Concept explainers
Scanning Confocal Microscopy
Although modern microscopes are marvels of optical engineering, their basic design is not too different from the 1665 compound microscope of Robert Hooke. Recently, advances in optics, lasers, and computer technology have made practical a new kind of optical microscope, the scanning confocal microscope. This microscope is capable of taking images of breathtaking clarity.
The figure shows the microscope’s basic principle of operation. The left part of the figure shows how the translucent specimen is illuminated by light from a laser. The laser beam is converted to a diverging bundle of rays by suitable optics, reflected off a mirror, then directed through a microscope objective lens to a focus within the sample. The microscope objective focuses the laser beam to a very small (≈ 0.5 μm) spot. Note that light from the laser passes through other regions of the specimen but, because the rays are not focused in those regions, they are not as intensely illuminated as is the point at the focus. This is the first important aspect of the design: Very intensely illuminate one very small volume of the sample while leaving other regions only weakly illuminated.
As shown in the right half of the figure, light is reflected from all illuminated points in the sample and passes back through the objective lens. The mirror that had reflected the laser light downward is actually a partially transparent
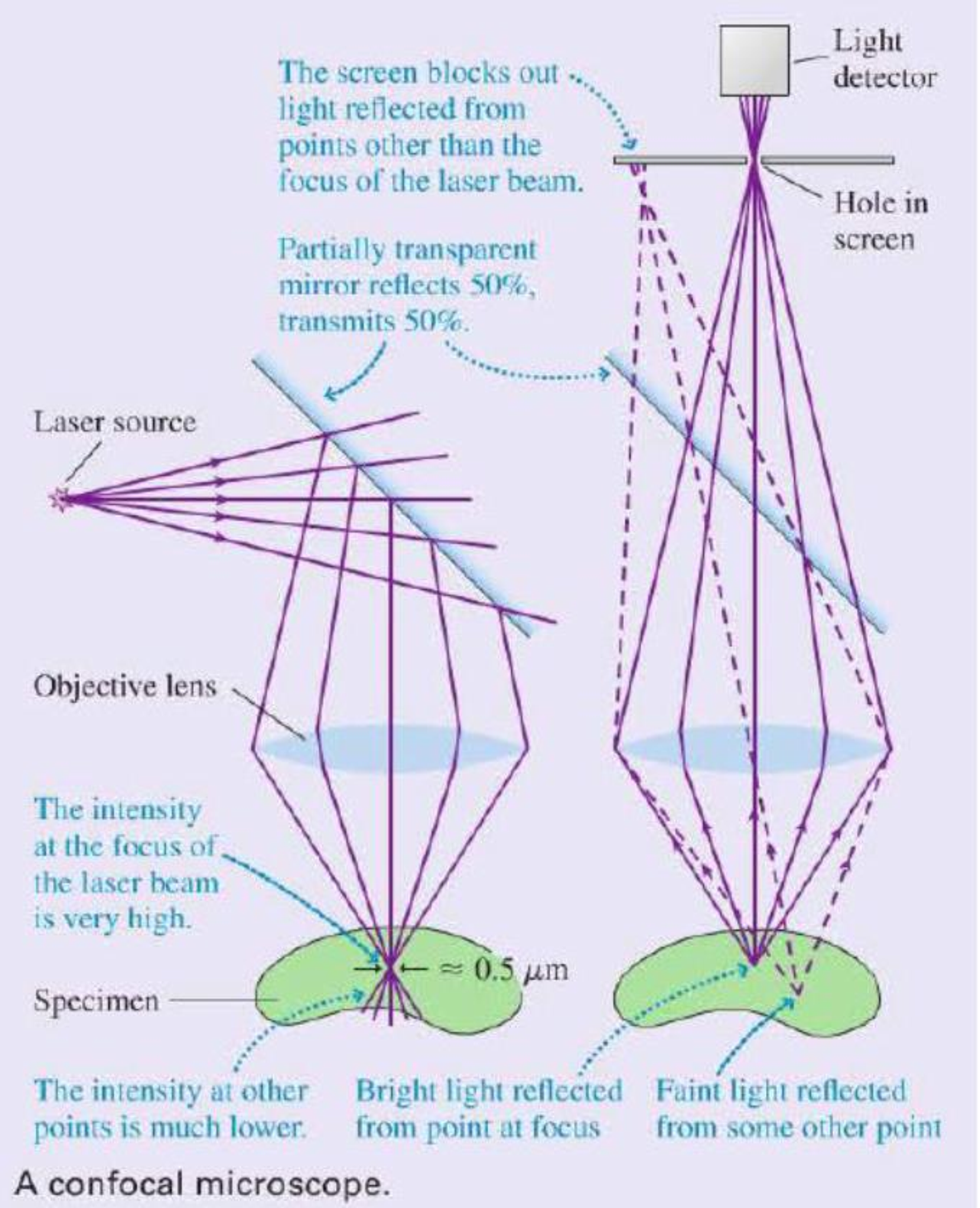
mirror that reflects 50% of the light and transmits 50%. Thus half of the light reflected upward from the sample passes through the mirror and is focused on a screen containing a small hole. Because of the hole, only light rays that emanate from the brightly illuminated volume in the sample can completely pass through the hole and reach the light detector behind it. Rays from other points in the sample either miss the hole completely or are out of locus when they reach the screen, so that only a small fraction of them pass through the hole. This second key design aspect limits the detected light to only those rays that are emitted from the point in the sample at which the laser light was originally focused.
So we see that (a) the point in the sample that is at the focus of the objective is much more intensely illuminated than any other point, so it reflects more rays than any other point, and (b) the hole serves to further limit the detected rays to only those that emanate from the focus. Taken together, these design aspects ensure the detected light comes from a very small, very well-defined volume in the sample.
The microscope as shown would only be useful for examining one small point in the sample. To make an actual image, the objective is scanned across the sample while the intensity is recorded by a computer. This procedure builds up an image of the sample one scan line at a time. The final result is a picture of the sample in the very narrow plane in which the laser beam is focused. Different planes within the sample can be imaged by moving the objective up or down before scanning. It is actually possible to make three dimensional images of a specimen in this way.
The improvement in contrast and resolution over conventional microscopy can be striking. The images show a section of a mouse kidney taken using conventional and confocal microscopy. Because light reflected from all parts of the specimen reaches the camera in a conventional microscope, that image appears blurred and has low contrast. The confocal microscope image represents a single plane or slice of the sample, and many details become apparent that are invisible in the conventional image.
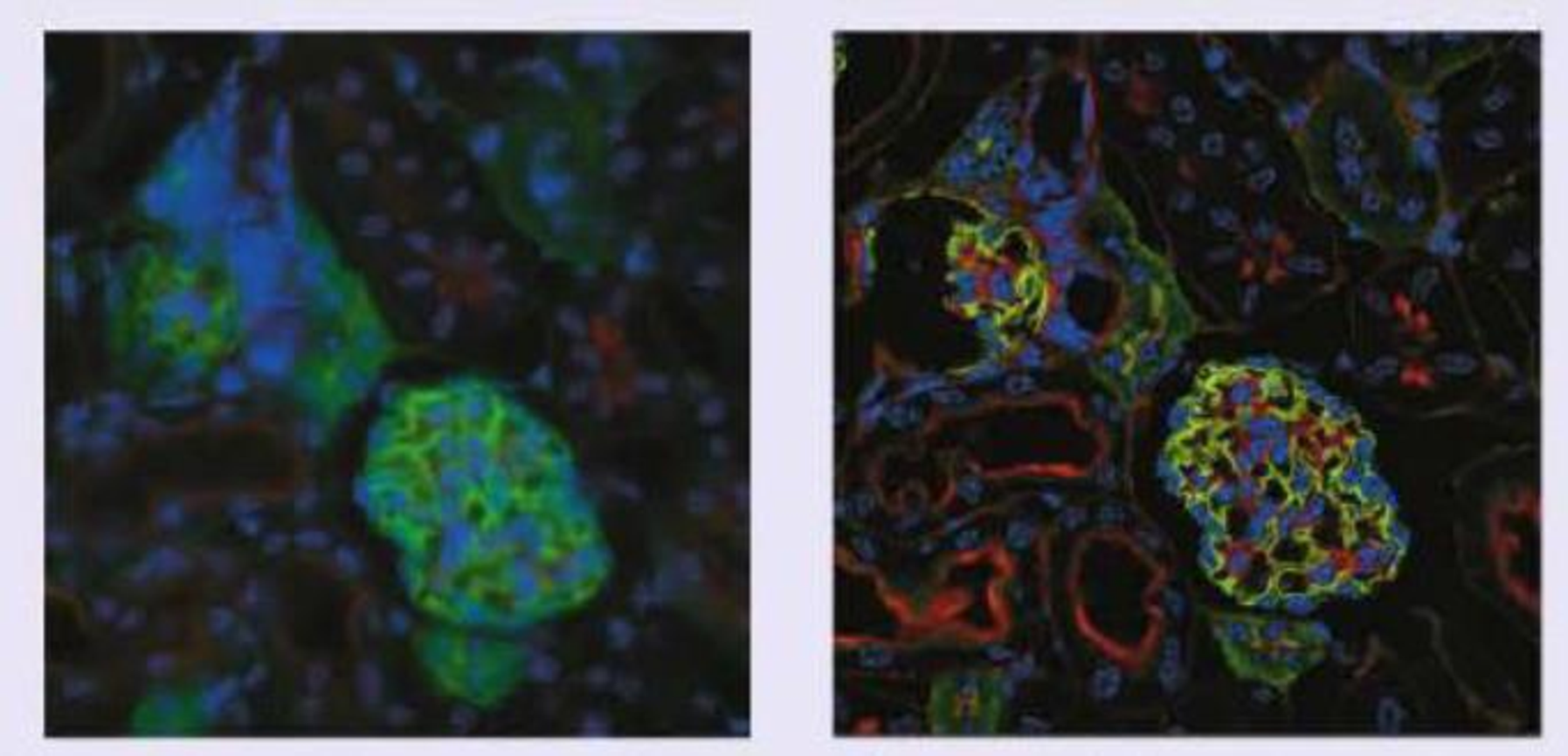
A section of fluorescently stained mouse kidney imaged using standard optical microscopy (left) and scanning confocal microscopy (right).
The following questions are related to the passage “Scanning Con focal Microscopy” on the previous page.
1. A laser beam consists of parallel rays of light. To convert this light to the diverging rays required for a scanning confocal microscope requires
- A. A converging lens.
- B. A diverging lens.
- C. Either a converging or a diverging lens.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter P Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Life in the Universe (4th Edition)
Conceptual Physics (12th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Conceptual Physical Science (6th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
- A movie camera with a (single) lens of focal length 60 mm takes a picture of a person standing 40 m away. If the person is 180 cm tall, what is the height of the image in millimeters on the film? Number i Unitsarrow_forwardHW8 Q2 A concave lens has a focal length of -43 cm. Find the image distance that results when an object is placed 32 cm in front of the lens. Express your answer using two significant figures. Find the magnification that results when an object is placed 32 cm in front of the lens. Express your answer using two significant figures.arrow_forwardWhat are the differences between real and virtual images? How can you tell (by looking) whether an image formed by a single lens or mirror is real or virtual?arrow_forward
- A certain slide projector has a 110 mm focal length lens. A. How far away is the screen (in m), if a slide is placed 115 mm from the lens and produces a sharp image? B. If the slide is 15.0 by 30.0 mm, what are the dimensions of the image? __ cm by __ cm.arrow_forwardIn a compound microscope, the objective lens and eyepiece have focal lengths of +0.50 cm and +4.5 cm respectively. The real image formed by the objective lens is 7 cm from the objective. Find the following: A. What is the linear magnification of the objective lens? B. What is the magnifying power of the eyepiece? C. What is the magnifying power of the instrument? D. The distance between the eyepiece and final image is 25.0 cm. What is the distance of the eyepiece to the image due to the objective lens?arrow_forwardWhen fully dilated, the pupil of a grey cat is approximately 6.75 mm wide. For 650 THz light ("T" stands for "tera" and means 1012), determine the minimum angle that can be resolved for the grey cats eye. Express your answer in degrees. ?min = The diagram below shows a grey parrot looking at two trees. The grey parrot is just able to resolve the two trees. The distance between the grey cat & the trees is 69.6 km. For the ?min you just determined, determine the distance between the two trees. distance between the two trees=arrow_forward
- = 1. Draw a ray diagram for a converging lens with a focal length of f = 60 cm and an object distance of do 100 cm. You must draw at least two of the three rays we talked about in class (P ray, M ray, F ray). Mark the focal point with an "F" and label your object and image on the figure.arrow_forwardAn object is 17 cm in front of a diverging lens that has a focal length of -8.1 cm. How far in front of the lens should the object be placed so that the size of its image is reduced by a factor of 2.4? Number i Unitsarrow_forwardThe sun is 150,000,000 km from earth; its diameter is 1,400,000 km. A student uses a 4.8-cm-diameter lens with f = 10 cm to cast an image of the sun on a piece of paper. Part A Where should the paper be placed relative to the lens to get a sharp image? Express your answer with the appropriate units. s'= 10 cm Submit ✓ Correct Part B Previous Answers What is the diameter of the image on the paper? Express your answer with the appropriate units. Submit μà d' = Value • Request Answer Units B ? DICTION VVIII TUMIVarrow_forward
- An object is placed in front of a converging lens in such a position that the lens (f = 12.8 cm) produces a real image located 19.7 cm from the lens. Then, with the object remaining in place, the lens is replaced with another converging lens (f = 15.2 cm). A new, real image is formed. What is the image distance of this new image? Number i Unitsarrow_forwardShown in the figure below is a system containing two lenses and an object. The focal lengths of the two lenses are f = 15 cm %3D and f, = -7.5 cm. The two lengths indicated in the figure are L, = 22.5 cm and L2 = 12 cm. f1 f2 L2 Determine all the following about the image from the first lens only: Object distance for the first lens, do1. cm Image distance for the first lens, di1. cm Magnification of the first lens, m1. The second lens uses the image from the first lens as its object. Determine all the following about the image from the second lens: Object distance for the second lens, do1. cm Image distance for the second lens, di1. cm Magnification of the second lens, m1. Determine the magnification of the whole system, mtot. Select the correct attributes of the final image of the system: O virtual O real O shrunk O enlarged right side up O upside downarrow_forwardA camera lens has a focal length of 900 mm. a. Compute for the image location and the size of the image on the film of a 5 m high monument that is at a distance of 20 m. b. Describe the image formed.(real or virtual)(inverted or upright)(diminished or enlarged)arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax

