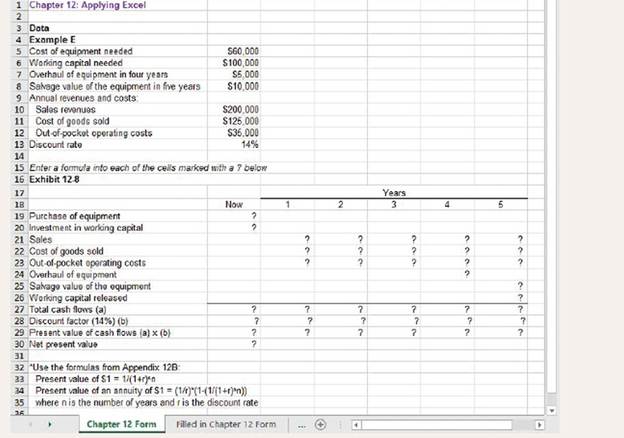 You should proceed to the requirements below only after completing your worksheet. Note that you may get a slightly different
You should proceed to the requirements below only after completing your worksheet. Note that you may get a slightly different
Required:
2. The company is considering another project involving the purchase of new equipment. Change the data area of your worksheet to match the following:
a. What is the net present value of the project?
b. Experiment with changing the discount rate in one percent increments (e.g.. 13%. 12%. 15%. etc.). At what interest rate does the net present value turn from negative to positive?
c. The
d. Reset the discount rate to 14%. Suppose the salvage value is uncertain. How large would the salvage value have to be to result in a positive net present value?
1
Net present value NPV is calculated by deducting present value of all the cash inflows from a particular project from the present value of initial cash outflow. NPV helps in identifying the profitability of a project or an investment.
To calculate: The amount of net present value (NPV) for the given project.
Answer to Problem 2AE
NPV is calculated as -$17.340.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of NPV will be done as follows:
| Particulars | Year 0 ($) | Year 1 ($) | Year 2 ($) | Year 3 ($) | Year 4 ($) | Year 5($) |
| Cost of equipment | -120,000 | |||||
| Working capital needed | -80,000 | |||||
| Sales revenue | 255,000 | 255,000 | 255,000 | 255,000 | 255,000 | |
| Cost of goods sold | -160,000 | -160,000 | -160,000 | -160,000 | -160,000 | |
| Out of pocket operating cost | -50,000 | -50,000 | -50,000 | -50,000 | -50,000 | |
| Working capital released | 80,000 | |||||
| Overhaul cost | -40,000 | |||||
| Salvage value | 20,000 | |||||
| Net cash flow | -200,000 | 45,000 | 45,000 | 45,000 | 5,000 | 145,000 |
| Discount rate (14%) | 1 | 0.877 | 0.769 | 0.675 | 0.592 | 0.519 |
| Present value | -200,000 | 39,465 | 34,605 | 30,375 | 2,960 | 75,255 |
| Net present value (NPV) | -17,340 |
Therefore, NPV is -$17,340.
2
Net present value NPV is calculated by deducting present value of all the cash inflows from a particular project from the present value of initial cash outflow. NPV helps in identifying the profitability of a project or an investment.
The discount rate at which NPV will be positive.
Answer to Problem 2AE
At 10% discount rate NPV will be positive ($5,330).
Explanation of Solution
At 15% discount rate, NPV will be:
| Particulars | Year 0 ($) | Year 1 ($) | Year 2 ($) | Year 3 ($) | Year 4 ($) | Year 5($) |
| Net cash flow | -200,000 | 45,000 | 45,000 | 45,000 | 5,000 | 145,000 |
| Discount rate (15%) | 1 | 0.867 | 0.756 | 0.657 | 0.572 | 0.497 |
| Present value | -200,000 | 39,015 | 34,020 | 29,565 | 2,860 | 72,065 |
| Net present value (NPV) | -22,475 |
At 13% discount rate, NPV will be:
| Particulars | Year 0 ($) | Year 1 ($) | Year 2 ($) | Year 3 ($) | Year 4 ($) | Year 5($) |
| Net cash flow | -200,000 | 45,000 | 45,000 | 45,000 | 5,000 | 145,000 |
| Discount rate (13%) | 1 | 0.885 | 0.783 | 0.693 | 0.613 | 0.543 |
| Present value | -200,000 | 39,825 | 35,235 | 31,185 | 3,065 | 78,735 |
| Net present value (NPV) | -11,955 |
At 12% discount rate, NPV will be:
| Particulars | Year 0 ($) | Year 1 ($) | Year 2 ($) | Year 3 ($) | Year 4 ($) | Year 5($) |
| Net cash flow | -200,000 | 45,000 | 45,000 | 45,000 | 5,000 | 145,000 |
| Discount rate (12%) | 1 | 0.893 | 0.797 | 0.711 | 0.635 | 0.567 |
| Present value | -200,000 | 40,185 | 35,865 | 31,995 | 3,175 | 82,215 |
| Net present value (NPV) | -6,565 |
At 11% discount rate, NPV will be:
| Particulars | Year 0 ($) | Year 1 ($) | Year 2 ($) | Year 3 ($) | Year 4 ($) | Year 5 ($) |
| Net cash flow | -200,000 | 45,000 | 45,000 | 45,000 | 5,000 | 145,000 |
| Discount rate (11%) | 1 | 0.901 | 0.812 | 0.731 | 0.658 | 0.593 |
| Present value | -200,000 | 40,545 | 36,540 | 32,895 | 3,290 | 85,985 |
| Net present value (NPV) | -745 |
At 10% discount rate, NPV will be:
| Particulars | Year 0 ($) | Year 1 ($) | Year 2 ($) | Year 3 ($) | Year 4 ($) | Year 5($) |
| Net cash flow | -200,000 | 45,000 | 45,000 | 45,000 | 5,000 | 145,000 |
| Discount rate (10%) | 1 | 0.909 | 0.826 | 0.751 | 0.683 | 0.621 |
| Present value | -200,000 | 40,905 | 37,170 | 33,795 | 3,415 | 90,045 |
| Net present value (NPV) | 5,330 |
Therefore, NPV will be positive at 10% discount rate.
3
Internal rate of return The interest rate at which NPV of cash flows from an investment is zero is IRR. It helps in identifying if the investment is profitable or not.
IRR is between what two discounting rates.
Answer to Problem 2AE
IRR is 10.884% which is between 10% and 11%.
Explanation of Solution
IRR will be calculated as follows:
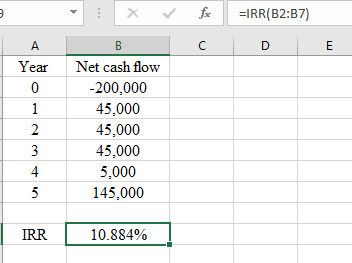
IRR is 10.884% which means that IRR is between 10% and 11%.
Also, IRR is the interest rate at which NPV is zero. At 10%, NPV is $5,330 (calculated in sub part 1) and at 11%, NPV is -745 (Calculated in sub part 1). This also shows that NPV will be zero at some discount rate between 10% and 11%.
4
Salvage value It represents the amount that a company receives by selling an asset at the end of its useful life. It is considered as a cash inflow.
To calculate: The increase in salvage value that will make the NPV positive at 14% discount rate.
Answer to Problem 2AE
Increase in salvage value is $29,560 and total salvage value is $49,560.
Explanation of Solution
| Particulars | Year 0 ($) | Year 1 ($) | Year 2 ($) | Year 3 ($) | Year 4 ($) | Year 5($) |
| Net cash flow | -200,000 | 45,000 | 45,000 | 45,000 | 5,000 | 145,000 |
| Discount rate (14%) | 1 | 0.877 | 0.769 | 0.675 | 0.592 | 0.519 |
| Present value | -200,000 | 39,465 | 34,605 | 30,375 | 2,960 | 75,255 |
| Net present value (NPV) | -17,340 |
At 14%, total cash outflow is -$200,000, present value of total cash inflows is 182,660 and NPV is negative. NPV will be positive if present value of cash flows will increase by $17,500. Therefore, in year 5 present value of salvage value will increase by $17,500. At year 0, total salvage value will be:
NPV will be positive if total salvage value will be $49,560.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Introduction To Managerial Accounting
- Please model the following decision in a spreadsheet, optimize it using MS-Excel Solver, and then upload that spreadsheet by attaching it to this question. I will grade this question on the accuracy of your () spreadsheet model (decision variables, objective, and constraints), (i) Solver parameters, (i optimal solution. Partial credit is available. The personnel-planning problem of Lexington Bank. The main branch of Lexington Bank is open for retail business from 8:00 AM to 4:00 PM on weekdays. The staffing requires from 8 to 15 tellers on duty depending on the time of day, as indicated in the following table. Time Period Minimum No. of Tellers 8:00 AM - 10:00 AM 10:00 AM - 12:00 PM 12:00 PM - 2:00 PM 10 15 2:00 PM - 4:00 PM 12 Full-time tellers work 8 consecutive hours (from 8:00 AM to 4:00 PM) at $15 per hour. Part-time workers work 4 consecutive hours at $8 per hour starting at 8:00 AM, 10:00 AM, or 12:00 noon. Assume workers never take breaks. Union regulations require that all…arrow_forwardOne day, the company chooses to buy their new accounting information system (AIS), and decide which activities in the systems development life cycle (SDLC) can be skipped? Justify your choice and explanation.arrow_forwardRequired information (The Excel worksheet form that appears below is to be used to recreate part of the example relating to Turbo Crafters that appears earlier in the chapter.) Download the Applying Excel form and enter formulas in all cells that contain question marks. For example, in cell B13 enter the formula "= B5". After entering formulas in all of the cells that contained question marks, verify that the dollar amounts match the example in the text. Check your worksheet by changing the estimated total amount of the allocation base in the Data area to 50,000 machine-hours, keeping all of the other data the same as in the original example. If your worksheet is operating properly, the predetermined overhead rate should now be $6.00 per machine-hour. If you do not get this answer, find the errors in your worksheet and correct them. Save your completed Applying Excel form to your computer and then upload it here by clicking "Browse." Next, click "Save." You will use this…arrow_forward
- Directions: Read the following sentences. Write the letter “T” if the statement is True and “F” if the statement is False. Write your answer on the space before the number. You may view this test at our google class. __________4. LCNRV should always be equal to net realizable value. __________5. Lower of cost and net realizable value gives the lowest valuation if applied to individual item of inventory. __________6. The amount of any writedown of inventory to net realizable value and all losses of inventory should be recognized as operating expense in the period the writedown or loss occurs. __________7. Professional fee arising directly from the acquisition of property and equipment are recognized as expense immediately. __________8. Exchange has a commercial substance when the exchange result in the difference in future cash flows. __________9. The cost of abnormal amounts of wasted materials is not included in the cost of self-constructed assets. __________10. An asset is not…arrow_forwardDirections: Read the following sentences. Write the letter “T” if the statement is True and “F” if the statement is False. Write your answer on the space before the number. You may view this test at our google class. __________4. LCNRV should always be equal to net realizable value. __________5. Lower of cost and net realizable value gives the lowest valuation if applied to individual item of inventory. __________6. The amount of any writedown of inventory to net realizable value and all losses of inventory should be recognized as operating expense in the period the writedown or loss occurs. __________7. Professional fee arising directly from the acquisition of property and equipment are recognized as expense immediatelyarrow_forwardLaurman inc. is considering the following project: Please provide excel formulas for all answersarrow_forward
- Using Excel, create a table that shows the relationship between the interestearned and the amount deposited, as shown. we will first create the dollar amount column and the interest row, as shown . Next we will type into cell B3 the formula = $A3*B$2. We can now use the Fill command to copy the formula in other cells, resulting in the table as shown. Note that the dollar sign before A3 means column A is to remain unchanged in the calculations when the formula is copied into other cells. Also note that the dollar sign before 2 means that row 2 is to remain unchanged in calculations when the Fill command is used.arrow_forwardPlease show your computations through excel format. Using FIFO, compute for the cost of WIP, end.arrow_forwardWhat are the Microsoft Excel formulaues used to input these? Is there a way to show each formula for how you came up with these. Not just the ratios but what you would input into excel that would automatically calculate the correct answers?arrow_forward
- The comparative financial statements of Global Technology are as follows: Open the file RATIOA from the website for this book at cengagebrain.com. Enter the formulas in the appropriate cells. Enter your name in cell A1. Save the completed model as RATIOA2. Print the worksheet when done. Also print your formulas. Check figure: Acid test (quick) ratio (cell C58), .82.arrow_forwardPlease include the excel formulas too! If someone can help me I will give a thumbs up! Please help me with the last two sections that are not filled out yet. Thanks! :)arrow_forwardI could use some help with this problem if you could answer in the form of an excel sheet that be great thxarrow_forward
 Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
