
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanism for the production of given compounds from the respective alkyne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 11.39P
The detailed mechanism for the given reaction with a major product is:
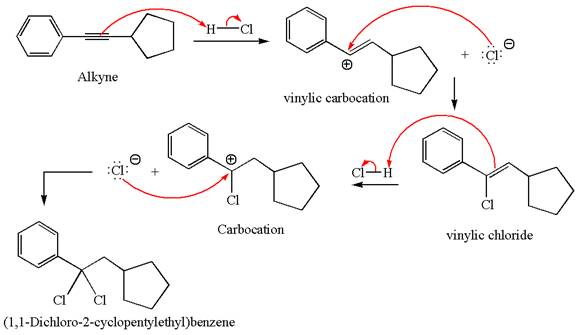
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound
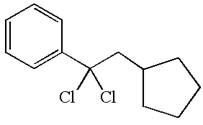
The given compound is germinal dichloride, and thus can be produced by electrophilic addition of an excess of
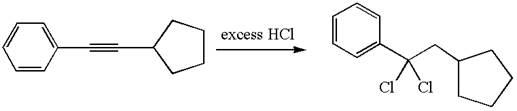
In the given reaction the alkyne is the electron rich site and the hydrogen from the
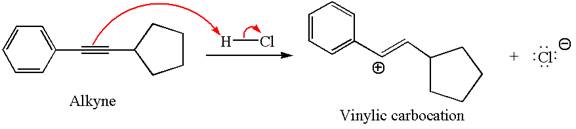
In the second step, the chloride ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks at vinylic carbocation forming vinylic chloride product.
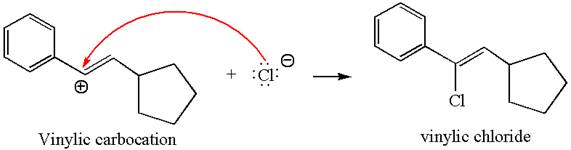
The vinylic chloride again undergoes the addition of
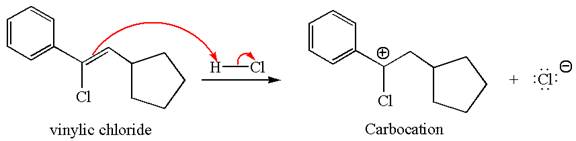
This carbocation further reacts with nucleophilic chloride ion to form a germinal dichloride product.
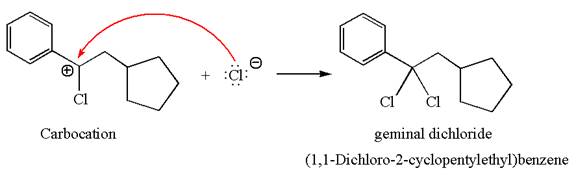
The detailed mechanism is drawn for the given reaction with showing the formation of stable carbocations and major product.
(b)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanism for the production of given compounds from respective alkyne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The alkynes are electron rich system like alkenes and can undergo an electrophilic addition reaction with strong Bronsted acids just like the alkenes do. The reaction proceeds with proton transfer reaction to form a stable carbocation followed by the action of water as a nucleophile. In excess of reagent, the reaction occurs twice forming a geminal dihalide compound as a major product.
Answer to Problem 11.39P
The detailed mechanism for the given reaction with the major product is:
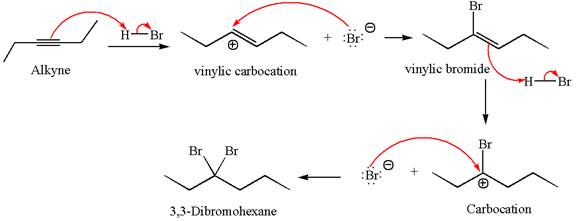
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound
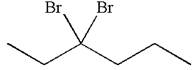
The given compound is germinal dibromide, thus can be produced by electrophilic addition of an excess of
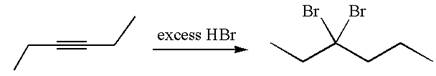
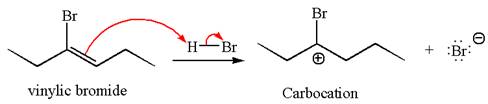
In the given reaction the alkyne is the electron rich site and the hydrogen from the
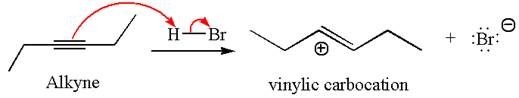
In the second step, the bromide ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks at vinylic carbocation forming vinylic bromide product.
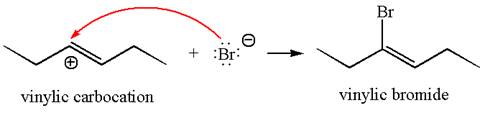
The vinylic bromide again undergoes the addition of
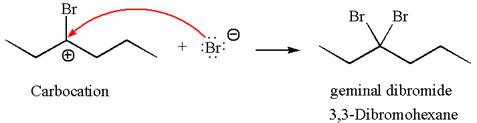
This carbocation further reacts with nucleophilic bromide ion to form germinal dibromide product.
The detailed mechanism is drawn for the given reaction with showing the formation of stable carbocations and major product.
(c)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanism for the production of given compounds from respective alkyne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The alkynes are electron rich system like alkenes and can undergo an electrophilic addition reaction with strong Bronsted acids just like the alkenes do. The reaction proceeds with proton transfer reaction to form a stable carbocation followed by the action of water as a nucleophile. In a single addition reaction, the reaction occurs only once forming a vibylic halide compound as a major product. The deuterium is an isotope of a hydrogen atom and reacts the same as hydrogen.
Answer to Problem 11.39P
The detailed mechanism for the given reaction with a major product is:
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound is:
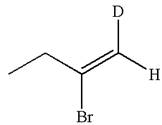
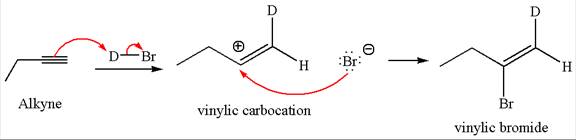
The given compound is vinylic bromide having deuterium at adjacent carbon, thus can be produced by single electrophilic addition of
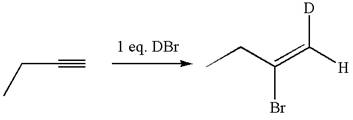
In the given reaction the alkyne is the electron rich site and the hydrogen from the
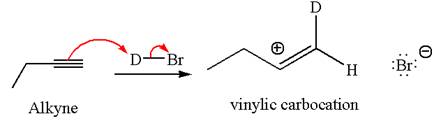
In the second step the bromide ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks at vinylic carbocation forming vinylic bromide product.
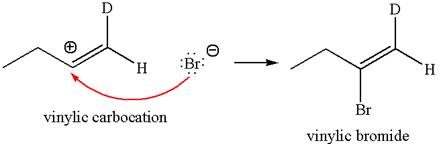
The detailed mechanism is drawn for the given reaction with showing the formation of stable carbocations and major product.
(d)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanism for the production of given compounds from respective alkyne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The alkynes are electron rich system like alkenes and can undergo an electrophilic addition reaction with strong Bronsted acids just like the alkenes do. The reaction proceeds with proton transfer reaction to form a stable carbocation followed by the action of water as a nucleophile. In excess of reagent, the reaction occurs twice forming a geminal dihalide compound as a major product.
Answer to Problem 11.39P
The detailed mechanism for the given reaction with the major product is:
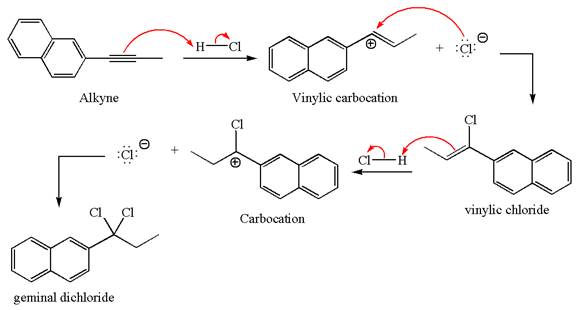
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound is:
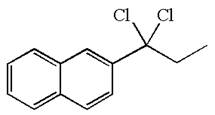
The given compound is germinal dichloride, thus can be produced by electrophilic addition of an excess of
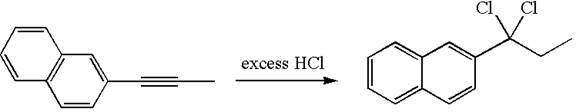
In the given reaction the alkyne is the electron rich site and the hydrogen from the
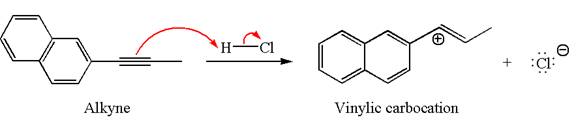
In the second step, the chloride ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks at vinylic carbocation forming vinylic chloride products.
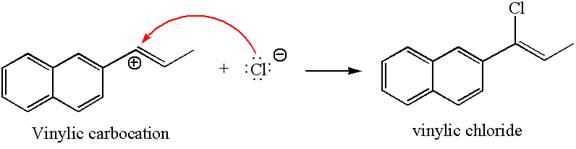
The vinylic chloride again undergoes the addition of
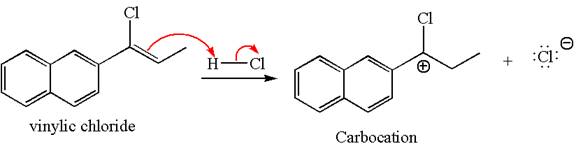
This carbocation further reacts with nucleophilic chloride ion to form a germinal dichloride product.
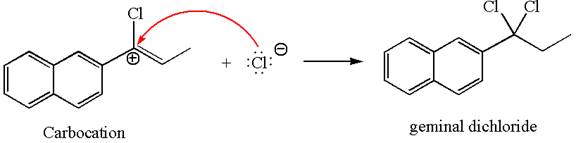
The detailed mechanism is drawn for the given reaction with showing the formation of stable carbocations and major product.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- Provide the major products of the given reaction.arrow_forwardPredict the major products of each of the following reactions. Draw the complete detailed mechanism that leads to the formation of these products.arrow_forwardComplete the following reaction and provide the detailed mechanism NaOH NaOH +arrow_forward
- Write the reaction mechanism for the reaction on the image and show the main organic product. Please include all of the steps in the explanation.arrow_forwardSupply the missing reagent for the following reactions.arrow_forwardDetermine the products of the following reactions, no reaction mechanism is necessary. In part b), where the question mark is, conditions can be proposed for any product of interest or that is feasible to obtain with the compound of the previous reaction.arrow_forward
- I understand what reagents and or solvents can be used to get from an alkene to an alkyne but if someone could please show me step by step how each is used to perform the actual synthesis? Like how does each thing work to get to the next portion of the synthesis. I am truly struggling. thank youarrow_forwardwhat is the product of the following reactions? please explain with full mechanism .arrow_forwardPredict the product for the reaction between methyl benzoate and each of the following. If no reaction is expected to occur, write “no reaction.” For those reactions that do occur, draw the complete, detailed mechanism. (a) NaBr; (b) NaN(CH3)2; (c) 3-chloropentane; (d) hexanal; (e) CH3Clarrow_forward

 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

