
Concept explainers
On the two diagrams below, indicate the direction of the induced current in the loop at each of the instants shown. If the current is zero, state that explicitly. Explain how you determined your answers.
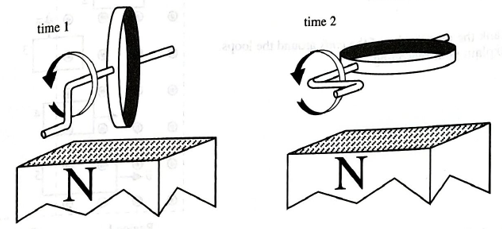
The direction of the induced current in the loop at each instant.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Write the expression to calculate the magnetic flux.
Here,
Write the expression to calculate induced emf.
Here,
Case 1:
Consider time 1.
Calculate the magnetic flux.
The magnetic flux will decrease as the angle reaches to
Calculate the induced emf.
The emf will increase which leads to the increase of current. The coil will produce a magnetic field in the same direction. According to Lenz’s law the direction of current will be anticlockwise when seen from the left side of the loop.
Case 2:
Calculate the magnetic flux.
The magnetic flux will decrease as the angle reaches to
Calculate the induced emf.
The emf is zero.
Calculate the current.
For the time 2, the emf induced will be zero which will lead to zero current in the loop.
Conclusion:
Therefore, for time 1 the current will be in anticlockwise direction and for time 2 the current is zero.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics: Principles with Applications
An Introduction to Thermal Physics
Conceptual Physics (12th Edition)
Modern Physics
Sears And Zemansky's University Physics With Modern Physics
Conceptual Physical Science (6th Edition)
- Use Lenz's law to answer the following questions concerning the direction of induced currents. Express your answers in terms of the letter labels a and b in each part of the figure below. (a) What is the direction of the induced current in the resistor R in Figure a when the bar magnet is moved to the left? (b) What is the direction of the current induced in the resistor R after the switch S in Figure b is closed? (c) What is the direction of the induced current in the resistor R when the current I in Figure c decreases rapidly to zero?arrow_forwardUse Lenz's law to answer the following questions concerning the direction of induced currents. Express your answers in terms of the letter labels a and b in each part of the figure below. (a) What is the direction of the induced current in the resistor R in Figure a when the bar magnet is moved to the left? O a to b O b to a O The magnitude is zero. (b) What is the direction of the current induced in the resistor R after the switch S in Figure b is closed? O a to b O b to a O The magnitude is zero. (c) What is the direction of the induced current in the resistor R when the current / in Figure c decreases rapidly to zero? O a to b O b to a O The magnitude is zero.arrow_forwardUse Lenz's law to answer the following questions concerning the direction of induced currents. Express your answers in terms of the letter labels a and b in each part of the figure below. R R b R b. (a) What is the direction of the induced current in the resistor R in Figure a when the bar magnet is moved to the left? a to b b to a The magnitude is zero. (b) What is the direction of the current induced in the resistor R after the switch S in Figure b is closed? O a to b Ob to a The magnitude is zero. (c) What is the direction of the induced current in the resistor R when the current I in Figure c decreases rapidly to zero? a to b O b to a O The magnitude is zero.arrow_forward
- The diagram below shows two long parallel wires, 1 & 2, each carrying a current of 98 A. The direction of the current for each wire is indicated in the diagram. The distance between the wires is 2.5 cm & the distance between wire 1 & point P is 6 cm. Use the standard cartesian coordinate system. 1 X P A.) At P, determine the directions of B₁ & B₂. direction of B₁ at P =- direction of B₂ at P => + ✓ B.) Determine the x & y components of B₁ at P. B1x = B₁y = C.) Determine the x & y components of B₂ at P. B₂x = B2y = вгу D.) Determine the magnitude & direction of Bnet at P. Bnet = direction of Bnet = to the HORIZONTAL in --- Choose quadrant --- Varrow_forwardUse Lenz's law to answer the following questions concerning the direction of induced currents. Express your answers in terms of the letter labels a and b in each part of the figure below. R R b R b (a) What is the direction of the induced current in the resistor R in Figure a when the bar magnet is moved to the left? a to b b to a The magnitude is zero. (b) What is the direction of the current induced in the resistor R after the switch S in Figure b is closed? a to b b to a The magnitude is zero. (c) What is the direction of the induced current in the resistor R when the current I in Figure c decreases rapidly to zero? a to b b to a The magnitude is zero.arrow_forwardUse the worked example above to help you solve this problem. A coil with 21 turns of wire is wrapped on a frame with a square cross-section 2.14 cm on a side. Each turn has the same area, equal to that of the frame, and the total resistance of the coil is 0.561 Ω. An applied uniform magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of the coil, as in the figure. Suppose the magnetic field changes uniformly from 0.540 T to 0.162 T in the next 0.666 s. (a) Compute the induced emf in the coil. = V(b) Compute the induced current.I = A counterclockwise as viewed from above the coilarrow_forward
- What is the expression for the magnetic dipole moment of a small loop of current, with the radius of the loop given by r and the current given by 1? Use I for current, r for radius, pi for T. Use * for multiplication and / for division and collect terms using (). Use ^ for exponent, i.e. for æ" write x^n. You can add an optional tip or note related to the prompt like this. Example: To test this example, the correct answer is R_1*R_2/R_3 Submit Previous bux.bracu.ac.bdarrow_forwardFor each of the current distributions below, determine and clearly label the regions where the magnetic field points into and out of the plane of the page. All figures are planar and the wires are long, insulated from each other, and carry constant current in the direction indicated.arrow_forwardThe current in the central branch of the circuit below (I3) is 2A. Use Kirchoff's rules to find the current flowing around the boundary of the upper loop (I1).arrow_forward
- For each diagram below, in which direction (as viewed from above) would the induced current in the loop flow? State your response and then discuss in detail how you know. -I decreasing (a) I increasing I constant (c) (b) I increasing (d)arrow_forwardNote: Elaborate and provide a screenshot of your observation including the corresponding equation (applicable to all questions) D. Can you produce a current when the magnet goes up and down in the loops? E. Next try two rings vs. four rings. What relationship can you make between the number of loops and the current produced?arrow_forwardShown in the figure below is a so-called "Bar Slide" apparatus. A bar of mass m, length L, and resistance R is electrically attached to a set of vertical rails that allow the bar and rails to form a closed loop. The whole system is immersed in a magnetic field B. The bar is released from rest and gravity causes it to accelerate downward. Please note that all answers to this problem are symbolic (formulas). We will assume no friction. Please enter POSITIVE formulas for every answer. L m, R B-field into the screen Determine all of the following formulas:arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





